Faculty教員紹介
Engineering Physicsエンジニアリングフィジクス
人や環境を対象としたマクロ〜メゾスコピックな学際的システム分野An interdisciplinary systems field, exploring macro to mesoscopic systems related to humans and the environment.
-
情報理論研究室 情報理論、情報セキュリティ
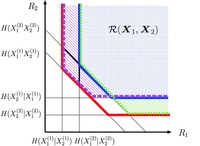 インターネットは私たちの生活を大変便利にしていますが,不特定多数の人が利用するため,大切な情報を守るための情報セキュリティ技術を確立していくことが不可欠です.私の研究室では,情報理論や離散数学などの知見に基づいて,動画などのライセンスのあるディジタルコンテンツの不正配信を防ぐための電子指紋符号,分散情報を再配布せずにいくらでも多く参加者を増やすことができる秘密分散法,分散情報の重ね合わせにより人間の目で復号できる効率的な視覚暗号などの研究をしています.
Read More
Information Theory Laboratory Information Theory, Information Security
インターネットは私たちの生活を大変便利にしていますが,不特定多数の人が利用するため,大切な情報を守るための情報セキュリティ技術を確立していくことが不可欠です.私の研究室では,情報理論や離散数学などの知見に基づいて,動画などのライセンスのあるディジタルコンテンツの不正配信を防ぐための電子指紋符号,分散情報を再配布せずにいくらでも多く参加者を増やすことができる秘密分散法,分散情報の重ね合わせにより人間の目で復号できる効率的な視覚暗号などの研究をしています.
Read More
Information Theory Laboratory Information Theory, Information Security We need to guarantee security of the Internet under various situations. We are interested in establishing new digital fingerprinting schemes for preventing Illegal redistribution of digital contents. We are also interested in onconventional secret sharing schemes with arbitrary number of participants and efficient visual cryptography schemes in which we can reconstruct a secret image by superimposing shares.
Read More
We need to guarantee security of the Internet under various situations. We are interested in establishing new digital fingerprinting schemes for preventing Illegal redistribution of digital contents. We are also interested in onconventional secret sharing schemes with arbitrary number of participants and efficient visual cryptography schemes in which we can reconstruct a secret image by superimposing shares.
Read More
-
スマートシステム研究室 人工知能、機械学習、適応アルゴリズム、実世界応用、インフラ診断
 本研究室では、社会課題を解決することを目的とした人工知能技術の活用方法について研究を行っています。機械学習に基づく画像解析や音響データ解析による異常検知などをコア技術とし、社会インフラ診断および医療診断・ヘルスケア支援に資する技術の実用化に向けて主に活動しています。社会インフラや産業インフラの点検や調査では、打音試験や近接目視、触診などが一次検査として広く行われ、異常が発見された場合には、その後の経過観察や精密な機器による二次検査に進みます。ここで重要なのは一次検査で異常を見落とさないことなのですが、検査員の経験や感覚に依存していることや、熟練検査員の数は高齢化に伴い減少していくことなどの問題点があります。そこで私たちは、コンクリート構造物の打音検査や、水道管、風力発電機などの異常振動の検査を人工知能で支援する取り組みを行っています。検査員の五感に頼らず、機械学習に基づく解析技術により検査結果を定量化することで、異常の見落としにつながる検査品質のバラツキやミスを防止します。
Read More
Smart System Laboratory Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Adaptive Algorithm, Real-world Application, Diagnosis of Infrastructure
本研究室では、社会課題を解決することを目的とした人工知能技術の活用方法について研究を行っています。機械学習に基づく画像解析や音響データ解析による異常検知などをコア技術とし、社会インフラ診断および医療診断・ヘルスケア支援に資する技術の実用化に向けて主に活動しています。社会インフラや産業インフラの点検や調査では、打音試験や近接目視、触診などが一次検査として広く行われ、異常が発見された場合には、その後の経過観察や精密な機器による二次検査に進みます。ここで重要なのは一次検査で異常を見落とさないことなのですが、検査員の経験や感覚に依存していることや、熟練検査員の数は高齢化に伴い減少していくことなどの問題点があります。そこで私たちは、コンクリート構造物の打音検査や、水道管、風力発電機などの異常振動の検査を人工知能で支援する取り組みを行っています。検査員の五感に頼らず、機械学習に基づく解析技術により検査結果を定量化することで、異常の見落としにつながる検査品質のバラツキやミスを防止します。
Read More
Smart System Laboratory Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Adaptive Algorithm, Real-world Application, Diagnosis of Infrastructure Our team is conducting social problem-solving oriented research on utilization of artificial intelligence technology. We are now tackling mainly toward practical use of AI-aided diagnosis systems based on anomaly detection with image and acoustic analysis for social-infrastructure maintenance, medical care, and healthcare.In the maintenance of social and industrial infrastructure, primary checking such as hammering test, close visual inspection and palpation, is commonly carried out by skilled-inspectors. It is important that not to overlook an anomaly, however, the checking process currently depends deeply on the experience and sense of inspectors. Furthermore, the number of skilled-inspector is decreasing due to aging. Therefore, we are engaging on developing AI-aided diagnosis systems for hammering test of concrete structures, detection of abnormal vibration of industrial machinery such as wind turvines. By quantification of the checking results using an analysis technique based on machine learning, rather than relying on human senses, our system will prevent mistakes and variation of checking quality that lead to oversight of anomalies.
Read More
Our team is conducting social problem-solving oriented research on utilization of artificial intelligence technology. We are now tackling mainly toward practical use of AI-aided diagnosis systems based on anomaly detection with image and acoustic analysis for social-infrastructure maintenance, medical care, and healthcare.In the maintenance of social and industrial infrastructure, primary checking such as hammering test, close visual inspection and palpation, is commonly carried out by skilled-inspectors. It is important that not to overlook an anomaly, however, the checking process currently depends deeply on the experience and sense of inspectors. Furthermore, the number of skilled-inspector is decreasing due to aging. Therefore, we are engaging on developing AI-aided diagnosis systems for hammering test of concrete structures, detection of abnormal vibration of industrial machinery such as wind turvines. By quantification of the checking results using an analysis technique based on machine learning, rather than relying on human senses, our system will prevent mistakes and variation of checking quality that lead to oversight of anomalies.
Read More
-
音響システム研究室 振動センサ、音楽音響、音響イメージング、音響工学、逆問題、数値シミュレーション
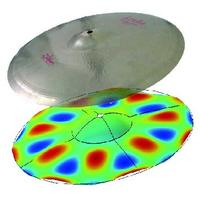 本研究室では、音波や振動を対象とする音響工学分野の研究を、シミュレーションと実験の両面から行っています。研究対象には、音楽・話し声・警告音・異常音のように音そのものが持つ情報を利用するもの、超音波診断装置・ソーナー・超音波風向風速計のように音が伝わる空間の情報を取得するためのプローブとして媒質と音波のインタラクション(相互作用)を利用するもの、さらに弾性表面波(SAW)フィルタのように電子部品を高機能化するために内部的に振動を利用し入出力には音波が陽に現れないようなものがあります。最近実施した(あるいは進行中の)研究テーマには、音楽音響関係では管・弦・打楽器などの特性計測にもとづく発音機構のモデル化および電子楽器への応用など、可視化(イメージング)関係では超音波による金属材料の非破壊検査法、時間反転波のシミュレーションあるいはCT法による音源や物体の可視化など、センサ関係では単純な構造で液体の密度・粘度を一度に測定できるセンサなどがあります。当研究室には、好奇心旺盛で何でもやってみないと気が済まない人、ハード・ソフトを問わずモノ作りが好きな人、探究心旺盛な人などが多数在籍しています。
Read More
Acoustic Laboratory Vibration Sensors, Musical Acoustics, Acoustical Imaging, Acoustic Engineering, Inverse Problems, Numerical Simulation
本研究室では、音波や振動を対象とする音響工学分野の研究を、シミュレーションと実験の両面から行っています。研究対象には、音楽・話し声・警告音・異常音のように音そのものが持つ情報を利用するもの、超音波診断装置・ソーナー・超音波風向風速計のように音が伝わる空間の情報を取得するためのプローブとして媒質と音波のインタラクション(相互作用)を利用するもの、さらに弾性表面波(SAW)フィルタのように電子部品を高機能化するために内部的に振動を利用し入出力には音波が陽に現れないようなものがあります。最近実施した(あるいは進行中の)研究テーマには、音楽音響関係では管・弦・打楽器などの特性計測にもとづく発音機構のモデル化および電子楽器への応用など、可視化(イメージング)関係では超音波による金属材料の非破壊検査法、時間反転波のシミュレーションあるいはCT法による音源や物体の可視化など、センサ関係では単純な構造で液体の密度・粘度を一度に測定できるセンサなどがあります。当研究室には、好奇心旺盛で何でもやってみないと気が済まない人、ハード・ソフトを問わずモノ作りが好きな人、探究心旺盛な人などが多数在籍しています。
Read More
Acoustic Laboratory Vibration Sensors, Musical Acoustics, Acoustical Imaging, Acoustic Engineering, Inverse Problems, Numerical Simulation In this laboratory, the research area covers acoustic engineering such as sound and vibration by using both the numerical simulations and the experiments. The research targets include the followings; (a) the sound whose informations are utilized such as music, voice, warning beep, and abnormal noise, (b) the interaction between the sound and the medium in which the sound propagates are utilized as a probe to obtain the spatial information, such as an ultrasonic diagnostic, sonar, ultrasonic anemometer, (c) the vibrations are only utilized to improve the functions of electronic components and do not appear as their input or output. Our recent reseearch themes include modeling of the sound generation mechanism based on the measurements and the applications to electronic musical instruments in musical acoustics area, non-destructive testing methods and visualization methods in acoustical imaging area, and the sensors for medium properties like density, viscosity, and elesticity in sensing area. In our laboratory, many students are so curious as to try everything, who love making things regardless of the hardware and software, or full of inquisitive spirit.
Read More
In this laboratory, the research area covers acoustic engineering such as sound and vibration by using both the numerical simulations and the experiments. The research targets include the followings; (a) the sound whose informations are utilized such as music, voice, warning beep, and abnormal noise, (b) the interaction between the sound and the medium in which the sound propagates are utilized as a probe to obtain the spatial information, such as an ultrasonic diagnostic, sonar, ultrasonic anemometer, (c) the vibrations are only utilized to improve the functions of electronic components and do not appear as their input or output. Our recent reseearch themes include modeling of the sound generation mechanism based on the measurements and the applications to electronic musical instruments in musical acoustics area, non-destructive testing methods and visualization methods in acoustical imaging area, and the sensors for medium properties like density, viscosity, and elesticity in sensing area. In our laboratory, many students are so curious as to try everything, who love making things regardless of the hardware and software, or full of inquisitive spirit.
Read More
-
機械システム研究室 機械システム、力学系理論、非線形現象の解析と制御と利用、ナノ・マイクロマシーン
 一般に機械システムは非線形特性を持ち、(複数の平衡点が存在し、それらの安定性も様々で、)予測不可能な非線形挙動を示す可能性がある。安全性や信頼性を確保するために、非線形挙動が生じないよう、高剛性な(その結果重量化してしまう)機械システムが、狭い動作範囲(振り子でいえば近似sinθ≒θが成り立つ狭い動作範囲)で利用されてきた。しかしながら近年の、機械システムの高機能・高機能化への期待は、柔軟化・軽量化や非線形挙動が生じるような広い範囲(振り子でいえば近似sinθ≒θが成り立たない範囲)への動作拡張を要請し、もはや無視できなくなったシステムの非線形性といかに向きあい、安全性や信頼性を確保し続けるかが重要な課題になっている。このような状況の中、ナノスケール(エネルギーハーベスターなど)からマクロスケール(鉄道車両など)まで幅広い機械システムを対象とし、これまでの発想とは逆に、元々システムに内在する非線形性によって生じる非線形現象の複雑性や多様性を積極的に利用して、従来不可能であった運動制御を実現する手法を、数理物理学に立脚した理論的アプローチと実験により研究している。
Read More
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Laboratory Dynamical Systems, Bifurcation Theory, Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS)
一般に機械システムは非線形特性を持ち、(複数の平衡点が存在し、それらの安定性も様々で、)予測不可能な非線形挙動を示す可能性がある。安全性や信頼性を確保するために、非線形挙動が生じないよう、高剛性な(その結果重量化してしまう)機械システムが、狭い動作範囲(振り子でいえば近似sinθ≒θが成り立つ狭い動作範囲)で利用されてきた。しかしながら近年の、機械システムの高機能・高機能化への期待は、柔軟化・軽量化や非線形挙動が生じるような広い範囲(振り子でいえば近似sinθ≒θが成り立たない範囲)への動作拡張を要請し、もはや無視できなくなったシステムの非線形性といかに向きあい、安全性や信頼性を確保し続けるかが重要な課題になっている。このような状況の中、ナノスケール(エネルギーハーベスターなど)からマクロスケール(鉄道車両など)まで幅広い機械システムを対象とし、これまでの発想とは逆に、元々システムに内在する非線形性によって生じる非線形現象の複雑性や多様性を積極的に利用して、従来不可能であった運動制御を実現する手法を、数理物理学に立脚した理論的アプローチと実験により研究している。
Read More
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Laboratory Dynamical Systems, Bifurcation Theory, Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) As mechanical systems become lighter, faster, and more flexible, various nonlinear instability phenomena can be easily produced in practical systems. Furthermore, while the control methods have been established to suppress the nonlinear instabilities, their positive utilization of nonlinear instability is more expected to realize innovative high-performance mechanical systems. In order to advance the sensitivity and feasibility much more, it is received much attention to utilize nonlinear instabilities other than conventional resonance phenomena, for example , parametric resonance, self-excited oscillation, nonlinear resonances as subharmonic and superharmonic resonances, and so on . In particular, in the fields of NEMS and MEMS, the positive utilization of the nonlinear instabilities is growing much more in 5 years. In my laboratory, toward the realization of high-performance mechanical systems in the various scales from nano to macro, innovative nonlinear control methods are proposed theoretically and experimentally.
Read More
As mechanical systems become lighter, faster, and more flexible, various nonlinear instability phenomena can be easily produced in practical systems. Furthermore, while the control methods have been established to suppress the nonlinear instabilities, their positive utilization of nonlinear instability is more expected to realize innovative high-performance mechanical systems. In order to advance the sensitivity and feasibility much more, it is received much attention to utilize nonlinear instabilities other than conventional resonance phenomena, for example , parametric resonance, self-excited oscillation, nonlinear resonances as subharmonic and superharmonic resonances, and so on . In particular, in the fields of NEMS and MEMS, the positive utilization of the nonlinear instabilities is growing much more in 5 years. In my laboratory, toward the realization of high-performance mechanical systems in the various scales from nano to macro, innovative nonlinear control methods are proposed theoretically and experimentally.
Read More
-
音響システム研究室【通信・農業施設・情報化施工】(通信システム研究室) 情報通信工学、水中音響工学、ネットワークセンシング
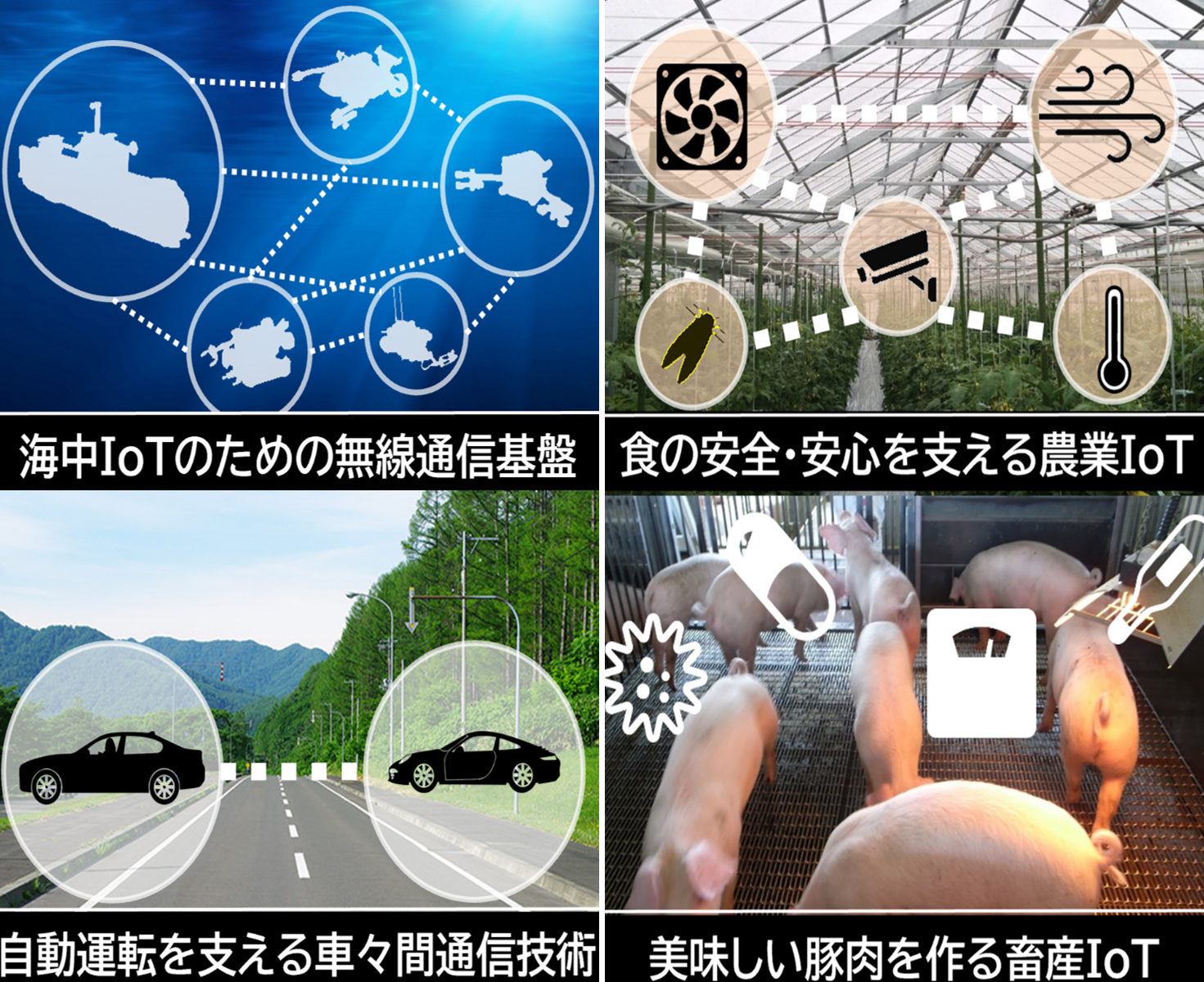 人と人の遠隔コミュニケーションを実現するために構築された情報通信技術は,いつしか人と(家電や自動車などの)モノ,モノとモノ同士を繋げる手段となりました.その対象の広がりは留まるところを知りませんが,本研究室では,情報通信技術の中でも,無線通信,および,ディジタル信号処理を活用した様々な形態のシステムを対象に,新しい信号処理方式の探求,シミュレーションによる最適化,実験による性能評価という3つのアプローチを行う事で,情報通信の進歩に貢献することを目指しています.具体的には,海中IoT実現のための音響通信システム,高度道路交通システムを支える可視光通信システム,次世代農業・畜産を支えるスマートセンシングシステム,ICTを活用した新たな土木施工システム等に関する研究を行っています.
Read More
Acoustic Laboratory (Wireless communication, Intelligent Agriculture, and Intelligent Construction) (Communication System Laboratory) Information and Communication Engineering, Ultrasonic Measurement Engineering, Underwater Acoustic Engineering, ICT Civil Engineering, Animal Health Engineering, Plant Protection Engineering, Network Sensing
人と人の遠隔コミュニケーションを実現するために構築された情報通信技術は,いつしか人と(家電や自動車などの)モノ,モノとモノ同士を繋げる手段となりました.その対象の広がりは留まるところを知りませんが,本研究室では,情報通信技術の中でも,無線通信,および,ディジタル信号処理を活用した様々な形態のシステムを対象に,新しい信号処理方式の探求,シミュレーションによる最適化,実験による性能評価という3つのアプローチを行う事で,情報通信の進歩に貢献することを目指しています.具体的には,海中IoT実現のための音響通信システム,高度道路交通システムを支える可視光通信システム,次世代農業・畜産を支えるスマートセンシングシステム,ICTを活用した新たな土木施工システム等に関する研究を行っています.
Read More
Acoustic Laboratory (Wireless communication, Intelligent Agriculture, and Intelligent Construction) (Communication System Laboratory) Information and Communication Engineering, Ultrasonic Measurement Engineering, Underwater Acoustic Engineering, ICT Civil Engineering, Animal Health Engineering, Plant Protection Engineering, Network Sensing Information and communication technology, which was originally developed to realize remote communication between people, has somehow become a means of connecting people and things (such as home appliances and automobiles), and things and things to each other. Our laboratory aims to contribute to the progress of information and communication technology through three approaches: exploration of new signal processing methods, optimization by simulation, and performance evaluation by experiment. Our goal is to contribute to the advancement of information and communication by taking three approaches: exploring new signal processing methods, optimization through simulation, and performance evaluation through experiments. Specifically, we are conducting research on acoustic communication systems for the realization of underwater IoT, visible light communication systems that support advanced road traffic systems, smart sensing systems that support next-generation agriculture and livestock breeding, and new civil engineering construction systems that utilize ICT.
Read More
Information and communication technology, which was originally developed to realize remote communication between people, has somehow become a means of connecting people and things (such as home appliances and automobiles), and things and things to each other. Our laboratory aims to contribute to the progress of information and communication technology through three approaches: exploration of new signal processing methods, optimization by simulation, and performance evaluation by experiment. Our goal is to contribute to the advancement of information and communication by taking three approaches: exploring new signal processing methods, optimization through simulation, and performance evaluation through experiments. Specifically, we are conducting research on acoustic communication systems for the realization of underwater IoT, visible light communication systems that support advanced road traffic systems, smart sensing systems that support next-generation agriculture and livestock breeding, and new civil engineering construction systems that utilize ICT.
Read More
-
濱崎研究室 ソーシャルメディア分析、ウェブマイニング、セマンティックウェブ、知識共有
 ソーシャルメディア分析やウェブマイニングを中心に、ウェブによって拡張された人々のコミュニケーション・コラボレーション・クリエーションを観察、分析、支援する研究に取り組んでいます。アプローチとしては特に関係性に着目し、人の関係性(ソーシャルネットワーク)や情報の関係性(知識ネットワーク)を、ネットワーク分析技術等を用いて解析し利活用します。これまでに研究者間の関係をウェブから自動抽出し情報支援システムに活用する研究や、コンテンツ間の派生関係をウェブから自動抽出し可視化する研究(音楽視聴支援サービスSongrium http://songrium.jp)、属性情報間の共起関係からスキーマを自動生成するシステムの研究(集合知データベース Social Infobox http://socialinfobox.jp)など、関係性という観点から幅広い研究開発に取り組んできました。人々の緩やかな協調・連携によって新しいコンテンツや知識が生まれる現象を理解する技術、それを支援する技術、さらにそれを活用する技術の研究開発を通して、情報基盤としてのオンラインコミュニティの強化を目指します。
Read More
Masahiro Hamasaki's Laboratory Social Media Analysis, Web Mining, Semantic Web, Knowledge Sharing
ソーシャルメディア分析やウェブマイニングを中心に、ウェブによって拡張された人々のコミュニケーション・コラボレーション・クリエーションを観察、分析、支援する研究に取り組んでいます。アプローチとしては特に関係性に着目し、人の関係性(ソーシャルネットワーク)や情報の関係性(知識ネットワーク)を、ネットワーク分析技術等を用いて解析し利活用します。これまでに研究者間の関係をウェブから自動抽出し情報支援システムに活用する研究や、コンテンツ間の派生関係をウェブから自動抽出し可視化する研究(音楽視聴支援サービスSongrium http://songrium.jp)、属性情報間の共起関係からスキーマを自動生成するシステムの研究(集合知データベース Social Infobox http://socialinfobox.jp)など、関係性という観点から幅広い研究開発に取り組んできました。人々の緩やかな協調・連携によって新しいコンテンツや知識が生まれる現象を理解する技術、それを支援する技術、さらにそれを活用する技術の研究開発を通して、情報基盤としてのオンラインコミュニティの強化を目指します。
Read More
Masahiro Hamasaki's Laboratory Social Media Analysis, Web Mining, Semantic Web, Knowledge Sharing With a focus on Social Media Analysis and Web Mining, Masahiro Hamasaki’s Laboratory conducts research on analysis and assistance technologies for communication, collaboration and creation between people. Our approach is utilizing relationship, e.g., social networks and knowledge networks. For example, a music browsing assistance service ‘Songrium (http://songrium.jp)’ focuses on relationship between musical content. A database system based on wisdom of crowds ‘Social Infobox (http://socialinfobox.jp)’ leverages relationship between vocabraries and attributes. Our aim is to improve online community as a commuinication/collaboration/creation platform.
Read More
With a focus on Social Media Analysis and Web Mining, Masahiro Hamasaki’s Laboratory conducts research on analysis and assistance technologies for communication, collaboration and creation between people. Our approach is utilizing relationship, e.g., social networks and knowledge networks. For example, a music browsing assistance service ‘Songrium (http://songrium.jp)’ focuses on relationship between musical content. A database system based on wisdom of crowds ‘Social Infobox (http://socialinfobox.jp)’ leverages relationship between vocabraries and attributes. Our aim is to improve online community as a commuinication/collaboration/creation platform.
Read More
-
システムモデル研究室 システム工学、計算物理学
 (広い意味での)局所探索法を用いた最適化とその周辺に現れる諸問題に関心を持っています.最適化は,生命活動を支えるタンパク質をはじめとする,種々の分子系の安定構造の探索から,人の生産活動の効率化に係る,様々な問題解決に至るまで,科学,工学のあらゆる分野で直面する課題です.その課題解決のアプローチとして,局所探索法で括られる一群の技法が用いられますが,これらの技法がなぜうまく動作するのか,必ずしも良く理解されていません.この背景の下,局所探索法の諸技法の有効性を,評価関数ならびに近傍関数が作る景観と探索ルールが編み出す,探索機能に注目した実験的解析を通して明らかにしていく基礎研究を行っています.探索機能の相似性をふまえた手続きの構成モデリングを通して,異種技法の包括的理解と個別特性の明確化を図っていくことにより,見通しの良い技法の選択,運用に資する,理解の獲得を目指しています.
Read More
Systems Modeling Laboratory Systems Engineering, Computational Physics
(広い意味での)局所探索法を用いた最適化とその周辺に現れる諸問題に関心を持っています.最適化は,生命活動を支えるタンパク質をはじめとする,種々の分子系の安定構造の探索から,人の生産活動の効率化に係る,様々な問題解決に至るまで,科学,工学のあらゆる分野で直面する課題です.その課題解決のアプローチとして,局所探索法で括られる一群の技法が用いられますが,これらの技法がなぜうまく動作するのか,必ずしも良く理解されていません.この背景の下,局所探索法の諸技法の有効性を,評価関数ならびに近傍関数が作る景観と探索ルールが編み出す,探索機能に注目した実験的解析を通して明らかにしていく基礎研究を行っています.探索機能の相似性をふまえた手続きの構成モデリングを通して,異種技法の包括的理解と個別特性の明確化を図っていくことにより,見通しの良い技法の選択,運用に資する,理解の獲得を目指しています.
Read More
Systems Modeling Laboratory Systems Engineering, Computational Physics Our research interests are in optimization by local search and the issues around this topic. Optimization is a ubiquitous task in various fields of science and engineering and a wide variety of examples can be cited, ranging from finding the lowest-energy configurations of various molecular systems to solving operations-research problems arising from real-life situations. Local search is a commonly accepted approach for approximate solutions, but why this technique works satisfactorily has not been well understood. Against this background, the study focuses on the origin of the effectiveness of each method; specifically, its search dynamics are observed in the landscape of the cost and neighborhood functions and analyzed from their functionality point of view. The study is intended to obtain a comprehensive and individual understanding of the methods through the structure modeling of the solution procedure on the basis of the similarity in search function. This is conducted with the hope of establishing a good basis conducive to the appropriate choice and successful application of the method.
Read More
Our research interests are in optimization by local search and the issues around this topic. Optimization is a ubiquitous task in various fields of science and engineering and a wide variety of examples can be cited, ranging from finding the lowest-energy configurations of various molecular systems to solving operations-research problems arising from real-life situations. Local search is a commonly accepted approach for approximate solutions, but why this technique works satisfactorily has not been well understood. Against this background, the study focuses on the origin of the effectiveness of each method; specifically, its search dynamics are observed in the landscape of the cost and neighborhood functions and analyzed from their functionality point of view. The study is intended to obtain a comprehensive and individual understanding of the methods through the structure modeling of the solution procedure on the basis of the similarity in search function. This is conducted with the hope of establishing a good basis conducive to the appropriate choice and successful application of the method.
Read More
-
数理科学・AI研究室 非平衡物理学、機械学習、制御理論、システム生物学
 数理科学・AI研究室では、物理学・生命科学・情報科学を横断する学際的な視点から、複雑なシステムの背後に潜む数理的な構造・普遍的な法則を探求しています。我々のアプローチの特徴は、「対称性」や「トポロジー」のような特定のモデルに依存しない数理的概念を活用する点にあり、これにより一見異なる多様な現象を貫く本質を捉えることを目指しています。具体的な研究テーマの例としては、生物システムにおける制御機構の解明、物理学の概念・手法を用いた機械学習モデルの解析、機械学習を用いた実験データからの対称性の発見、一般化対称性を用いた物質相の解析などがあります。
Read More
Integral Mathematical Science Laboratory Non-equilibrium physics, Machine learning, Control theory, Systems biology
数理科学・AI研究室では、物理学・生命科学・情報科学を横断する学際的な視点から、複雑なシステムの背後に潜む数理的な構造・普遍的な法則を探求しています。我々のアプローチの特徴は、「対称性」や「トポロジー」のような特定のモデルに依存しない数理的概念を活用する点にあり、これにより一見異なる多様な現象を貫く本質を捉えることを目指しています。具体的な研究テーマの例としては、生物システムにおける制御機構の解明、物理学の概念・手法を用いた機械学習モデルの解析、機械学習を用いた実験データからの対称性の発見、一般化対称性を用いた物質相の解析などがあります。
Read More
Integral Mathematical Science Laboratory Non-equilibrium physics, Machine learning, Control theory, Systems biology The Integral Mathematical Science Laboratory explores mathematical structures and universal laws underlying complex systems through an interdisciplinary perspective that spans physics, life sciences, and information science. Our approach is characterized by utilizing
model-independent mathematical concepts such as "symmetry" and "topology," which enables us to capture the essential nature common to seemingly diverse phenomena. Examples of our research topics include elucidating control mechanisms in biological systems, analyzing
machine learning models using physical concepts and methods, discovering symmetries from experimental data using machine learning, and analyzing phases of matter using generalized symmetries.
Read More
The Integral Mathematical Science Laboratory explores mathematical structures and universal laws underlying complex systems through an interdisciplinary perspective that spans physics, life sciences, and information science. Our approach is characterized by utilizing
model-independent mathematical concepts such as "symmetry" and "topology," which enables us to capture the essential nature common to seemingly diverse phenomena. Examples of our research topics include elucidating control mechanisms in biological systems, analyzing
machine learning models using physical concepts and methods, discovering symmetries from experimental data using machine learning, and analyzing phases of matter using generalized symmetries.
Read More
-
新里研究室 集団的創発現象・認知錯覚の起源・生き物のトラッキングシステム
 なにか新しい事が起こるということを考えるときに、我々は次のようなパラドクスに直面することになる。たとえば、新しい知識の学習について考えてみる。我々は、知識の獲得というものは暗に、今まで未知だったものを既知化することだろうと理解している。ところが、それを認めたとたんに、未知はたんなる観測者の無知として扱われ、新しい事を学習するということが不可能になってしまう。というのも、既知の外側という意味で未知は既知化されてしまうからだ。では、いったい、未知の未知性とはなんなのだろうか。 私は、未知なるものが事物としての側面(トークン)と集合としての側面(タイプ)を両方になうからこそ、未知の未知性は保証され、学習や創発などを積極的に語る事ができると考える。このようなタイプ・トークンの両義性を担った過程は、とくに身体としての群れを理解する上で重要になってくるだろう(下の写真は沖縄に生息するミナミコメツキガニ。撮影:西山雄太)。各個体の担う個体性(トークン)と社会性(タイプ)の両義性は、常にミクロとマクロの境界を無効にし、その結果、群れは一つの身体を獲得する。このようなことを,鮎の群れやカニの群れなどの実験を通して理解していく.
Read More
Niizato Laboratory Collective Behaviour, Origin of the Cognitive Illusion, Tracking System
なにか新しい事が起こるということを考えるときに、我々は次のようなパラドクスに直面することになる。たとえば、新しい知識の学習について考えてみる。我々は、知識の獲得というものは暗に、今まで未知だったものを既知化することだろうと理解している。ところが、それを認めたとたんに、未知はたんなる観測者の無知として扱われ、新しい事を学習するということが不可能になってしまう。というのも、既知の外側という意味で未知は既知化されてしまうからだ。では、いったい、未知の未知性とはなんなのだろうか。 私は、未知なるものが事物としての側面(トークン)と集合としての側面(タイプ)を両方になうからこそ、未知の未知性は保証され、学習や創発などを積極的に語る事ができると考える。このようなタイプ・トークンの両義性を担った過程は、とくに身体としての群れを理解する上で重要になってくるだろう(下の写真は沖縄に生息するミナミコメツキガニ。撮影:西山雄太)。各個体の担う個体性(トークン)と社会性(タイプ)の両義性は、常にミクロとマクロの境界を無効にし、その結果、群れは一つの身体を獲得する。このようなことを,鮎の群れやカニの群れなどの実験を通して理解していく.
Read More
Niizato Laboratory Collective Behaviour, Origin of the Cognitive Illusion, Tracking System Aristotle's famous proposition states that life is more than the sum of its parts. What does this proposition mean actually? Can the parts and the whole be separated? Instead, isn't the framework of part and whole one of the devices we use to understand life? Our laboratory tries to attack this question, differing from the so-called "parts and wholes" interaction; mutual anticipation, for instance. By taking each other's futures into their systems, they can achieve a dynamic system as a whole. In our laboratory, we are trying to understand the mysteries of living systems by devising various conceptual devices.
Read More
Aristotle's famous proposition states that life is more than the sum of its parts. What does this proposition mean actually? Can the parts and the whole be separated? Instead, isn't the framework of part and whole one of the devices we use to understand life? Our laboratory tries to attack this question, differing from the so-called "parts and wholes" interaction; mutual anticipation, for instance. By taking each other's futures into their systems, they can achieve a dynamic system as a whole. In our laboratory, we are trying to understand the mysteries of living systems by devising various conceptual devices.
Read More
-
ライフエンジニアリング研究室 深層学習、コンピュータビジョン
 情報化がますます進む一方で、さまざまな分野でいまだに人手に頼らざるを得ない仕事がたくさんあります。それらには、非常に単調かつ膨大であったり、困難で一部の「職人」にしかできなかったりするものもあります。我々は主に、水産業と作業療法の分野において、深層学習やコンピュータ・ビジョンの技術を適切に応用することで、人の主観に寄らず客観的に評価・計測ができるソフトウェアの設計と開発をしています。具体的には、例えば、自動的かつ高精度にまぐろの卵の質を評価するシステムや、人には難しい粒度で子供の姿勢を計測するシステムの開発をしています。さらに、深層学習により人の認知機能の理解を深めるための研究もしています。
Read More
Life Engineering Laboratory Deep Learning, Computer Vision
情報化がますます進む一方で、さまざまな分野でいまだに人手に頼らざるを得ない仕事がたくさんあります。それらには、非常に単調かつ膨大であったり、困難で一部の「職人」にしかできなかったりするものもあります。我々は主に、水産業と作業療法の分野において、深層学習やコンピュータ・ビジョンの技術を適切に応用することで、人の主観に寄らず客観的に評価・計測ができるソフトウェアの設計と開発をしています。具体的には、例えば、自動的かつ高精度にまぐろの卵の質を評価するシステムや、人には難しい粒度で子供の姿勢を計測するシステムの開発をしています。さらに、深層学習により人の認知機能の理解を深めるための研究もしています。
Read More
Life Engineering Laboratory Deep Learning, Computer Vision While information technology is advancing rapidly, there are still many tasks in various fields that must be done by humans. Some of them are very monotonous and time-consuming, or so difficult that only a few "craftsmen" can do. We are designing and developing software by appropriately using deep learning and computer vision techniques for solving practical problems in some fields such as fisheries and occupational therapy. For example, we have been developing a system that automatically and accurately evaluates the quality of tuna eggs or a system that quantitatively measures the posture of children with a fine granularity that is difficult for humans to achieve. Recent research topic also includes deepening our understanding of human cognitive functions through deep learning.
Read More
While information technology is advancing rapidly, there are still many tasks in various fields that must be done by humans. Some of them are very monotonous and time-consuming, or so difficult that only a few "craftsmen" can do. We are designing and developing software by appropriately using deep learning and computer vision techniques for solving practical problems in some fields such as fisheries and occupational therapy. For example, we have been developing a system that automatically and accurately evaluates the quality of tuna eggs or a system that quantitatively measures the posture of children with a fine granularity that is difficult for humans to achieve. Recent research topic also includes deepening our understanding of human cognitive functions through deep learning.
Read More
-
ディジタル制御研究室 制御理論、離散時間化、デスクリプタシステム
 様々なシステムにおいて、そのモデル化から制御系設計までを見通し良く行える理論の実現を目指して研究を行っています。近年、システムは複雑・多様化してきており、さらに、それらの解析や制御系設計にはディジタル機器の使用が前提となってきております。そのため、従来よりも広範なシステムを扱える柔軟なモデルとそれに基づく解析や制御系設計、特に、与えられた対象・環境・機器の基で、最適な性能を得るためのディジタル機器を意識した手法の開発が望まれています。このような統合的な視野から、先駆的・独創的な学術研究の実施を理論だけでなく実機による応用までを見据え目指しています。
Read More
Digital Control Laboratory Control Theory, Discretization, Descriptor System
様々なシステムにおいて、そのモデル化から制御系設計までを見通し良く行える理論の実現を目指して研究を行っています。近年、システムは複雑・多様化してきており、さらに、それらの解析や制御系設計にはディジタル機器の使用が前提となってきております。そのため、従来よりも広範なシステムを扱える柔軟なモデルとそれに基づく解析や制御系設計、特に、与えられた対象・環境・機器の基で、最適な性能を得るためのディジタル機器を意識した手法の開発が望まれています。このような統合的な視野から、先駆的・独創的な学術研究の実施を理論だけでなく実機による応用までを見据え目指しています。
Read More
Digital Control Laboratory Control Theory, Discretization, Descriptor System Our study aims to realize a theory that can provide a good perspective of various systems from modeling to control system design. In recent years, systems have become increasingly more complex and diverse, and the use of digital devices for their analysis and control system design has become a common practice. Therefore, developing flexible models that can handle a wider range of systems than in the past, as well as an analysis and control system design based on it is desired. In particular, it is desirable to develop a method that is conscious of digital devices to obtain optimum performance based on given systems, environments, and devices. From this integrated perspective, we aim to conduct pioneering and original academic research not only in theory but also in practical applications.
Read More
Our study aims to realize a theory that can provide a good perspective of various systems from modeling to control system design. In recent years, systems have become increasingly more complex and diverse, and the use of digital devices for their analysis and control system design has become a common practice. Therefore, developing flexible models that can handle a wider range of systems than in the past, as well as an analysis and control system design based on it is desired. In particular, it is desirable to develop a method that is conscious of digital devices to obtain optimum performance based on given systems, environments, and devices. From this integrated perspective, we aim to conduct pioneering and original academic research not only in theory but also in practical applications.
Read More
-
ディジタル制御研究室 デジタル制御、電力システム、スマート電力ルータ
 本研究室はデジタル制御とデジタルグリッドという2つの柱で研究をしています。1)フィジカルシステムは連続時間領域で存在しますが、そのシステムの解析、予測、制御などはサイバー空間において離散時間領域で行われます。そこでフィジカルシステムを離散時間モデルとして再現し、そのダイナミクスやデジタル制御の解析・設計方法を考案し、実システムへの応用に挑戦しています。2)近年、風力発電、太陽光発電など再生可能エネルギーの導入が推奨されていますが、現存する電力系統は、余剰電力発生や周波数調整力不足の問題があるため再生可能エネルギーの導入に限界があります。そこで再生可能エネルギーの接続限界を高めるために、旧来の巨大な電力系統を複数の小さなセルに細分化し、ICTを活かしたデジタルグリッドという新電力システムの構築や電力制御装置の開発をします。上記の2柱で理論から実証実験までの研究を進めていきます。
Read More
Digital Control Laboratory Digital Control, Electrical Power System, Smart Power Router
本研究室はデジタル制御とデジタルグリッドという2つの柱で研究をしています。1)フィジカルシステムは連続時間領域で存在しますが、そのシステムの解析、予測、制御などはサイバー空間において離散時間領域で行われます。そこでフィジカルシステムを離散時間モデルとして再現し、そのダイナミクスやデジタル制御の解析・設計方法を考案し、実システムへの応用に挑戦しています。2)近年、風力発電、太陽光発電など再生可能エネルギーの導入が推奨されていますが、現存する電力系統は、余剰電力発生や周波数調整力不足の問題があるため再生可能エネルギーの導入に限界があります。そこで再生可能エネルギーの接続限界を高めるために、旧来の巨大な電力系統を複数の小さなセルに細分化し、ICTを活かしたデジタルグリッドという新電力システムの構築や電力制御装置の開発をします。上記の2柱で理論から実証実験までの研究を進めていきます。
Read More
Digital Control Laboratory Digital Control, Electrical Power System, Smart Power Router Our research interests focus on the two main areas: digital control and electrical power system. In digital control area, we develop a discretization method, which allows us to derive a discrete-time model from a continuous-time model of nonlinear systems, considering the relationship between the discrete-time (digital) and continuous-time (analog). The research interests include, but not limited to digital control design and dynamics analysis based on the discrete-time model and their application. In electrical power system area, we arm to develop a new electrical power system called Digital Grid, which allows us to control the power system more flexibly and conduct more renewable energy. In Digital Grid, the largely unidirectional power network is divided into multiple cells, which can be operated as microgrid and controlled by smart power routers. The above research topics are approached from both theory and experiment.
Read More
Our research interests focus on the two main areas: digital control and electrical power system. In digital control area, we develop a discretization method, which allows us to derive a discrete-time model from a continuous-time model of nonlinear systems, considering the relationship between the discrete-time (digital) and continuous-time (analog). The research interests include, but not limited to digital control design and dynamics analysis based on the discrete-time model and their application. In electrical power system area, we arm to develop a new electrical power system called Digital Grid, which allows us to control the power system more flexibly and conduct more renewable energy. In Digital Grid, the largely unidirectional power network is divided into multiple cells, which can be operated as microgrid and controlled by smart power routers. The above research topics are approached from both theory and experiment.
Read More
-
中尾研究室 データ同化,流体力学,数値モデリング,地球内部ダイナミクス
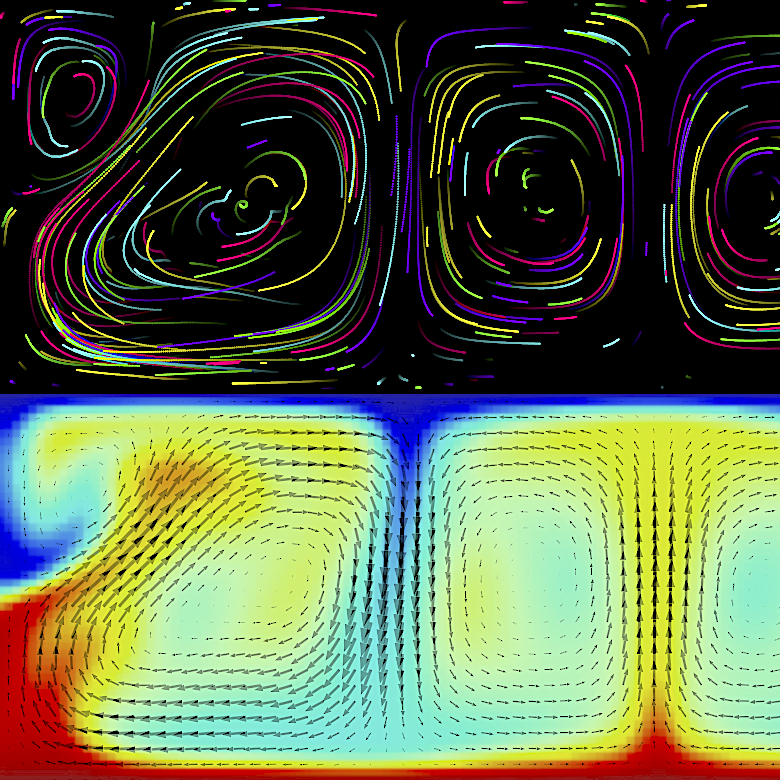 私たちの身のまわりには,空気や海の流れ,溶鉱炉の中の物質の動き,人の流れなど,複数の要素が関わりながら複雑に動くシステムが数多く存在します.こうしたシステムは,スケールが大きかったり,技術的な制約があったりするため,観測やモニタリングだけではその全体像を正確にとらえることが難しい場合があります.本研究室では,このような複雑なシステムを理解するために,「データ同化」と呼ばれる手法を用いています.これは,限られた観測データと数値モデルとを組み合わせることで,システム内部で起きている現象を推定する方法です.私たちは,データ同化の理論的な研究を進めるとともに,地震や火山といった自然災害のメカニズムの解明や,工学分野におけるさまざまな流体システムへの応用も目指しています.
Read More
Nakao Laboratory Data Assimilation, Fluid Dynamics, Numerical Modeling, Geodynamics
私たちの身のまわりには,空気や海の流れ,溶鉱炉の中の物質の動き,人の流れなど,複数の要素が関わりながら複雑に動くシステムが数多く存在します.こうしたシステムは,スケールが大きかったり,技術的な制約があったりするため,観測やモニタリングだけではその全体像を正確にとらえることが難しい場合があります.本研究室では,このような複雑なシステムを理解するために,「データ同化」と呼ばれる手法を用いています.これは,限られた観測データと数値モデルとを組み合わせることで,システム内部で起きている現象を推定する方法です.私たちは,データ同化の理論的な研究を進めるとともに,地震や火山といった自然災害のメカニズムの解明や,工学分野におけるさまざまな流体システムへの応用も目指しています.
Read More
Nakao Laboratory Data Assimilation, Fluid Dynamics, Numerical Modeling, Geodynamics There are many complex systems in which multiple components interact and flow dynamically, such as the air and ocean currents, the flow of materials inside blast furnaces, and the movement of people. These systems often operate on large spatial and temporal scales or are constrained by technical limitations, making it difficult to fully capture their behavior through observation and monitoring alone. Our laboratory aims to understand such complex systems using a technique known as data assimilation. This approach combines limited observational data with numerical models to estimate the internal state and dynamics of the system. We are conducting theoretical research on data assimilation, while also applying it to understand natural phenomena with disaster potential, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, as well as to a wide range of flow systems in engineering fields.
Read More
There are many complex systems in which multiple components interact and flow dynamically, such as the air and ocean currents, the flow of materials inside blast furnaces, and the movement of people. These systems often operate on large spatial and temporal scales or are constrained by technical limitations, making it difficult to fully capture their behavior through observation and monitoring alone. Our laboratory aims to understand such complex systems using a technique known as data assimilation. This approach combines limited observational data with numerical models to estimate the internal state and dynamics of the system. We are conducting theoretical research on data assimilation, while also applying it to understand natural phenomena with disaster potential, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, as well as to a wide range of flow systems in engineering fields.
Read More
Human Roboticsヒューマンロボティクス
AI、サイバニクス、人間拡張、モビリティを含む学際的システム分野An interdisciplinary systems field, encompassing AI, cybernics, human augmentation, and mobility.
-
マニピュレーション・システム研究室 ロボットによる器用な物体操作、人間の器用さの移植、産業用ロボットの高度化等
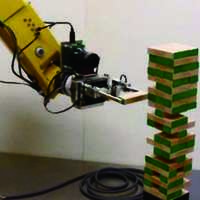 人間のように器用な操り(物体操作)をロボットで実現するためには,その操りの力学的,幾何学的なモデル化が重要となります.大きなもの,重いものを持ち上げずに押したり転がしたりするとどんな力学的なメリットがあるのか,どんな動かし方の計画をすればよいのか,このような観点で定式化できれば,ロボットでも同様に器用な操りができるのではないか,と考え,研究に取り組んでいます. 例えばロッカーを移動させる際に,傾けてある一点の周りに回すと,移動量は少ないけれど,とても小さい力で動かすことができます.また,隙間のとても狭い穴と棒の挿入作業では,しっかりと握りしめて作業するよりも,ある程度力を抜いて作業をしたほうが簡単に入ります. このような器用さを解析,検討することで,現在は単純に決められた動作しか行わない産業用ロボット,自動機械の用途を広げることができるだろうと考えています.現在行われている作業を解析し,それを改善する手法を考案,モデル化,実験を進めていきたいと考えています.
Read More
Manipulation System Laboratory Human-like Dexterous Robot Manipulation, Advanced Industrial Robot
人間のように器用な操り(物体操作)をロボットで実現するためには,その操りの力学的,幾何学的なモデル化が重要となります.大きなもの,重いものを持ち上げずに押したり転がしたりするとどんな力学的なメリットがあるのか,どんな動かし方の計画をすればよいのか,このような観点で定式化できれば,ロボットでも同様に器用な操りができるのではないか,と考え,研究に取り組んでいます. 例えばロッカーを移動させる際に,傾けてある一点の周りに回すと,移動量は少ないけれど,とても小さい力で動かすことができます.また,隙間のとても狭い穴と棒の挿入作業では,しっかりと握りしめて作業するよりも,ある程度力を抜いて作業をしたほうが簡単に入ります. このような器用さを解析,検討することで,現在は単純に決められた動作しか行わない産業用ロボット,自動機械の用途を広げることができるだろうと考えています.現在行われている作業を解析し,それを改善する手法を考案,モデル化,実験を進めていきたいと考えています.
Read More
Manipulation System Laboratory Human-like Dexterous Robot Manipulation, Advanced Industrial Robot For the realization of human-like dexterous robot manipulation, it is important to kinematical and geometrical modeling of manipulation. Why human can manipulate a heavy or large object even if it cannot be picked up by his/her hand. When he/she manipulates such objects, they may push, tilt or tumble the object on a floor or a table. We should analyze such a manipulation model to show why it is possible and the merits of such manipulation methods. With this process, we can translate such human dexterity to robot manipulation. We realize several dexterous robot manipulations; pivoting a large and heavy object on a floor, environment-contacting manipulation task, throwing and catching without landing impact, etc. We also try to implement these dexterous robot manipulation methods and analysis methods into advanced industrial robots and factory automation systems.
Read More
For the realization of human-like dexterous robot manipulation, it is important to kinematical and geometrical modeling of manipulation. Why human can manipulate a heavy or large object even if it cannot be picked up by his/her hand. When he/she manipulates such objects, they may push, tilt or tumble the object on a floor or a table. We should analyze such a manipulation model to show why it is possible and the merits of such manipulation methods. With this process, we can translate such human dexterity to robot manipulation. We realize several dexterous robot manipulations; pivoting a large and heavy object on a floor, environment-contacting manipulation task, throwing and catching without landing impact, etc. We also try to implement these dexterous robot manipulation methods and analysis methods into advanced industrial robots and factory automation systems.
Read More
-
分散システムデザイン研究室 分散型機械システム、自律分散ネットワーク、自己組織化、インフラ・災害調査用ロボット
 生物を始め自然界では各階層における要素同士が影響し合うことで複雑なシステムを構成しています。要素間の相互作用から人が予想もつかない機能や形態が創発し、かつ動的にシステムが維持されているのが特徴です。本研究室では、そのような要素間の相互作用による全体機能の創出に着目し、工学への応用を研究しています。具体的には、ロボットを複数の細胞機械(モジュール)から構成することで、環境や用途に応じて形態を変更可能な分散型機械システムの研究や、センサネットワークを構成する無線ノード同士が自律分散的にお互いの通信タイミングを調整することで、全体として通信衝突のない安定したネットワークを維持する自律分散ネットワーク手法の研究開発を実施しています。また、近年インフラの維持管理、災害調査用ロボットが注目されていますが、そのような過酷な環境で動作する陸海空フィールドロボットシステムの研究開発を進めています。
Read More
Distributed System Design Laboratory Distributed Mechanical Systems, Autonomous Distributed Networks, Self-organization, Robots for Infrastructure and Disaster Investigation
生物を始め自然界では各階層における要素同士が影響し合うことで複雑なシステムを構成しています。要素間の相互作用から人が予想もつかない機能や形態が創発し、かつ動的にシステムが維持されているのが特徴です。本研究室では、そのような要素間の相互作用による全体機能の創出に着目し、工学への応用を研究しています。具体的には、ロボットを複数の細胞機械(モジュール)から構成することで、環境や用途に応じて形態を変更可能な分散型機械システムの研究や、センサネットワークを構成する無線ノード同士が自律分散的にお互いの通信タイミングを調整することで、全体として通信衝突のない安定したネットワークを維持する自律分散ネットワーク手法の研究開発を実施しています。また、近年インフラの維持管理、災害調査用ロボットが注目されていますが、そのような過酷な環境で動作する陸海空フィールドロボットシステムの研究開発を進めています。
Read More
Distributed System Design Laboratory Distributed Mechanical Systems, Autonomous Distributed Networks, Self-organization, Robots for Infrastructure and Disaster Investigation In the natural world, including living organisms, elements at each level interact with each other to form a complex system. It is characterized by the emergence of functions and forms that humans cannot expect from the interaction between elements, and such systems are dynamically maintained. In our laboratory, we focus on the creation of overall functions by the interaction between such elements, and study its application to engineering. Specifically, we’ve been working on a modular robot composed of a plurality of cell machines (modules) so that the form can be changed according to the environment and application, and a self-organized wireless network method that maintains a stable network without communication collisions by interactions of wireless nodes in a distributed manner. In recent years, we are also conducting researches on field robots for infrastructure maintenance and disaster investigation that work in such harsh environments.
Read More
In the natural world, including living organisms, elements at each level interact with each other to form a complex system. It is characterized by the emergence of functions and forms that humans cannot expect from the interaction between elements, and such systems are dynamically maintained. In our laboratory, we focus on the creation of overall functions by the interaction between such elements, and study its application to engineering. Specifically, we’ve been working on a modular robot composed of a plurality of cell machines (modules) so that the form can be changed according to the environment and application, and a self-organized wireless network method that maintains a stable network without communication collisions by interactions of wireless nodes in a distributed manner. In recent years, we are also conducting researches on field robots for infrastructure maintenance and disaster investigation that work in such harsh environments.
Read More
-
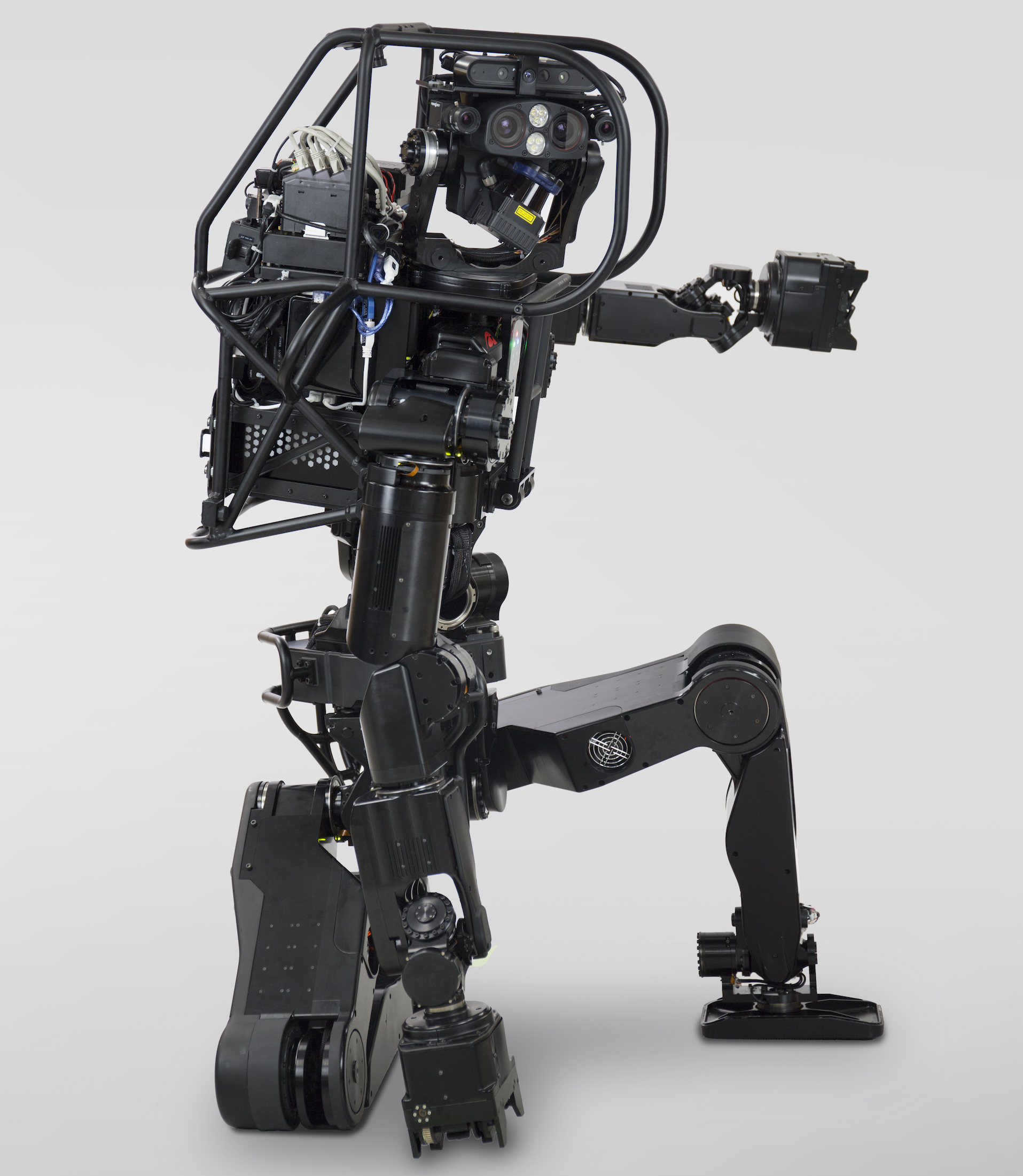
ヒューマノイド研究室 ヒューマノイドロボット、動作計画及び制御、ハードウェアデザイン、遠隔操作
 当研究室では、人間工学的に不適切な姿勢での作業や重負荷作業、単純繰り返し作業、自然災害等によってダメージを受けたプラント等の有害・危険な環境での作業等、過酷環境で働く人間の活動を代替し解放するヒューマノイドロボットを実現するため、過酷環境でも働けるヘビーデューティーヒューマノイドロボットの実現に必要な基盤研究・工学的研究を行っています。具体的には、二足歩行ロボットに常に付きまとう問題である転倒に対し、転倒時の衝撃を受けても壊れにくい関節構造やエアバッグを用いた衝撃吸収機構、転倒時の衝撃を最小限に抑えるための動作制御技術、手足の区別なく全身を使って複雑な環境を移動するための動作計画・制御技術、複雑環境において周囲の環境の3次元計測を行って自己の状態を正確に推定し、計測結果から手や足をつける場所を認識する技術、多数の関節を持ち環境に固定されていないロボットを簡単な操作で遠隔操作したり新たな行動を教示したりする技術等の研究を行っています。研究室は産業技術総合研究所つくばセンター内にあり、HRP-2改を初めとした複数の等身大ヒューマノイドロボットを有し、このようなロボットを研究に使用することができる国内でも数少ない研究室の一つです。
Read More
Humanoid Robotics Laboratory Humanoid robot, motion planning and control, hardware design, teleoperation
当研究室では、人間工学的に不適切な姿勢での作業や重負荷作業、単純繰り返し作業、自然災害等によってダメージを受けたプラント等の有害・危険な環境での作業等、過酷環境で働く人間の活動を代替し解放するヒューマノイドロボットを実現するため、過酷環境でも働けるヘビーデューティーヒューマノイドロボットの実現に必要な基盤研究・工学的研究を行っています。具体的には、二足歩行ロボットに常に付きまとう問題である転倒に対し、転倒時の衝撃を受けても壊れにくい関節構造やエアバッグを用いた衝撃吸収機構、転倒時の衝撃を最小限に抑えるための動作制御技術、手足の区別なく全身を使って複雑な環境を移動するための動作計画・制御技術、複雑環境において周囲の環境の3次元計測を行って自己の状態を正確に推定し、計測結果から手や足をつける場所を認識する技術、多数の関節を持ち環境に固定されていないロボットを簡単な操作で遠隔操作したり新たな行動を教示したりする技術等の研究を行っています。研究室は産業技術総合研究所つくばセンター内にあり、HRP-2改を初めとした複数の等身大ヒューマノイドロボットを有し、このようなロボットを研究に使用することができる国内でも数少ない研究室の一つです。
Read More
Humanoid Robotics Laboratory Humanoid robot, motion planning and control, hardware design, teleoperation In our laboratory, we are conducting research on fundamental technologies required to build heavy-duty humanoid robots. The humanoid robots are expected to work in place of humans who are working in hazardous and dangerous environments such as industrial plans damaged by natural disasters and who are working in ergonomically undesirable postures. In order to develop such humanoid robots, we have been developing a durable joint structure and an airbag system, a motion control algorithm to minimize falling impact, whole-body motion planning and control algorithms to move around in complex environment, a teleoperation system which enable to control redundant and underactuated robots with minimal effort and so on. Our laboratory is placed in Tsukuba Center of National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) . Students can work with experience humanoid robotics researchers using life-sized humanoid robots we developed.
Read More
In our laboratory, we are conducting research on fundamental technologies required to build heavy-duty humanoid robots. The humanoid robots are expected to work in place of humans who are working in hazardous and dangerous environments such as industrial plans damaged by natural disasters and who are working in ergonomically undesirable postures. In order to develop such humanoid robots, we have been developing a durable joint structure and an airbag system, a motion control algorithm to minimize falling impact, whole-body motion planning and control algorithms to move around in complex environment, a teleoperation system which enable to control redundant and underactuated robots with minimal effort and so on. Our laboratory is placed in Tsukuba Center of National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) . Students can work with experience humanoid robotics researchers using life-sized humanoid robots we developed.
Read More
-
生体信号基盤モデル研究室 生体信号、基盤モデル、自己教師あり学習、継続学習、パーソナライズ、BCI/筋電制御
 本研究室では、脳波・筋電・心電・IMUなどの生体信号を対象に、計測・整備の難しさがボトルネックになりがちな領域で、まず大規模データセット構築とベンチマーキングを行い、汎用的に使える生体信号基盤モデルの確立を目指します。さらに、実運用では被験者や装着条件、環境が変化し続けるため、過去の知識を失わずに性能を伸ばす継続学習が不可欠です。本研究室では、実世界の限られたメモリ制約の下でオンラインに学習し続ける手法を開発し、BCIや筋電制御などのヒューマンマシンインタフェースを、より頑健・高精度・長期安定にすることを目指します。加えて、映像など他モダリティと組み合わせたラベル付け・状態推定の自動化にも取り組み、実験フレームワークとアルゴリズムを往復しながら、人とAIが協調する次世代の生体情報知能基盤を構築します。
Read More
Biosignal Foundation Model Laboratory Biosignals, Foundation Models, Self-supervised Learning, Continual Learning, Personalization, BCI, Myoelectric Control
本研究室では、脳波・筋電・心電・IMUなどの生体信号を対象に、計測・整備の難しさがボトルネックになりがちな領域で、まず大規模データセット構築とベンチマーキングを行い、汎用的に使える生体信号基盤モデルの確立を目指します。さらに、実運用では被験者や装着条件、環境が変化し続けるため、過去の知識を失わずに性能を伸ばす継続学習が不可欠です。本研究室では、実世界の限られたメモリ制約の下でオンラインに学習し続ける手法を開発し、BCIや筋電制御などのヒューマンマシンインタフェースを、より頑健・高精度・長期安定にすることを目指します。加えて、映像など他モダリティと組み合わせたラベル付け・状態推定の自動化にも取り組み、実験フレームワークとアルゴリズムを往復しながら、人とAIが協調する次世代の生体情報知能基盤を構築します。
Read More
Biosignal Foundation Model Laboratory Biosignals, Foundation Models, Self-supervised Learning, Continual Learning, Personalization, BCI, Myoelectric Control We construct large-scale bio-signal datasets and benchmarks to establish foundation models. We further develop continual learning methods that can adapt online under limited memory in real-world settings, enabling robust long-term human–AI interfaces such as BCI and myoelectric control. We also explore multimodal integration (e.g., vision) to automate labeling and state estimation, bridging experimental frameworks and algorithms.
Read More
We construct large-scale bio-signal datasets and benchmarks to establish foundation models. We further develop continual learning methods that can adapt online under limited memory in real-world settings, enabling robust long-term human–AI interfaces such as BCI and myoelectric control. We also explore multimodal integration (e.g., vision) to automate labeling and state estimation, bridging experimental frameworks and algorithms.
Read More
-
サイバニクス研究センター 人間・機械一体化,サイバニクス,生体運動・生理解析,運動転送,ロボット治療,ロボット安全
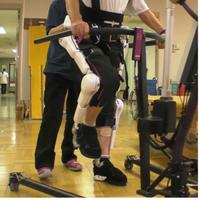 身体機能改善・補助・獲得,および生理機能診断などの医療・ヘルスケア分野,移乗介助・重作業の軽減などの介護・労働分野,さらに,アスリート・障がい者アスリートに対する運動転送などの競技スポーツ分野などに焦点をあてた人支援研究の分野開拓に挑戦しています. 医療・福祉・生活・労働・スポーツ等が行われる環境の実際の課題を対象とし,原理の理解,検証などの基礎的な研究から,人に対して安全で実用的な応用研究開発,有効性を検証する臨床・実証研究までを一体的に推進し,実社会に貢献する人支援機器/技術の研究開発を行います.具体的には,人の身体・生理特性および人を取り巻く実環境の解析を通じて,生体・環境情報センシング,生体フィードバック,人・機械系インタラクションを活用し,人・機械一体化技術,生体運動・生理解析,生体制御システム,ロボット治療技術,ロボット安全技術,運動転送技術,アスリート支援等に関する研究開発を行っていきます. 本研究室で大切にしていることは,現場から得られる課題をもとに,それらを解決するための手法を開発・適用し,そこから得られる新たな課題を解決していく研究開発サイクルを好スパイラルで進めていくことです.
Read More
Cybernics Laboratory Integration of Human and Robot, Biological Control Systems, Biological Motion & Physiology Analysis, Robot Therapy, Robot Safety
身体機能改善・補助・獲得,および生理機能診断などの医療・ヘルスケア分野,移乗介助・重作業の軽減などの介護・労働分野,さらに,アスリート・障がい者アスリートに対する運動転送などの競技スポーツ分野などに焦点をあてた人支援研究の分野開拓に挑戦しています. 医療・福祉・生活・労働・スポーツ等が行われる環境の実際の課題を対象とし,原理の理解,検証などの基礎的な研究から,人に対して安全で実用的な応用研究開発,有効性を検証する臨床・実証研究までを一体的に推進し,実社会に貢献する人支援機器/技術の研究開発を行います.具体的には,人の身体・生理特性および人を取り巻く実環境の解析を通じて,生体・環境情報センシング,生体フィードバック,人・機械系インタラクションを活用し,人・機械一体化技術,生体運動・生理解析,生体制御システム,ロボット治療技術,ロボット安全技術,運動転送技術,アスリート支援等に関する研究開発を行っていきます. 本研究室で大切にしていることは,現場から得られる課題をもとに,それらを解決するための手法を開発・適用し,そこから得られる新たな課題を解決していく研究開発サイクルを好スパイラルで進めていくことです.
Read More
Cybernics Laboratory Integration of Human and Robot, Biological Control Systems, Biological Motion & Physiology Analysis, Robot Therapy, Robot Safety We are developing human support systems and the technology for the following areas: (1) improvement of the impaired physical body functions, (2) physiologic functions examination for medical and health care fields, (3) reducing heavy load in manual labor and care fields, and (4) controlling the motion and sensation of the athletes for the sports
training.
Our developments include human-machine integration systems, biological motor control systems, biological/physiological system analysis, robot treatment technology, motion and skill learning support system, robot safety technology.
We conduct the research in area of the human support systems to contribute to the society by integrally implementing the fundamental researches related with proof of concept, applied researches for actual use and safety, and empirical study to investigate the effectiveness in actual environment.
We are solving various issues which rises and occurs in actual fields.
Read More
We are developing human support systems and the technology for the following areas: (1) improvement of the impaired physical body functions, (2) physiologic functions examination for medical and health care fields, (3) reducing heavy load in manual labor and care fields, and (4) controlling the motion and sensation of the athletes for the sports
training.
Our developments include human-machine integration systems, biological motor control systems, biological/physiological system analysis, robot treatment technology, motion and skill learning support system, robot safety technology.
We conduct the research in area of the human support systems to contribute to the society by integrally implementing the fundamental researches related with proof of concept, applied researches for actual use and safety, and empirical study to investigate the effectiveness in actual environment.
We are solving various issues which rises and occurs in actual fields.
Read More
-
柔軟ロボット学研究室 柔軟ロボティクス・ハプティクス(触覚学)
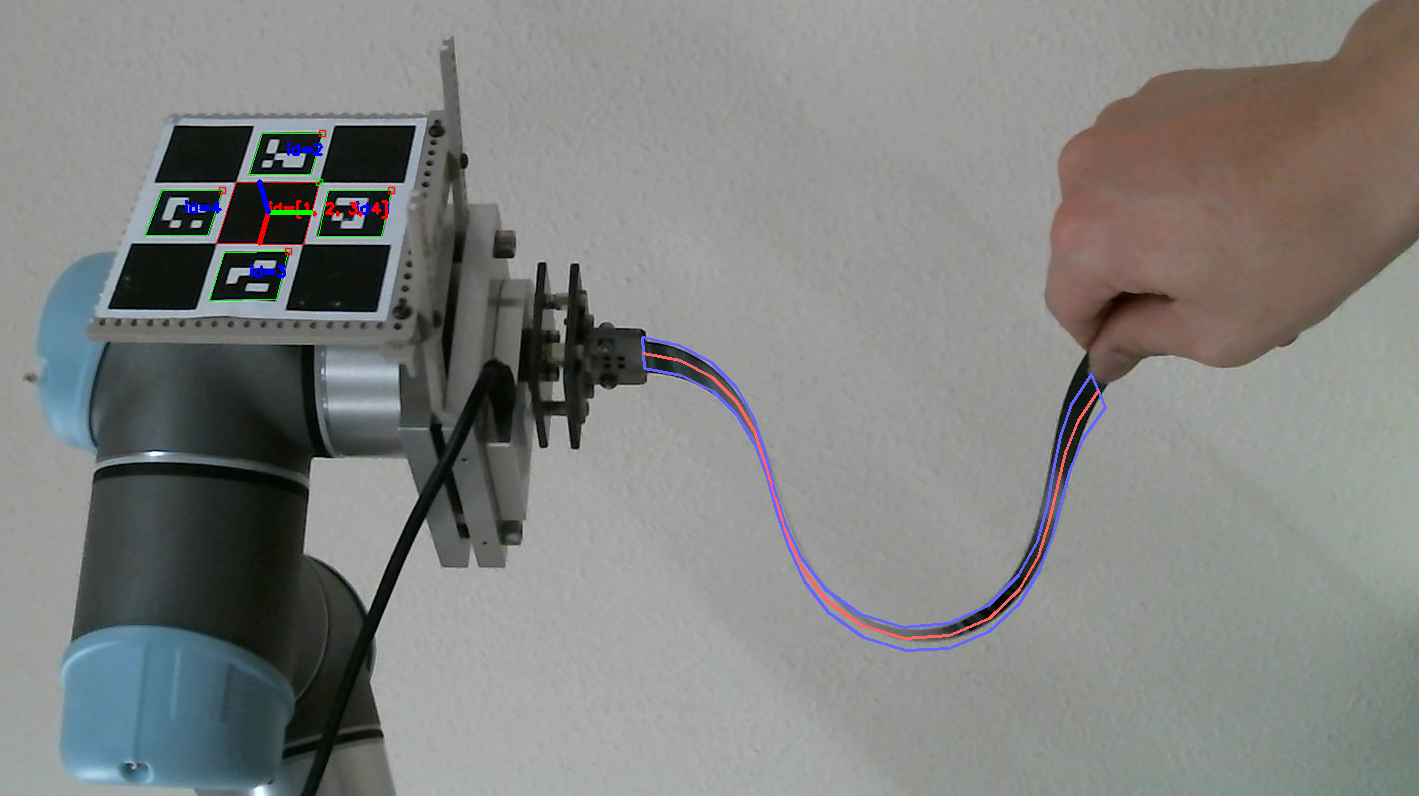 柔軟ロボット学研究室では,やわらかい素材を積極的に活用した新しいロボットに関するテクノロジとシステム・制御理論の創出を目指し,幅広い研究テーマに挑戦しています.1) ソフト素材の急激な大変形を利用した撃力発生機構『スナップモータ』などのソフトアクチュエータ,2) ひずみゲージを人工皮膚に埋め込んだ『ひずみゲージサンド』などのソフトセンサ,3) 大変形を伴うソフトロボットのシステム制御理論,4) スマートメカニクス: ロボット関節における柔軟性と剛性の融合のためのロボティクス理論, など.
Read More
Flexible Robotics Laboratory Soft Robotics, Haptics
柔軟ロボット学研究室では,やわらかい素材を積極的に活用した新しいロボットに関するテクノロジとシステム・制御理論の創出を目指し,幅広い研究テーマに挑戦しています.1) ソフト素材の急激な大変形を利用した撃力発生機構『スナップモータ』などのソフトアクチュエータ,2) ひずみゲージを人工皮膚に埋め込んだ『ひずみゲージサンド』などのソフトセンサ,3) 大変形を伴うソフトロボットのシステム制御理論,4) スマートメカニクス: ロボット関節における柔軟性と剛性の融合のためのロボティクス理論, など.
Read More
Flexible Robotics Laboratory Soft Robotics, Haptics ‘Flexible Robot’-ics Laboratory aims at creating new technologies and theory of system and control for advanced robots that positively utilize outstanding properties of soft materials, and is challenging a wide variety of related research topics: 1) Soft Actuators such as "Snap Motors" for generating impulsive forces by means of quick and large deformation of soft materials, 2) Soft Sensors such as “Strain-Sensitive Artificial Skin” where strain gauges are embedded into a soft and thin artificial skin, 3) System and Control Theory of soft robots which undergoes large deformation of soft materials and system and control theory, 4) Smart Mechanics: robotics theory for fusing softness and rigidity in robot joints, etc.
Read More
‘Flexible Robot’-ics Laboratory aims at creating new technologies and theory of system and control for advanced robots that positively utilize outstanding properties of soft materials, and is challenging a wide variety of related research topics: 1) Soft Actuators such as "Snap Motors" for generating impulsive forces by means of quick and large deformation of soft materials, 2) Soft Sensors such as “Strain-Sensitive Artificial Skin” where strain gauges are embedded into a soft and thin artificial skin, 3) System and Control Theory of soft robots which undergoes large deformation of soft materials and system and control theory, 4) Smart Mechanics: robotics theory for fusing softness and rigidity in robot joints, etc.
Read More
-
ヒューマン・ロボット・インタラクション研究室 ヒューマン・ロボット・インタフェース、センサ融合、環境知能化
 ヒューマン・ロボット・インタラクション研究室では,人とロボットのインタラクション(相互作用)に関わる幅広い研究を行っています.ロボットは外界の状況をセンシングし,考えて,行動しますが,ロボット単体によるセンシング能力には限界があります.そこで,人を取り囲む環境をロボットに見立て,環境内にセンサを遍在させることにより,部屋全体が人の活動状況を見守り,支援を行う環境知能化という新しい考えに基づく研究も行っています.環境に遍在させるセンサとして,無線通信により情報を収集することのできるオリジナルなセンサデバイス(インテリジェント電源タップ,温湿度センサ,照度センサ,人感センサ等)を開発するとともに,環境知能化の応用として,エネルギーの無駄を見つけて省エネを促すHEMS(Home Energy Management System),独居高齢者の普段の様子をモニタリングすることにより普段の状況と異なることを検知・通知する高齢者モニタリングシステム等を開発しています.また,様々な機器にセンサを埋め込むことにより,視覚障害者の駅における転落事故を未然に防ぐインテリジェント白杖,服薬状況を見守るインテリジェント薬箱など,ユニークなデバイスの開発を行なっています.
Read More
Human-Robot Interaction Laboratory Human-Robot Interface, Sensor Fusion, Intelligent Environment
ヒューマン・ロボット・インタラクション研究室では,人とロボットのインタラクション(相互作用)に関わる幅広い研究を行っています.ロボットは外界の状況をセンシングし,考えて,行動しますが,ロボット単体によるセンシング能力には限界があります.そこで,人を取り囲む環境をロボットに見立て,環境内にセンサを遍在させることにより,部屋全体が人の活動状況を見守り,支援を行う環境知能化という新しい考えに基づく研究も行っています.環境に遍在させるセンサとして,無線通信により情報を収集することのできるオリジナルなセンサデバイス(インテリジェント電源タップ,温湿度センサ,照度センサ,人感センサ等)を開発するとともに,環境知能化の応用として,エネルギーの無駄を見つけて省エネを促すHEMS(Home Energy Management System),独居高齢者の普段の様子をモニタリングすることにより普段の状況と異なることを検知・通知する高齢者モニタリングシステム等を開発しています.また,様々な機器にセンサを埋め込むことにより,視覚障害者の駅における転落事故を未然に防ぐインテリジェント白杖,服薬状況を見守るインテリジェント薬箱など,ユニークなデバイスの開発を行なっています.
Read More
Human-Robot Interaction Laboratory Human-Robot Interface, Sensor Fusion, Intelligent Environment Research in Human-Robot Interaction Lab. encompasses a variety of sensor-applied systems for better human life. In general, robotic systems are composed of the cycle of sensing, recognition, planning, and actuation. We applied it to the human surrounding environments such as room, home, office, and hospital. This notion is the so-called intelligent environment. The ubiquitous sensors embedded in the human surrounding environment senses and recognize human behaviors plans how it supports human, and provide support to human using multimedia (i.e. graphics, gestures, voices). The application encompasses HEMS (Home Energy Management System), an elderly person monitoring system, and security systems. We also are developing a variety of sensor embedded systems such as an intelligent white cane to prevent falling off at station for visually impaired persons and intelligent medicine cases to prevent incorrect dosing.
Read More
Research in Human-Robot Interaction Lab. encompasses a variety of sensor-applied systems for better human life. In general, robotic systems are composed of the cycle of sensing, recognition, planning, and actuation. We applied it to the human surrounding environments such as room, home, office, and hospital. This notion is the so-called intelligent environment. The ubiquitous sensors embedded in the human surrounding environment senses and recognize human behaviors plans how it supports human, and provide support to human using multimedia (i.e. graphics, gestures, voices). The application encompasses HEMS (Home Energy Management System), an elderly person monitoring system, and security systems. We also are developing a variety of sensor embedded systems such as an intelligent white cane to prevent falling off at station for visually impaired persons and intelligent medicine cases to prevent incorrect dosing.
Read More
-
人工知能研究室 人工知能、サイバニクス、人間拡張技術、ソフトロボティクス、社会的インタラクション、情動コンピューティング
 誰でも使える察しの良いシステムを実現するため,身体による知覚と行動に関する生理学・認知神経科学,及び人間の認知特性の理解を中心とした認知科学的アプローチの両方に基づき、人の「身体・知能・情動・意思」の理解に基づく人の支援や拡張を目標としています. 人間社会と密接に関係し,環境にシームレスに統合される未来のロボット・機械系を実現するため,系内に人が含まれる新たな認知ロボティクス(人支援ロボット,社会的ロボティクス,生体ロボティクス,人の知覚・行動の理解を含む)の研究を行っています.さらに,人の知能の理解を深化するため,人が必要なときに人に必要な支援を行う人支援技術、柔らかい素材を用いたソフト・ロボティクス、人の意思と人工物をシームレスに繋ぐインタフェースや,実世界における人々の社会行動の計測と情報提示を通じた,人と人との社会的インタラクションを理解するための研究を行います.特に,医学・芸術・心理・発達支援の分野と連携し,子どもから高齢者,健常者から身体・発達障がい者まで,人の意識・無意識と機械系を結ぶ次代の人工知能研究を推進します.
Read More
Artificial Intelligence Laboratory AI, Cybernics, Augmented Human, Soft Robotics, Social Interaction, Affective Computing
誰でも使える察しの良いシステムを実現するため,身体による知覚と行動に関する生理学・認知神経科学,及び人間の認知特性の理解を中心とした認知科学的アプローチの両方に基づき、人の「身体・知能・情動・意思」の理解に基づく人の支援や拡張を目標としています. 人間社会と密接に関係し,環境にシームレスに統合される未来のロボット・機械系を実現するため,系内に人が含まれる新たな認知ロボティクス(人支援ロボット,社会的ロボティクス,生体ロボティクス,人の知覚・行動の理解を含む)の研究を行っています.さらに,人の知能の理解を深化するため,人が必要なときに人に必要な支援を行う人支援技術、柔らかい素材を用いたソフト・ロボティクス、人の意思と人工物をシームレスに繋ぐインタフェースや,実世界における人々の社会行動の計測と情報提示を通じた,人と人との社会的インタラクションを理解するための研究を行います.特に,医学・芸術・心理・発達支援の分野と連携し,子どもから高齢者,健常者から身体・発達障がい者まで,人の意識・無意識と機械系を結ぶ次代の人工知能研究を推進します.
Read More
Artificial Intelligence Laboratory AI, Cybernics, Augmented Human, Soft Robotics, Social Interaction, Affective Computing Our goal is to support and extend people's understanding of the body, intelligence, emotion, and intention, toward the integration of human intelligence and machine/robotic functions. We conduct research on a new type of human-machine fusion technology that includes human-in-the-loop systems. To deepen our understanding of human intelligence, we are developing human-assistive technologies that provide robotic assist-as-needed, soft robotics using soft materials, interfaces that seamlessly connect human intentions and machines, and social interactions between people. Target users range from children to the elderly, and from healthy people to people with physical and developmental disabilities, in cooperation with the University hospital and special-needs schools, as well as in the fields of medicine, art, and developmental psychology.
Read More
Our goal is to support and extend people's understanding of the body, intelligence, emotion, and intention, toward the integration of human intelligence and machine/robotic functions. We conduct research on a new type of human-machine fusion technology that includes human-in-the-loop systems. To deepen our understanding of human intelligence, we are developing human-assistive technologies that provide robotic assist-as-needed, soft robotics using soft materials, interfaces that seamlessly connect human intentions and machines, and social interactions between people. Target users range from children to the elderly, and from healthy people to people with physical and developmental disabilities, in cooperation with the University hospital and special-needs schools, as well as in the fields of medicine, art, and developmental psychology.
Read More
-
田中文英研究室 ソーシャルロボティクス,エージェント,安心人工知能,HRI/HCI,機械学習,教育支援,良心拡張,孤独対策
 【研究活動のビジョン】AI/ロボットやVR/ARを始めとする先端技術から心理学知見に到るまであらゆる手段を用いて,人々に安心をもたらすための技術(安心テクノロジー)を研究開発します.具体トピック例:高齢者の社会的孤立抑止,注射時の痛みや不安の軽減,人の良心を拡張する技術,次世代のオンライン教育環境.
【教育活動のビジョン】独創性,積極性,引き出しの多さ,コミュニケーション力,英語力など,研究力に留まらない幅広い人間力を育成し,世界規模で活躍できる人材を輩出します.恵まれた研究室環境の中で,対話を重視し,各人に合わせた細やかな指導を行います.
Read More
Fumihide Tanaka Laboratory Social Robotics, Agent, Relieving AI, HRI/HCI, Machine Learning, Education Support, Conscience Expansion, Support for Loneliness
【研究活動のビジョン】AI/ロボットやVR/ARを始めとする先端技術から心理学知見に到るまであらゆる手段を用いて,人々に安心をもたらすための技術(安心テクノロジー)を研究開発します.具体トピック例:高齢者の社会的孤立抑止,注射時の痛みや不安の軽減,人の良心を拡張する技術,次世代のオンライン教育環境.
【教育活動のビジョン】独創性,積極性,引き出しの多さ,コミュニケーション力,英語力など,研究力に留まらない幅広い人間力を育成し,世界規模で活躍できる人材を輩出します.恵まれた研究室環境の中で,対話を重視し,各人に合わせた細やかな指導を行います.
Read More
Fumihide Tanaka Laboratory Social Robotics, Agent, Relieving AI, HRI/HCI, Machine Learning, Education Support, Conscience Expansion, Support for Loneliness [Vision for Research] Create technologies which bring a sense of security and relief to humans. To this end, we make use of various approaches in the latest AI, robotics, VR/AR, and findings in psychologies. Recent topics include preventing social isolation in elderly people, pain/anxiety relief in vaccination, expanding human conscience, and the next generation online educational environment.
[Vision for Education] Cultivate active and creative individuals who can have a place globally. Provide students with an international and diverse study environment equipped with latest facilities. Keep communicative atmosphere.
Read More
[Vision for Research] Create technologies which bring a sense of security and relief to humans. To this end, we make use of various approaches in the latest AI, robotics, VR/AR, and findings in psychologies. Recent topics include preventing social isolation in elderly people, pain/anxiety relief in vaccination, expanding human conscience, and the next generation online educational environment.
[Vision for Education] Cultivate active and creative individuals who can have a place globally. Provide students with an international and diverse study environment equipped with latest facilities. Keep communicative atmosphere.
Read More
-
制御・ロボティクス研究室 非線形システムのモデル予測制御、自律移動ロボット・自動運転、多自由度機構、機構設計
 「制御しづらいものを実際に制御してみせる」をメインテーマとして,主にロボットを対象とした制御の問題に取り組みます.制御しづらい対象の多くが非線形性を持っています.非線形性とは,挙動がその時の状態や入力の大きさに対して比例しない性質です.例えば自転車で右に倒れそうになった時右にハンドルを回すことで転倒を防ぎますが,ハンドル回し続けるとやがて左右が反転し,逆の操作をしなければ走り続けることができなくなります.これは極端な例ですが,身の回りには程度の差こそあれ非線形性を持つものであふれています.その中でも特にロボットは様々な非線形性を有していて制御しがいあるものばかりです.
制御のしづらさを克服するには,数学を中心とした制御理論で頑張るか,機械構造の工夫で解決するか,あるいはソフトウェアのアルゴリズムの工夫で乗り切るなど,様々なアプローチがありますが,あくまでも「実際に制御してみせる」ことが目標ですので,方法にこだわらず手を尽くして問題に臨みます.限られたセンサ情報から適切に行動しなければならない自律移動ロボットの制御,非常に多数の関節を持つ蛇型ロボットを巧みに制御する問題に取り組んでいきます.
Read More
Control and Robotics Laboratory Nonlinear Model Predictive Control, Autonomous Mobile Robot, Redundant Mechanism, Mechanism Design
「制御しづらいものを実際に制御してみせる」をメインテーマとして,主にロボットを対象とした制御の問題に取り組みます.制御しづらい対象の多くが非線形性を持っています.非線形性とは,挙動がその時の状態や入力の大きさに対して比例しない性質です.例えば自転車で右に倒れそうになった時右にハンドルを回すことで転倒を防ぎますが,ハンドル回し続けるとやがて左右が反転し,逆の操作をしなければ走り続けることができなくなります.これは極端な例ですが,身の回りには程度の差こそあれ非線形性を持つものであふれています.その中でも特にロボットは様々な非線形性を有していて制御しがいあるものばかりです.
制御のしづらさを克服するには,数学を中心とした制御理論で頑張るか,機械構造の工夫で解決するか,あるいはソフトウェアのアルゴリズムの工夫で乗り切るなど,様々なアプローチがありますが,あくまでも「実際に制御してみせる」ことが目標ですので,方法にこだわらず手を尽くして問題に臨みます.限られたセンサ情報から適切に行動しなければならない自律移動ロボットの制御,非常に多数の関節を持つ蛇型ロボットを巧みに制御する問題に取り組んでいきます.
Read More
Control and Robotics Laboratory Nonlinear Model Predictive Control, Autonomous Mobile Robot, Redundant Mechanism, Mechanism Design The mission of this research group is to demonstrate to control what is not easy to control. Controlled objects of our interest thus often contain nonlinearity and can be found in robot systems. Recent topics include parallelized model predictive control on GPU, design and control of various type of snake like robot, and control system for intelligent autonomous mobile robot. Since our control target covers a variety of objects, some may be solved by sophisticated algorithms and some may require elaborate mechanical structure. We pursue the solution by whatever means possible.
Read More
The mission of this research group is to demonstrate to control what is not easy to control. Controlled objects of our interest thus often contain nonlinearity and can be found in robot systems. Recent topics include parallelized model predictive control on GPU, design and control of various type of snake like robot, and control system for intelligent autonomous mobile robot. Since our control target covers a variety of objects, some may be solved by sophisticated algorithms and some may require elaborate mechanical structure. We pursue the solution by whatever means possible.
Read More
-
モビリティサービス研究室 モビリティサービス、自動運転、MaaS、運転支援システム、ITS
 モビリティサービス研究室では、自動車交通に変革をもたらしているCASE(Connected:接続性、Autonomous:自動運転、Shared/Service:共有とサービス、Electric:電動化)やMaaS(Mobility as a Service:移動のシームレス化)に関しての研究・開発を推進しています.特に、無人自動運転サービスの実現を目指し、自動運転に関する基礎研究から標準化を見据えた技術開発を始めとして、障害を持った方の移動支援アプリやその基となる情報収集アプリの開発、MaaSにおける移動手段の選択モデルや行動変容を見据えた移動手段の提供方法やユーザの分析手法などを研究対象としています。本研究室では、構築した技術を、これまで培った日本各地とのネットワークを用い、実環境、実ユーザを対象とした実証実験を行うことで、実用化を見据えた本格的な研究・開発を行っていくとともに、様々なプロジェクトを通して、国・企業・大学とともに、移動の分野で社会に貢献します。
Read More
Mobility Service Laboratory Mobility Services, Automated Driving, MaaS, Driver Assistance Systems, ITS
モビリティサービス研究室では、自動車交通に変革をもたらしているCASE(Connected:接続性、Autonomous:自動運転、Shared/Service:共有とサービス、Electric:電動化)やMaaS(Mobility as a Service:移動のシームレス化)に関しての研究・開発を推進しています.特に、無人自動運転サービスの実現を目指し、自動運転に関する基礎研究から標準化を見据えた技術開発を始めとして、障害を持った方の移動支援アプリやその基となる情報収集アプリの開発、MaaSにおける移動手段の選択モデルや行動変容を見据えた移動手段の提供方法やユーザの分析手法などを研究対象としています。本研究室では、構築した技術を、これまで培った日本各地とのネットワークを用い、実環境、実ユーザを対象とした実証実験を行うことで、実用化を見据えた本格的な研究・開発を行っていくとともに、様々なプロジェクトを通して、国・企業・大学とともに、移動の分野で社会に貢献します。
Read More
Mobility Service Laboratory Mobility Services, Automated Driving, MaaS, Driver Assistance Systems, ITS We, the Mobility Service Laboratory, are doing research on CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Sharing, Electricity) and MaaS (mobility as a service). In particular, aiming to realize unmanned autonomous driving services, we are dealing with the following research topics:
1. Basic research on autonomous driving and technological development considering standardization
2. Development of mobility support apps for people with disabilities and information gathering apps that are the basis for them,
3. Mobility in MaaS including methods for selecting means, methods for providing means of transportation with behavior change, and methods for analyzing users.
In our laboratory, we are doing research and development with an eye on practical application by conducting demonstration experiments targeting actual environments and actual users using the network with various parts of Japan that we have cultivated so far. Through various projects, we will contribute to society in the field of mobility together with the national government, companies, and universities.
Read More
We, the Mobility Service Laboratory, are doing research on CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Sharing, Electricity) and MaaS (mobility as a service). In particular, aiming to realize unmanned autonomous driving services, we are dealing with the following research topics:
1. Basic research on autonomous driving and technological development considering standardization
2. Development of mobility support apps for people with disabilities and information gathering apps that are the basis for them,
3. Mobility in MaaS including methods for selecting means, methods for providing means of transportation with behavior change, and methods for analyzing users.
In our laboratory, we are doing research and development with an eye on practical application by conducting demonstration experiments targeting actual environments and actual users using the network with various parts of Japan that we have cultivated so far. Through various projects, we will contribute to society in the field of mobility together with the national government, companies, and universities.
Read More
-
モーションコントロール研究室 メカトロニクス、ハプティクス、マニピュレーション
 人間とロボットが協調するためのシステムを計測・制御の側面から追求しています。外界に対してロボットの動作をとても硬くする位置制御と、逆に外界に対してとても柔軟に倣う力制御を、加速度に基づいた制御系を構成した上で組み合わせることで様々な機能をロボットに発現させることができます。例えば、2台のロボットに対して適切な位置・力制御を実装することで、遠隔地のロボットが物体を操作している触覚を操作者にフィードバックすることも可能になります。また、制御対象はロボットに限らず、人間の筋に電流を流すことで身体を制御する手法についても研究しています。
逆に、位置と力のセンサ情報を利活用することで、人間の物体操作技能の抽出とそのロボットへの転写も可能になります。現在、人間並の物体操作技能を有するロボットは存在しませんが、これは位置制御と力制御から機能が発現されるという構造を正しく捉えられていなかったからではないでしょうか。このような低レベル層の制御系と連携した技能データ収集機構・学習機構を開発することで人間並の物体操作技能を持つロボットの実現を目指しています。
Read More
Motion Control Laboratory Mechatronics, Haptics, Manipulation
人間とロボットが協調するためのシステムを計測・制御の側面から追求しています。外界に対してロボットの動作をとても硬くする位置制御と、逆に外界に対してとても柔軟に倣う力制御を、加速度に基づいた制御系を構成した上で組み合わせることで様々な機能をロボットに発現させることができます。例えば、2台のロボットに対して適切な位置・力制御を実装することで、遠隔地のロボットが物体を操作している触覚を操作者にフィードバックすることも可能になります。また、制御対象はロボットに限らず、人間の筋に電流を流すことで身体を制御する手法についても研究しています。
逆に、位置と力のセンサ情報を利活用することで、人間の物体操作技能の抽出とそのロボットへの転写も可能になります。現在、人間並の物体操作技能を有するロボットは存在しませんが、これは位置制御と力制御から機能が発現されるという構造を正しく捉えられていなかったからではないでしょうか。このような低レベル層の制御系と連携した技能データ収集機構・学習機構を開発することで人間並の物体操作技能を持つロボットの実現を目指しています。
Read More
Motion Control Laboratory Mechatronics, Haptics, Manipulation We are pursuing cooperation between humans and robots from the aspect of measurement and control. Integration based on acceleration control of position control, which makes robot motion against outer environments stiff, and force control, which makes it soft, produces various robot functions. For example, by implementing appropriate position and force control on two robots, haptic sensation of a remote robot can be transmitted to a local robot. In addition, we control not only robots but also human bodies by injecting current on human muscles.
On the contrary, by utilizing both position and force information, object manipulation skills of humans can be extracted and the skills can be transmitted to robots. Currently, there is no robot having high manipulation skills as humans. This may be because the structure of controllers composed of position and force control has not been properly understood. We aim to obtain a robot having human-level object manipulation skills by developing skill data collection and learning mechanisms linked to such low-level control systems.
Read More
We are pursuing cooperation between humans and robots from the aspect of measurement and control. Integration based on acceleration control of position control, which makes robot motion against outer environments stiff, and force control, which makes it soft, produces various robot functions. For example, by implementing appropriate position and force control on two robots, haptic sensation of a remote robot can be transmitted to a local robot. In addition, we control not only robots but also human bodies by injecting current on human muscles.
On the contrary, by utilizing both position and force information, object manipulation skills of humans can be extracted and the skills can be transmitted to robots. Currently, there is no robot having high manipulation skills as humans. This may be because the structure of controllers composed of position and force control has not been properly understood. We aim to obtain a robot having human-level object manipulation skills by developing skill data collection and learning mechanisms linked to such low-level control systems.
Read More
-
計測情報工学研究室 マルチメディアセンシング、小型移動ロボティクス、身体的音響メディア技術
 身体を含んだ人間の機能と感覚の工学的な知見に基づき,人間―機械,機械―機械,人間―人間の新しい関係を築くことにより,安全かつ安心な社会環境を実現することを目指しています.これまで,視覚,聴覚,体性感覚などに注目し,画像信号を扱った画像処理と画像計測手法の研究,音響信号を用いた音響計測や音響表現の研究,そして身体計測を行うことで身体表現の研究を行い,これらに付随した移動ロボット制御やコミュニケーション技術などの研究開発も行っています.これらのシステムを構築する上で不可欠な計測技術は,マイクロコンピュータを応用することでセンシング技術として飛躍的に進歩していますが,システムに要求される精度と速度を考慮した適切なセンシング手法の選択や,センシングデータの高度な情報処理が必要となります.また,そのシステムが人の介在する場所での適用か否かによっても,アプローチの仕方が異なります.そこで,本研究では建造物などの人間の介在が困難な場所において,計測・検査を自動化する自動計測ロボットの研究と,人間が常に介在している状況である対面コミュニケーション計測の研究に着目し,これらの研究成果を社会に還元できる技術革新を図ります.
Read More
Instrumentation and Computing Engineering Laboratory Sensing, Robotics, Embodied Media Interface
身体を含んだ人間の機能と感覚の工学的な知見に基づき,人間―機械,機械―機械,人間―人間の新しい関係を築くことにより,安全かつ安心な社会環境を実現することを目指しています.これまで,視覚,聴覚,体性感覚などに注目し,画像信号を扱った画像処理と画像計測手法の研究,音響信号を用いた音響計測や音響表現の研究,そして身体計測を行うことで身体表現の研究を行い,これらに付随した移動ロボット制御やコミュニケーション技術などの研究開発も行っています.これらのシステムを構築する上で不可欠な計測技術は,マイクロコンピュータを応用することでセンシング技術として飛躍的に進歩していますが,システムに要求される精度と速度を考慮した適切なセンシング手法の選択や,センシングデータの高度な情報処理が必要となります.また,そのシステムが人の介在する場所での適用か否かによっても,アプローチの仕方が異なります.そこで,本研究では建造物などの人間の介在が困難な場所において,計測・検査を自動化する自動計測ロボットの研究と,人間が常に介在している状況である対面コミュニケーション計測の研究に着目し,これらの研究成果を社会に還元できる技術革新を図ります.
Read More
Instrumentation and Computing Engineering Laboratory Sensing, Robotics, Embodied Media Interface The target of our laboratory is to create a safety and cozy social environment by developing a new interface between human-machine, machine-machine, and human-human. We have been conducting the research of software and hardware related to vision, auditory system, somatosensory. The studies that our focus are image processing and image measurement dealing with the image signal as visual information, audio measurement and sound expression based on the audio signal as auditory information, bodily expression by measuring acceleration and gyro information as somatosensory, and mobile robot and communication technology which was associated with these senses.
Read More
The target of our laboratory is to create a safety and cozy social environment by developing a new interface between human-machine, machine-machine, and human-human. We have been conducting the research of software and hardware related to vision, auditory system, somatosensory. The studies that our focus are image processing and image measurement dealing with the image signal as visual information, audio measurement and sound expression based on the audio signal as auditory information, bodily expression by measuring acceleration and gyro information as somatosensory, and mobile robot and communication technology which was associated with these senses.
Read More
-
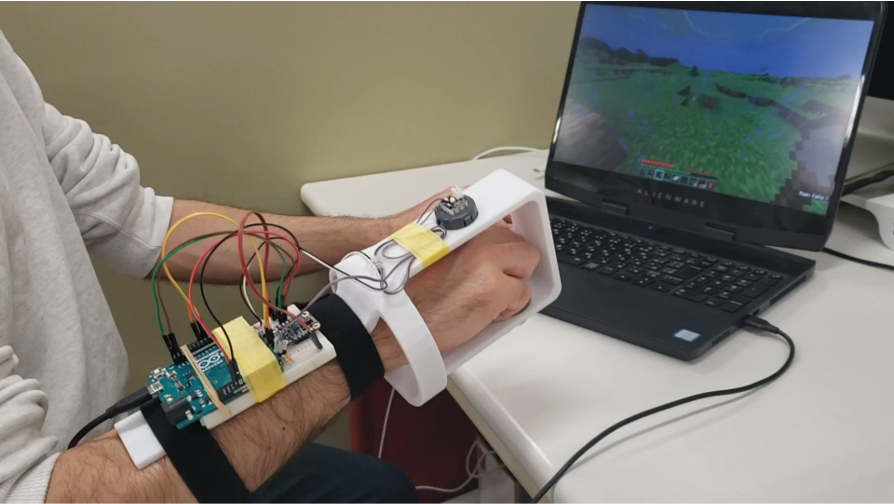
人工知能研究室 サイバー・フィジカルインターフェース、ウェアラブル技術、メカトロニクス、ヒューマンパフォーマンス
 サイバー・フィジカル空間での人運動支援や拡張するウェアラブルデバイス・ロボットの研究開発を行っています.eスポーツなどのサイバー空間での人運動技能や認知能力を研究し、それに基づく新なインタフェース・ゲームコントローラー・義手を開発することで、体が不自由な方でも参加できるパラeスポーツを目指しています。目標は「アクセシビリティ」よりも「パフォーマンス」を実現するサイバー・フィジカルインタフェースです.さらに、工学・医科学・認知心理学分野を活用した学際的なアプローチによりリハビリテーション・ゲーミフィケーション・テレプレゼンス・遠隔操作に応用するとともに、サイバー・フィジカル空間を最大限に活用する社会や事業を目指します.
Read More
Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Cyber-physical Interfaces, Wearable Technology, Mechatronics, Human Performance
サイバー・フィジカル空間での人運動支援や拡張するウェアラブルデバイス・ロボットの研究開発を行っています.eスポーツなどのサイバー空間での人運動技能や認知能力を研究し、それに基づく新なインタフェース・ゲームコントローラー・義手を開発することで、体が不自由な方でも参加できるパラeスポーツを目指しています。目標は「アクセシビリティ」よりも「パフォーマンス」を実現するサイバー・フィジカルインタフェースです.さらに、工学・医科学・認知心理学分野を活用した学際的なアプローチによりリハビリテーション・ゲーミフィケーション・テレプレゼンス・遠隔操作に応用するとともに、サイバー・フィジカル空間を最大限に活用する社会や事業を目指します.
Read More
Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Cyber-physical Interfaces, Wearable Technology, Mechatronics, Human Performance We investigate wearable devices and wearable robotics to assist and augment the human function and performance in cyber and physical spaces. We study the human motor control and cognitive performance in esports by amateurs and athletes. We develop novel interfaces, controllers and gaming prostheses that enable the participation of persons with various physical disabilities in para-esports. Our goal is not only to provide accessibility, but competitive performance. We also develop wearable robotics for movement and ADL assistance, and novel prosthetic hands for children and adults. We follow a strong interdisciplinary approach utilizing methods of engineering and robotics combined with medical science and cognitive psychology, and we focus on topics that have strong and tangible impact on society, culture, and industry.
Read More
We investigate wearable devices and wearable robotics to assist and augment the human function and performance in cyber and physical spaces. We study the human motor control and cognitive performance in esports by amateurs and athletes. We develop novel interfaces, controllers and gaming prostheses that enable the participation of persons with various physical disabilities in para-esports. Our goal is not only to provide accessibility, but competitive performance. We also develop wearable robotics for movement and ADL assistance, and novel prosthetic hands for children and adults. We follow a strong interdisciplinary approach utilizing methods of engineering and robotics combined with medical science and cognitive psychology, and we focus on topics that have strong and tangible impact on society, culture, and industry.
Read More
-
サイバニクス研究室 サイバニクス、ロボティクス、アクセシブルインタラクション、医工学、サイバニクス治療、IoH/IoT
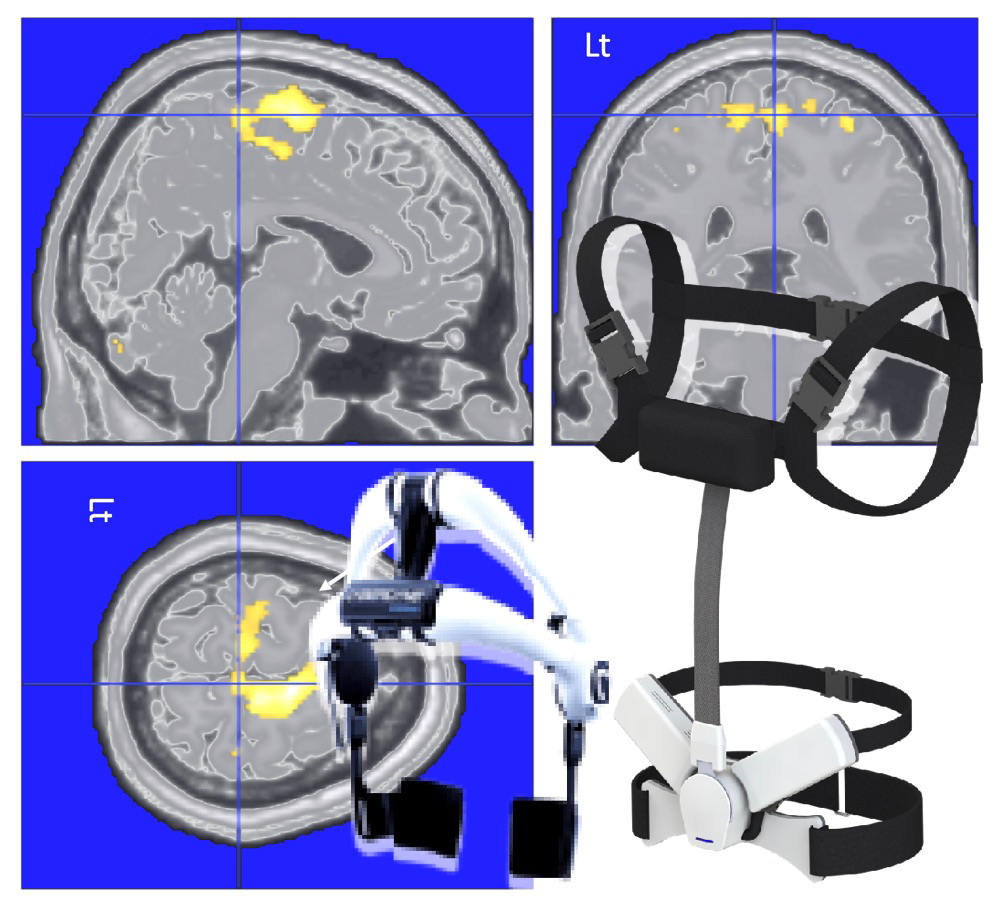 年齢や障害によらずあらゆる人が可能性を広げることができる社会を実現するため、脳神経系の随意機能との接続による脳・神経系、筋系の難病患者の自立支援・治療を軸としたサイバニクス領域の更なる発展と新領域開拓に挑戦しています。
人・ロボット・情報系を融合複合した「サイバニクス」は、脳・神経科学、行動科学、ロボット工学、情報技術、人工知能、システム統合技術、生理学、心理学、哲学、倫理、法学、経営などの異分野を融合した新学術領域です。
本研究室では、サイバニクスを駆使することで、人(脳神経系・生理系・身体系など)とテクノロジーの一体化技術や、インタラクティブなバイオフィードバック(iBF)で構成されるサイバニクス治療技術など革新的サイバニックシステムに関する研究開発を行います。また、再生医療や創薬などの異分野とサイバニクスの更なる融合推進、患者の生理系・身体系に関するヒューマンビッグデータの集積・AI解析にいたるまで、基礎研究開発と社会実装を同時展開し、好循環のイノベーションスパイラル形成と未来開拓型人材の育成を世界規模で推進していきます。
Read More
Cybernics Laboratory Cybernics, Robotics, Accessible interaction, Medical technology, Cybernics treatment, IoH/IoT
年齢や障害によらずあらゆる人が可能性を広げることができる社会を実現するため、脳神経系の随意機能との接続による脳・神経系、筋系の難病患者の自立支援・治療を軸としたサイバニクス領域の更なる発展と新領域開拓に挑戦しています。
人・ロボット・情報系を融合複合した「サイバニクス」は、脳・神経科学、行動科学、ロボット工学、情報技術、人工知能、システム統合技術、生理学、心理学、哲学、倫理、法学、経営などの異分野を融合した新学術領域です。
本研究室では、サイバニクスを駆使することで、人(脳神経系・生理系・身体系など)とテクノロジーの一体化技術や、インタラクティブなバイオフィードバック(iBF)で構成されるサイバニクス治療技術など革新的サイバニックシステムに関する研究開発を行います。また、再生医療や創薬などの異分野とサイバニクスの更なる融合推進、患者の生理系・身体系に関するヒューマンビッグデータの集積・AI解析にいたるまで、基礎研究開発と社会実装を同時展開し、好循環のイノベーションスパイラル形成と未来開拓型人材の育成を世界規模で推進していきます。
Read More
Cybernics Laboratory Cybernics, Robotics, Accessible interaction, Medical technology, Cybernics treatment, IoH/IoT Our mission is to realize the society in which people can expand their potential regardless of age or disability by empowering their cognitive and physical functions. We are challenging to explore Cybernics, focusing on the independence support and treatment of patients by interaction with the human nervous system.
”Cybernics” is a new academic field that is centered around human, robots, Information fused/combined with various other fields including brain/neuroscience, behavioral science, robotics, Information Technology, Artificial Intelligence, System Engineering, psychology, philosophy, ethics, law and business administration.
This laboratory will research innovative Cybernic systems such as integrating people (cranial nervous system, physiological system, physical system, etc.) and technology, and Cybernics treatment technology consisting of interactive BioFeedback (iBF) by utilizing Cybernics. In addition, we will promote the further integration of Cybernics with other fields such as regenerative medicine and drug discovery, as well as the accumulation and AI analysis of human big data on the physiological/physical systems of patients, in order to simultaneously develop fundamental research and social implementation. We will promote the formation of a virtuous innovation spiral and the development of future pioneers on a global scale.
Read More
Our mission is to realize the society in which people can expand their potential regardless of age or disability by empowering their cognitive and physical functions. We are challenging to explore Cybernics, focusing on the independence support and treatment of patients by interaction with the human nervous system.
”Cybernics” is a new academic field that is centered around human, robots, Information fused/combined with various other fields including brain/neuroscience, behavioral science, robotics, Information Technology, Artificial Intelligence, System Engineering, psychology, philosophy, ethics, law and business administration.
This laboratory will research innovative Cybernic systems such as integrating people (cranial nervous system, physiological system, physical system, etc.) and technology, and Cybernics treatment technology consisting of interactive BioFeedback (iBF) by utilizing Cybernics. In addition, we will promote the further integration of Cybernics with other fields such as regenerative medicine and drug discovery, as well as the accumulation and AI analysis of human big data on the physiological/physical systems of patients, in order to simultaneously develop fundamental research and social implementation. We will promote the formation of a virtuous innovation spiral and the development of future pioneers on a global scale.
Read More
-
田中文英研究室 サイバーフィジカルエージェント、ソーシャルロボティクス、痛み・ストレス・不安軽減
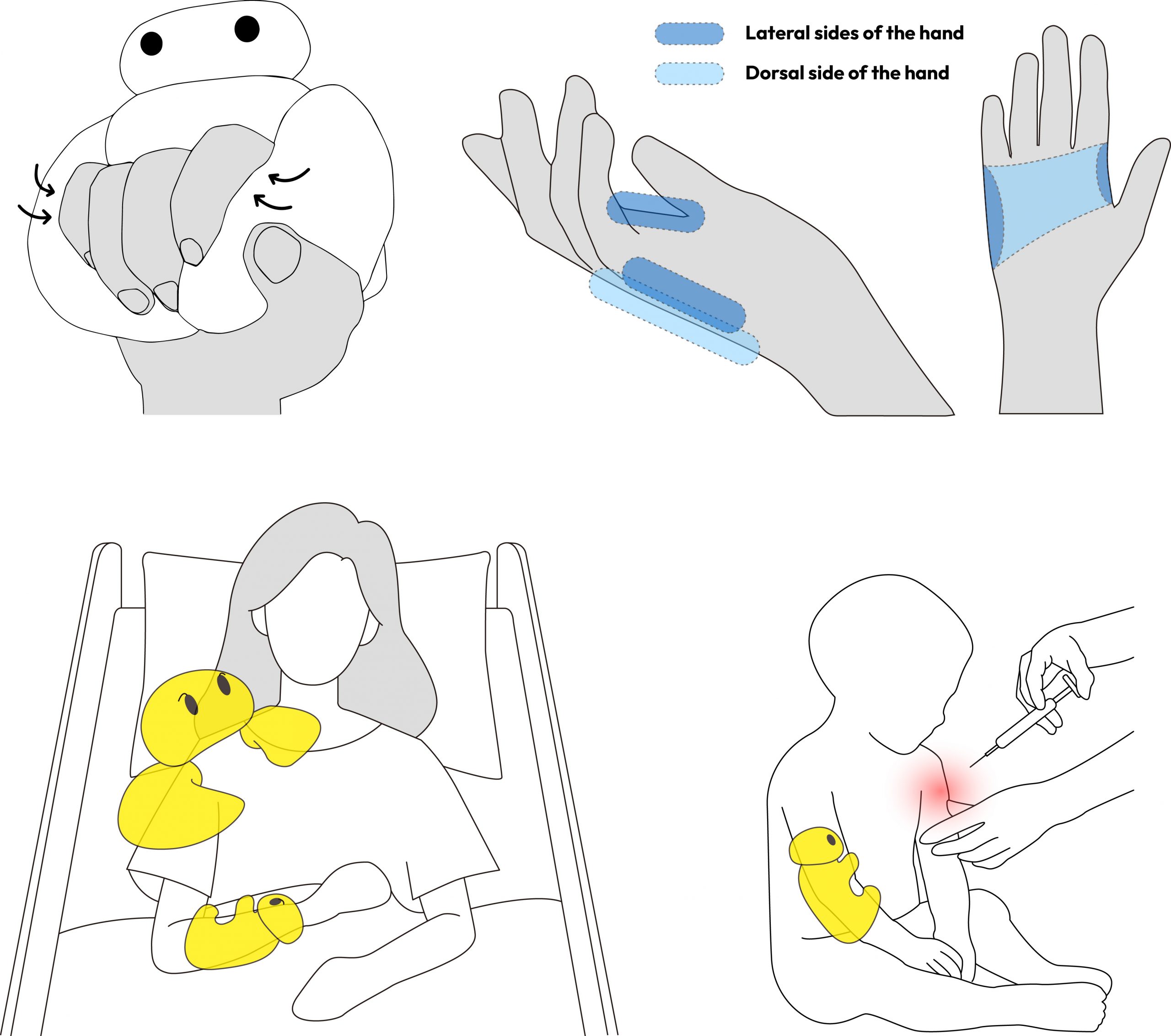 物理デバイスやVR環境内のエージェントを通じて人と人とのソーシャルタッチを再現し、安心感、安定感、愛着、不安やストレスの軽減、痛みの緩和など、さまざまなポジティブな情動効果をもたらす技術を研究しています。その過程で、人間の知覚過程や情動反応を定量的に分析し、触覚や視覚といった感覚的介入を通じて痛みやストレスを軽減するインタラクションデザインおよび介入手法を設計しています。これらの介入を、物理空間のデバイスと仮想空間の知的エージェントを統合した「サイバーフィジカルエージェント」として発展させることを目指しています。このシステムは、ユーザーの状態を把握し、適切な介入を行う伴走型インタラクション・プラットフォームとして、痛みやストレスのようなネガティブな要素を軽減する新たな形のHuman-Computer Interaction (HCI) 技術としての確立を目指しています。
Read More
Fumihide Tanaka Laboratory サイバーフィジカルエージェント、ソーシャルロボティクス、痛み・ストレス・不安軽減
物理デバイスやVR環境内のエージェントを通じて人と人とのソーシャルタッチを再現し、安心感、安定感、愛着、不安やストレスの軽減、痛みの緩和など、さまざまなポジティブな情動効果をもたらす技術を研究しています。その過程で、人間の知覚過程や情動反応を定量的に分析し、触覚や視覚といった感覚的介入を通じて痛みやストレスを軽減するインタラクションデザインおよび介入手法を設計しています。これらの介入を、物理空間のデバイスと仮想空間の知的エージェントを統合した「サイバーフィジカルエージェント」として発展させることを目指しています。このシステムは、ユーザーの状態を把握し、適切な介入を行う伴走型インタラクション・プラットフォームとして、痛みやストレスのようなネガティブな要素を軽減する新たな形のHuman-Computer Interaction (HCI) 技術としての確立を目指しています。
Read More
Fumihide Tanaka Laboratory サイバーフィジカルエージェント、ソーシャルロボティクス、痛み・ストレス・不安軽減 We are conducting research on technologies that recreate social touch between individuals through physical devices and virtual agents in VR environments. These technologies aim to evoke a range of positive emotional effects, such as reassurance, emotional stability, attachment, reduction of anxiety and stress, and pain relief. In this process, we quantitatively analyze human perceptual processes and emotional responses, and design interaction and intervention methods that mitigate pain and stress through sensory modalities such as touch and vision. Our goal is to advance these interventions into an integrated "Cyber-Physical Agent" that combines physical devices in the real world with intelligent agents in virtual environments. We aim to establish this approach as a novel form of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) technology for reducing negative experiences such as pain and stress.
Read More
We are conducting research on technologies that recreate social touch between individuals through physical devices and virtual agents in VR environments. These technologies aim to evoke a range of positive emotional effects, such as reassurance, emotional stability, attachment, reduction of anxiety and stress, and pain relief. In this process, we quantitatively analyze human perceptual processes and emotional responses, and design interaction and intervention methods that mitigate pain and stress through sensory modalities such as touch and vision. Our goal is to advance these interventions into an integrated "Cyber-Physical Agent" that combines physical devices in the real world with intelligent agents in virtual environments. We aim to establish this approach as a novel form of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) technology for reducing negative experiences such as pain and stress.
Read More
Neuroengineeringニューロエンジニアリング
認知神経工学および工学的脳・神経基盤に関する学際的システム分野An interdisciplinary systems field addressing cognitive neuroengineering and engineering-based brain and neural systems.
-
脳情報システム研究室 計算論的神経科学、生体運動学習機構、意思決定機構、VRリハビリテーション、脳情報解析、ニューロハッキング
 ロボット・人工知能・機械学習との比較や対照を通じて、我々の脳が行っている運動学習や意思決定の計算プロセスを数理と実験の両面から明らかにします。この工学からアプローチする脳の理解によって、エンジニアリングサイエンスとしての脳科学を目指します。具体的には、脳における学習や機能回復の計算モデルに基づいたVRリハビリテーションロボットの開発や生体情報デコーディングに基づく運動機能回復シミュレーターの開発を行います。また、人間の柔軟な学習に倣った新しい機械学習アルゴリズムを開発します。
Read More
Brain Informatics Laboratory Computational Neuroscience, Motor Learning, Decision Making, Neurocybernetics, Rehabilitation Science, Neurohacking
ロボット・人工知能・機械学習との比較や対照を通じて、我々の脳が行っている運動学習や意思決定の計算プロセスを数理と実験の両面から明らかにします。この工学からアプローチする脳の理解によって、エンジニアリングサイエンスとしての脳科学を目指します。具体的には、脳における学習や機能回復の計算モデルに基づいたVRリハビリテーションロボットの開発や生体情報デコーディングに基づく運動機能回復シミュレーターの開発を行います。また、人間の柔軟な学習に倣った新しい機械学習アルゴリズムを開発します。
Read More
Brain Informatics Laboratory Computational Neuroscience, Motor Learning, Decision Making, Neurocybernetics, Rehabilitation Science, Neurohacking Recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning were achieved by the accumulation of studies of neuroscience and cognitive science which were not merely a collection of empirical evidence but a combination of computational modeling and its vilification. We study how the brain adaptively controls the body, how the brain recovers its function from the damage such as stroke, and how the cognition and the perception alter our decisions on motor behaviors. We use a number of tools to approach these problems: mathematical modeling, robotics, virtual reality, brain imaging, and the neuromodulation. We aim to apply this unique integrative research style of brain science to develop new machine learning architecture and robotic rehabilitation.
Read More
Recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning were achieved by the accumulation of studies of neuroscience and cognitive science which were not merely a collection of empirical evidence but a combination of computational modeling and its vilification. We study how the brain adaptively controls the body, how the brain recovers its function from the damage such as stroke, and how the cognition and the perception alter our decisions on motor behaviors. We use a number of tools to approach these problems: mathematical modeling, robotics, virtual reality, brain imaging, and the neuromodulation. We aim to apply this unique integrative research style of brain science to develop new machine learning architecture and robotic rehabilitation.
Read More
-
生体情報処理研究室 ニューラルネット、脳型情報処理、機械学習、計算論的神経科学
 予めプログラムされた規則に従って推論する古典的な人工知能は,限られた状況下では動作しても,複雑な現実の世界にうまく対応することができません.一方,人間のみならずイヌなどの動物は,自ら学習することによって,現実世界において適切に判断し行動することができます.我々は,脳の情報処理メカニズムの解明と,動物がもつ柔軟な知能の実現とは表裏一体の関係にあると考え,両者を行き来しながら研究を進めています.具体的には,視覚や記憶といった脳機能や海馬など脳の神経回路のモデル化,モデルの理論的検討と計算機シミュレーション,生理データとの比較や心理物理実験によるモデルの検証といった基礎的なものから,学習能力やパターン認識能力の高い新型ニューラルネットの開発,筋電や脳波といった生体信号の処理などの応用まで,幅広い研究を行っています.
Read More
Biological Information Processing Laboratory Neural Network, Brain-like Computing, Machine Learning, Computational Neuroscience
予めプログラムされた規則に従って推論する古典的な人工知能は,限られた状況下では動作しても,複雑な現実の世界にうまく対応することができません.一方,人間のみならずイヌなどの動物は,自ら学習することによって,現実世界において適切に判断し行動することができます.我々は,脳の情報処理メカニズムの解明と,動物がもつ柔軟な知能の実現とは表裏一体の関係にあると考え,両者を行き来しながら研究を進めています.具体的には,視覚や記憶といった脳機能や海馬など脳の神経回路のモデル化,モデルの理論的検討と計算機シミュレーション,生理データとの比較や心理物理実験によるモデルの検証といった基礎的なものから,学習能力やパターン認識能力の高い新型ニューラルネットの開発,筋電や脳波といった生体信号の処理などの応用まで,幅広い研究を行っています.
Read More
Biological Information Processing Laboratory Neural Network, Brain-like Computing, Machine Learning, Computational Neuroscience Classical artificial intelligence that infers according to preprogrammed rules works well under limited conditions but cannot cope well with the complex real world. Meanwhile, human beings, and also animals such as dogs, can learn by themselves to make proper decisions and actions in the real world. The essential part of how the brain performs such intelligent and flexible information processing has hardly been made clear.
We are focusing on both the clarification of the brain mechanism and the realization of flexible intelligence, which we believe are closely tied to each other.
Our current research widely ranges from fundament to application. Fundamental researches include modeling of the brain functions such as vision and memory and brain neural circuits such as the hippocampus, theoretical examination and computer simulation of the model, and its verification by means of psychophysical experiment or comparison with physiological data. Applied researches include the development of a new-type neural network with high learning ability and pattern recognition ability and processing of biological signals such as EMG and EEG.
Read More
Classical artificial intelligence that infers according to preprogrammed rules works well under limited conditions but cannot cope well with the complex real world. Meanwhile, human beings, and also animals such as dogs, can learn by themselves to make proper decisions and actions in the real world. The essential part of how the brain performs such intelligent and flexible information processing has hardly been made clear.
We are focusing on both the clarification of the brain mechanism and the realization of flexible intelligence, which we believe are closely tied to each other.
Our current research widely ranges from fundament to application. Fundamental researches include modeling of the brain functions such as vision and memory and brain neural circuits such as the hippocampus, theoretical examination and computer simulation of the model, and its verification by means of psychophysical experiment or comparison with physiological data. Applied researches include the development of a new-type neural network with high learning ability and pattern recognition ability and processing of biological signals such as EMG and EEG.
Read More
-
スマートシステム研究室 機械学習、パターン認識、画像解析、医療診断支援技術
 情報通信技術に関する研究を通じて医工連携を推進する立場から、医師や医療従事者の負担を軽減し、診断能力を補助・強化する手法の実現など、高品質な医療を広く普及させるための基盤技術の確立を目指しています。最近では、超音波検査やMRI、内視鏡、病理検査を対象に、がん等の病変の自動的検出、データベースからの高速な類似症例検索などにより、医師の診断を支援する手法やシステムの研究開発を行っています。また、知的な情報処理を実現すべく、様々な技術領域に強い関心を持って、新しい計算原理に関する基礎研究から、それらの応用研究まで、幅広く活動しています。研究の成果については、国内外の学会で発表するだけでなく、企業との共同研究などを通じた実用化・製品化を積極的に推進します。
超高齢社会を迎えた現在、社会全体で健康長寿を実現する仕組みが不可欠となっています。我々は、工学的なアプローチにより多くの命を救う技術開発を行い、安心して暮らせる社会の実現に貢献します。
Read More
Smart System Laboratory Machine Learning, Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer-Aided Diagnosis
情報通信技術に関する研究を通じて医工連携を推進する立場から、医師や医療従事者の負担を軽減し、診断能力を補助・強化する手法の実現など、高品質な医療を広く普及させるための基盤技術の確立を目指しています。最近では、超音波検査やMRI、内視鏡、病理検査を対象に、がん等の病変の自動的検出、データベースからの高速な類似症例検索などにより、医師の診断を支援する手法やシステムの研究開発を行っています。また、知的な情報処理を実現すべく、様々な技術領域に強い関心を持って、新しい計算原理に関する基礎研究から、それらの応用研究まで、幅広く活動しています。研究の成果については、国内外の学会で発表するだけでなく、企業との共同研究などを通じた実用化・製品化を積極的に推進します。
超高齢社会を迎えた現在、社会全体で健康長寿を実現する仕組みが不可欠となっています。我々は、工学的なアプローチにより多くの命を救う技術開発を行い、安心して暮らせる社会の実現に貢献します。
Read More
Smart System Laboratory Machine Learning, Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer-Aided Diagnosis The mission of our laboratory is to develop the medical engineering technologies for assisting and enhancing the diagnostic capabilities, and for reduce the burden on doctors and co-medicals. Recently, we are developing the computer assisted diagnosis systems for breast ultrasound examination, endoscopy, and histopathological diagnosis, based on the techniques of the anomaly detection, the content based image retrieval, and so on. We encourage to publish the results of the research projects in the academic society, and actively promote to collaborate with the medical institutions and the medical equipment manufacturers.
Read More
The mission of our laboratory is to develop the medical engineering technologies for assisting and enhancing the diagnostic capabilities, and for reduce the burden on doctors and co-medicals. Recently, we are developing the computer assisted diagnosis systems for breast ultrasound examination, endoscopy, and histopathological diagnosis, based on the techniques of the anomaly detection, the content based image retrieval, and so on. We encourage to publish the results of the research projects in the academic society, and actively promote to collaborate with the medical institutions and the medical equipment manufacturers.
Read More
-
統合脳機能研究室 MRIによる脳機能の統合的トランスレーショナル研究、医療物理学
 研究内容:本研究室は脳機能を統合的に解明するため、MRIを横串として動物モデルからヒトの脳機能まで研究を行っています。我々の脳の神経細胞から構成される機能的ネットワークは動的に変動している4次元的なネットワークとして構成され、様々な感覚情報をダイナミックに処理しています。この4次元ネットワークは、非侵襲的かつ時間・空間分解能をもつMRIを用いて計測することで、解析が可能となります。さらにヒトMRIデータと動物モデルにおける深部脳波計測、蛍光イメージングといったミクロスコピックな研究と組み合わせることで、脳の4次元ネットワークを細胞レベルで解釈することを可能にします。また神経細胞以外にも、グリア細胞や血管内皮細胞、血液循環、そしてグリンパティックシステムなどによる脳内の環境を維持するホメオスタシスも、脳活動を正常に維持する機能として注目されています。MRIを用いた新しい計測法・解析法を開発することで、これらすべての「脳の機能」を統合的に明らかにし、精神神経疾患のメカニズム解明や脳の老化予防といった脳の健康への貢献をします。
Read More
Integrative Brain Function Laboratory Integrative Translational Research of Brain Function Using MRI, Medical Physics
研究内容:本研究室は脳機能を統合的に解明するため、MRIを横串として動物モデルからヒトの脳機能まで研究を行っています。我々の脳の神経細胞から構成される機能的ネットワークは動的に変動している4次元的なネットワークとして構成され、様々な感覚情報をダイナミックに処理しています。この4次元ネットワークは、非侵襲的かつ時間・空間分解能をもつMRIを用いて計測することで、解析が可能となります。さらにヒトMRIデータと動物モデルにおける深部脳波計測、蛍光イメージングといったミクロスコピックな研究と組み合わせることで、脳の4次元ネットワークを細胞レベルで解釈することを可能にします。また神経細胞以外にも、グリア細胞や血管内皮細胞、血液循環、そしてグリンパティックシステムなどによる脳内の環境を維持するホメオスタシスも、脳活動を正常に維持する機能として注目されています。MRIを用いた新しい計測法・解析法を開発することで、これらすべての「脳の機能」を統合的に明らかにし、精神神経疾患のメカニズム解明や脳の老化予防といった脳の健康への貢献をします。
Read More
Integrative Brain Function Laboratory Integrative Translational Research of Brain Function Using MRI, Medical Physics Our laboratory is conducting translational research from animal models to humans with MRI for the purpose of clarifying integrative brain function. The functional network composed of neurons in the brain is dynamically changing as a four-dimensional network that processes multi-sensory information from the body. Therefore, measuring the functional network of the whole brain using MRI, which has temporal and spatial resolution, is required to analyze four-dimensional functional network. Furthermore, by combining mesoscopic MRI research with microscopic research such as electrophysiology and fluorescence imaging in animal models, we will explain the dynamic functional network at the cellular level. In addition to neuronal events, functional homeostasis in the brain by glial cells, vascular endothelial cells, blood circulation, and glymphatic system, is also an essential function in the brain. By developing novel research techniques and analysis methods using MRI, we will comprehensively clarify these "brain functions" and contribute to brain health such as clarifying the mechanism of neuropsychiatric disease and prevention of brain aging.
Read More
Our laboratory is conducting translational research from animal models to humans with MRI for the purpose of clarifying integrative brain function. The functional network composed of neurons in the brain is dynamically changing as a four-dimensional network that processes multi-sensory information from the body. Therefore, measuring the functional network of the whole brain using MRI, which has temporal and spatial resolution, is required to analyze four-dimensional functional network. Furthermore, by combining mesoscopic MRI research with microscopic research such as electrophysiology and fluorescence imaging in animal models, we will explain the dynamic functional network at the cellular level. In addition to neuronal events, functional homeostasis in the brain by glial cells, vascular endothelial cells, blood circulation, and glymphatic system, is also an essential function in the brain. By developing novel research techniques and analysis methods using MRI, we will comprehensively clarify these "brain functions" and contribute to brain health such as clarifying the mechanism of neuropsychiatric disease and prevention of brain aging.
Read More
-
神経情報科学研究室 機械学習、計算論的神経科学、信号処理
 脳における情報処理がどのように行われているかを理解することは神経科学の大きな目標です。しかし脳は複雑なシステムであり、そこから得られる膨大なデータを人が個別に見ていくだけではその仕組みを知ることが困難です。そこで我々の研究室では計算機によるデータ解析により脳のメカニズムに迫る研究を行っています。スパイク系列、LFP、脳波、カルシウムイメージングといった脳や神経組織から記録されるデータに対し、深層学習やカーネル法、情報理論などの道具立てを用い、情報の縮約や頻出パターンの発見、可視化を行うソフトウェアを開発しています。特に神経生物学の研究室や企業との共同研究により、検出されたパターンに応じたフィードバックを光遺伝学などの手段で脳に送る閉ループ実験系を実現し、受動的な観察だけでなく直接的な操作によって脳の各部位の役割や機能を探る研究に取り組んでいます。
Read More
Neuroinformatics Laboratory Machine Learning, Computational Neuroscience, Signal Processing
脳における情報処理がどのように行われているかを理解することは神経科学の大きな目標です。しかし脳は複雑なシステムであり、そこから得られる膨大なデータを人が個別に見ていくだけではその仕組みを知ることが困難です。そこで我々の研究室では計算機によるデータ解析により脳のメカニズムに迫る研究を行っています。スパイク系列、LFP、脳波、カルシウムイメージングといった脳や神経組織から記録されるデータに対し、深層学習やカーネル法、情報理論などの道具立てを用い、情報の縮約や頻出パターンの発見、可視化を行うソフトウェアを開発しています。特に神経生物学の研究室や企業との共同研究により、検出されたパターンに応じたフィードバックを光遺伝学などの手段で脳に送る閉ループ実験系を実現し、受動的な観察だけでなく直接的な操作によって脳の各部位の役割や機能を探る研究に取り組んでいます。
Read More
Neuroinformatics Laboratory Machine Learning, Computational Neuroscience, Signal Processing Understanding information processing in the brain is a primary goal in neuroscience. Since the brain is a complicated system, it's necessary to use computer systems to understand its mechanism. To this end, we apply machine learning methods such as deep learning, Gaussian process regression, and information-theoretic analysis for processing spike trains, LFP, EEG, and calcium imaging data. Collaborating with biology labs and corporations, we develop software for data summarization, pattern recognition, and visualization of neural data. Most notably, we're implementing feedback loop systems that not only observe the brain but also control it by combining real-time pattern recognition with optogenetics.
Read More
Understanding information processing in the brain is a primary goal in neuroscience. Since the brain is a complicated system, it's necessary to use computer systems to understand its mechanism. To this end, we apply machine learning methods such as deep learning, Gaussian process regression, and information-theoretic analysis for processing spike trains, LFP, EEG, and calcium imaging data. Collaborating with biology labs and corporations, we develop software for data summarization, pattern recognition, and visualization of neural data. Most notably, we're implementing feedback loop systems that not only observe the brain but also control it by combining real-time pattern recognition with optogenetics.
Read More
-
自然言語処理研究室 自然言語処理,生成AI(大規模言語モデル・大規模推論モデル・大規模マルチ モーダルモデル),ウェブ検索,音声言語情報処理,感情理解,娯楽・教育コンテン ツの理解と創作,ディープ・ラーニング言語処理,人工知能
 言語は人の知能の根幹であり、人の叡智を記録する重要なメディアです。言語を
用いた人の知的作業の原理を解明し、計算機に模倣・支援させる技術について研
究しています。
(1) 基本的な研究ツールとして生成AI(大規模言語モデル・大規模推論モデル・
大規模マルチモーダルモデル)を駆使して,以下の各論研究を実施。
(2) ウェブ検索エンジンをより賢く使い易くするために、
文で対話しながら検索する技術、
言葉の推論を組み込んだ検索エンジン、ディープ・
ラーニングにより製品・人物・会社などの評判を探し出す技術。
(3) 音声を用いた人間・機械間のコミュニケーションの技術、
身体動作によって感情を表現しながら人間と対話するロボットの技術、
音声言語理解により喜び・悲しみの感情
を理解する技術、音声認識技術を用いて手軽にメモをとる技術。
(4) 言葉の壁を越えるために、翻訳のために必要な辞書や規則を学習する技術、
多言語のウェブ文書を集めてきて、内容の微妙な差異と各国の文化的差異
の間の関係を解読する技術、ニューラルネットによる機械翻訳技術。
(5) 外国語の学習過程を支援するために、難しい言葉を易しく言い換えてくれる
ツール、語法や文法の誤りを指摘してくれるツール。
Read More
Natural Language Processing Laboratory Natural Language Processing, Generative AI (Large Language Models, Large Reasoning Models, Large Multi-Modal Model), Web Retrieval, Language Processing by Deep Learning, Human-Machine Communication by Speech and Language, Recognizing Emotion, Artificial Intelligence
言語は人の知能の根幹であり、人の叡智を記録する重要なメディアです。言語を
用いた人の知的作業の原理を解明し、計算機に模倣・支援させる技術について研
究しています。
(1) 基本的な研究ツールとして生成AI(大規模言語モデル・大規模推論モデル・
大規模マルチモーダルモデル)を駆使して,以下の各論研究を実施。
(2) ウェブ検索エンジンをより賢く使い易くするために、
文で対話しながら検索する技術、
言葉の推論を組み込んだ検索エンジン、ディープ・
ラーニングにより製品・人物・会社などの評判を探し出す技術。
(3) 音声を用いた人間・機械間のコミュニケーションの技術、
身体動作によって感情を表現しながら人間と対話するロボットの技術、
音声言語理解により喜び・悲しみの感情
を理解する技術、音声認識技術を用いて手軽にメモをとる技術。
(4) 言葉の壁を越えるために、翻訳のために必要な辞書や規則を学習する技術、
多言語のウェブ文書を集めてきて、内容の微妙な差異と各国の文化的差異
の間の関係を解読する技術、ニューラルネットによる機械翻訳技術。
(5) 外国語の学習過程を支援するために、難しい言葉を易しく言い換えてくれる
ツール、語法や文法の誤りを指摘してくれるツール。
Read More
Natural Language Processing Laboratory Natural Language Processing, Generative AI (Large Language Models, Large Reasoning Models, Large Multi-Modal Model), Web Retrieval, Language Processing by Deep Learning, Human-Machine Communication by Speech and Language, Recognizing Emotion, Artificial Intelligence (1) As fundamental tools for research, generative AI
models (large language models, large reasoning models, large
multi-modal models) are intensively utilized and
the subsequent (2)-(6) topics are studied.
(2) Web retrieval and mining technologies such as review analysis by
deep learning, search engine suggests analysis, and topic modeling of
Web pages.
(3) human-machine communication by speech and language,
recognizing emotion in speech such as joy and sadness, converting
emotion in speech.
(4) machine translation technologies including
learning translation lexicon and rules, and neural machine
translation.
(5) detecting cultural gaps between countries by collecting
and comparatively analyzing multilingual Web pages.
(6) assisting the
process of foreign language learning by utilizing a tool for
paraphrasing expressions into easier ones, and a tool for detecting
errors in word usages and grammars.
Read More
(1) As fundamental tools for research, generative AI
models (large language models, large reasoning models, large
multi-modal models) are intensively utilized and
the subsequent (2)-(6) topics are studied.
(2) Web retrieval and mining technologies such as review analysis by
deep learning, search engine suggests analysis, and topic modeling of
Web pages.
(3) human-machine communication by speech and language,
recognizing emotion in speech such as joy and sadness, converting
emotion in speech.
(4) machine translation technologies including
learning translation lexicon and rules, and neural machine
translation.
(5) detecting cultural gaps between countries by collecting
and comparatively analyzing multilingual Web pages.
(6) assisting the
process of foreign language learning by utilizing a tool for
paraphrasing expressions into easier ones, and a tool for detecting
errors in word usages and grammars.
Read More
-
脳コミュニケーション研究室 脳科学、認知科学、認知心理学、コミュニケーション、脳波、生体信号処理
 人と社会の円滑なコミュニケーションを実現させるために、「人間の様々なコミュニケーションに関する脳メカニズムの解明」と「それを用いた新たなコミュニケーションの提案と開発」を行っています。記憶や感情、創造など様々な認知機能を実現する我々の脳を理解し、応用することを目標として、心理課題時の脳波やfMRIなどを用いた脳機能計測実験を行い、データ解析を行います。私の研究室では大きく3つの柱で研究を行います。1つめは、人の脳内におけるコミュニケーションの解明です。各脳部位の相互作用に注目して、脳内のネットワークを実験的かつ数理モデル的に理解します。2つめは、人と人のコミュニケーションのメカニズムの解明です。コミュニケーション時の行動や脳活動を複数名で同時計測する実験や発達障害者との比較実験を行います。3つめは、新しいコミュニケーション技術への応用です。1と2より得られた脳指標を用いたコミュニケーション障害の改善プログラム開発、ロボット開発、ニューロマーケティングなどの社会応用を試みます。 以上のような多岐にわたる学問分野の融合及び協力によって、脳科学という壮大な研究テーマに挑みます。
Read More
Brain Communication Laboratory Cognitive Neuroscience, Cognitive Science, Cognitive Psychology, Communication, EEG, Signal Processing
人と社会の円滑なコミュニケーションを実現させるために、「人間の様々なコミュニケーションに関する脳メカニズムの解明」と「それを用いた新たなコミュニケーションの提案と開発」を行っています。記憶や感情、創造など様々な認知機能を実現する我々の脳を理解し、応用することを目標として、心理課題時の脳波やfMRIなどを用いた脳機能計測実験を行い、データ解析を行います。私の研究室では大きく3つの柱で研究を行います。1つめは、人の脳内におけるコミュニケーションの解明です。各脳部位の相互作用に注目して、脳内のネットワークを実験的かつ数理モデル的に理解します。2つめは、人と人のコミュニケーションのメカニズムの解明です。コミュニケーション時の行動や脳活動を複数名で同時計測する実験や発達障害者との比較実験を行います。3つめは、新しいコミュニケーション技術への応用です。1と2より得られた脳指標を用いたコミュニケーション障害の改善プログラム開発、ロボット開発、ニューロマーケティングなどの社会応用を試みます。 以上のような多岐にわたる学問分野の融合及び協力によって、脳科学という壮大な研究テーマに挑みます。
Read More
Brain Communication Laboratory Cognitive Neuroscience, Cognitive Science, Cognitive Psychology, Communication, EEG, Signal Processing In order to realize smooth communication between people and society, we are conducting "Elucidation of brain mechanisms related to various human communication" and "Proposal and development of new communication using it". We conduct brain function measurement experiments using brain waves and fMRI during psychological tasks and analyze data with the goal of understanding and applying our brain that realizes various cognitive functions such as memory, emotion, creation, etc. . In my laboratory, I conduct research with three main pillars. The first is to elucidate communication in the human brain. Focusing on the interaction of each brain site, we understand the network in the brain experimentally and mathematically. The second is to elucidate the mechanism of communication between people. We will conduct experiments to simultaneously measure behavior and brain activity during communication with multiple people, and conduct comparative experiments with people with developmental disabilities. The third is application to new communication technologies. We will try to apply social developments such as development of improvement program of communication disorder, robot development, neuromarketing, etc. using brain index obtained from 1 and 2. Through the fusion and cooperation of the various disciplines described above, we will challenge the grand research theme of brain science.
Read More
In order to realize smooth communication between people and society, we are conducting "Elucidation of brain mechanisms related to various human communication" and "Proposal and development of new communication using it". We conduct brain function measurement experiments using brain waves and fMRI during psychological tasks and analyze data with the goal of understanding and applying our brain that realizes various cognitive functions such as memory, emotion, creation, etc. . In my laboratory, I conduct research with three main pillars. The first is to elucidate communication in the human brain. Focusing on the interaction of each brain site, we understand the network in the brain experimentally and mathematically. The second is to elucidate the mechanism of communication between people. We will conduct experiments to simultaneously measure behavior and brain activity during communication with multiple people, and conduct comparative experiments with people with developmental disabilities. The third is application to new communication technologies. We will try to apply social developments such as development of improvement program of communication disorder, robot development, neuromarketing, etc. using brain index obtained from 1 and 2. Through the fusion and cooperation of the various disciplines described above, we will challenge the grand research theme of brain science.
Read More
-
アフェクティブコンピューティング研究室 アフェクティブコンピューティング
 アフェクティブコンピューティングとは、機械に人の感情を理解させる、機械に感情的に振る舞わせる、機械に感情を持たせることで人の社会生活に役立てるための比較的新しい学問分野です。本研究室では、その名のとおり計算論を核として、機械に共感を扱わせるための研究を行っています。喜怒哀楽といった主観的体験の裏には、脳活動や心拍、発汗などの生体反応があり、また、それが表情や視線等の身体表出や意思決定という形で他者にも見える形で現れ、最終的に相手に感情が伝わります。これが共感の基本的な概念です。これら複数要素・複数人物の間の関係性を数理モデルで記述することで、センサから得られる生体反応や身体表出のデータから主観や意思決定、さらには共感を機械が推定・予測できると考えられます。このような技術を教育や行動変容などに応用するには、機械がなぜそう判断したかを説明出来ることも重要です。このため、信号処理や深層学習/統計的機械学習といった機械学習に、数理心理学や行動経済学など確立された数理的理論を融合した研究を進めています。
Read More
Affective Computing Laboratory Affective Computing
アフェクティブコンピューティングとは、機械に人の感情を理解させる、機械に感情的に振る舞わせる、機械に感情を持たせることで人の社会生活に役立てるための比較的新しい学問分野です。本研究室では、その名のとおり計算論を核として、機械に共感を扱わせるための研究を行っています。喜怒哀楽といった主観的体験の裏には、脳活動や心拍、発汗などの生体反応があり、また、それが表情や視線等の身体表出や意思決定という形で他者にも見える形で現れ、最終的に相手に感情が伝わります。これが共感の基本的な概念です。これら複数要素・複数人物の間の関係性を数理モデルで記述することで、センサから得られる生体反応や身体表出のデータから主観や意思決定、さらには共感を機械が推定・予測できると考えられます。このような技術を教育や行動変容などに応用するには、機械がなぜそう判断したかを説明出来ることも重要です。このため、信号処理や深層学習/統計的機械学習といった機械学習に、数理心理学や行動経済学など確立された数理的理論を融合した研究を進めています。
Read More
Affective Computing Laboratory Affective Computing Affective computing is a relatively new academic area that aims to make machines understand human emotions, behave emotionally, have emotions in order to support human social life. As the name implies, our laboratory conducts research on empathy using computational theory as the core. Behind subjective experiences such as joy, anger, sadness and surprise, there are biological reactions such as brain activity, heartbeat, and perspiration, and these reactions are visible to others in the form of physical expressions such as facial expressions and gazes, as well as in the form of decision-making, and finally the emotions are transmitted to the other person. This is the basic concept of empathy. By describing the relationships between these multiple elements and people using mathematical models, it is thought that a machine can estimate and predict subjectivity, decision-making, and empathy from biological responses and physical expression data obtained from sensors. In order to apply such technology to education and behavioral change, it is also important to be able to explain why the machine made the decision it did. For this reason, we are conducting research that combines established mathematical theories such as mathematical psychology and behavioral economics with machine learning such as signal processing and deep learning/statistical machine learning.
Read More
Affective computing is a relatively new academic area that aims to make machines understand human emotions, behave emotionally, have emotions in order to support human social life. As the name implies, our laboratory conducts research on empathy using computational theory as the core. Behind subjective experiences such as joy, anger, sadness and surprise, there are biological reactions such as brain activity, heartbeat, and perspiration, and these reactions are visible to others in the form of physical expressions such as facial expressions and gazes, as well as in the form of decision-making, and finally the emotions are transmitted to the other person. This is the basic concept of empathy. By describing the relationships between these multiple elements and people using mathematical models, it is thought that a machine can estimate and predict subjectivity, decision-making, and empathy from biological responses and physical expression data obtained from sensors. In order to apply such technology to education and behavioral change, it is also important to be able to explain why the machine made the decision it did. For this reason, we are conducting research that combines established mathematical theories such as mathematical psychology and behavioral economics with machine learning such as signal processing and deep learning/statistical machine learning.
Read More
-
生体計測システム研究室 非侵襲・無拘束生体計測、在宅健康モニタリング、ウェアラブルデバイス、光電脈波
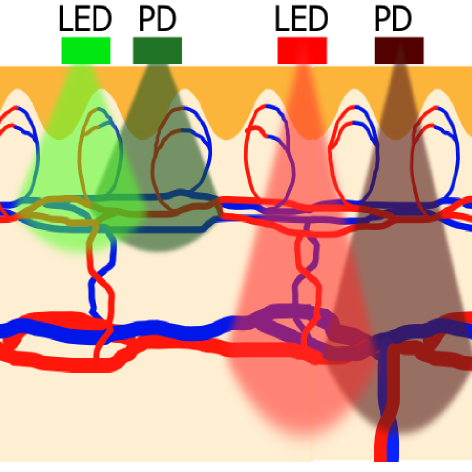 生体計測システム研究室では、生命の維持はもちろんのこと高いQOL(Quality of Life:生活の質)やROL(Respect of Living:尊厳ある生活)を維持したまま生活を送るための支援技術・機器に関する研究を行っています。
日常生活の妨げとならないシステムの構築を目指し、また生体に傷をつけない新たな非侵襲計測の実現に向け、光や超音波などを用いた非接触計測法の基礎的な研究も実施しています。
現在は生体情報モニタリングに向けたウェアラブル脈波計開発を主に行っています。脈波とは心臓の拍動に伴う血管内の血圧や体積の変化のことを指し、血液が光を吸収する特性を利用して皮膚表層から非侵襲的に計測することができます。これまでは生体内の透過性に優れた近赤外域の光を用いた脈波計測が行われてきましたが、近年の光デバイスの向上により可視光域での計測も可能となりました。可視光は近赤外光に比べ皮膚深部まで到達しないため、従来の計測範囲よりも表層部の末梢血流情報を得ることが可能と考えられ、その特徴を生かしたウェアラブル脈拍計の開発を行っています。
Read More
Bioinstrumentation System Laboratory Non-invasive and Unobtrusive Bioinstrumentation, Home Health Monitoring, Wearable Devices, PPG (Photoplethysmography)
生体計測システム研究室では、生命の維持はもちろんのこと高いQOL(Quality of Life:生活の質)やROL(Respect of Living:尊厳ある生活)を維持したまま生活を送るための支援技術・機器に関する研究を行っています。
日常生活の妨げとならないシステムの構築を目指し、また生体に傷をつけない新たな非侵襲計測の実現に向け、光や超音波などを用いた非接触計測法の基礎的な研究も実施しています。
現在は生体情報モニタリングに向けたウェアラブル脈波計開発を主に行っています。脈波とは心臓の拍動に伴う血管内の血圧や体積の変化のことを指し、血液が光を吸収する特性を利用して皮膚表層から非侵襲的に計測することができます。これまでは生体内の透過性に優れた近赤外域の光を用いた脈波計測が行われてきましたが、近年の光デバイスの向上により可視光域での計測も可能となりました。可視光は近赤外光に比べ皮膚深部まで到達しないため、従来の計測範囲よりも表層部の末梢血流情報を得ることが可能と考えられ、その特徴を生かしたウェアラブル脈拍計の開発を行っています。
Read More
Bioinstrumentation System Laboratory Non-invasive and Unobtrusive Bioinstrumentation, Home Health Monitoring, Wearable Devices, PPG (Photoplethysmography) The increase in the elderly population and the prevention of lifestyle diseases such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes highlight the importance of personal health care.
The photoplethysmograph (PPG) is popular for physiological monitoring, because it is simple, inexpensive, and easy to use. In addition, no special techniques are necessary to attach the sensors, but monitoring pulse rates in daily life is difficult because the PPG is sensitive to body movement. The artifacts from body movement are caused by changes in the blood volume at the measurement site.
Here, we consider the motion artifacts related to measurement volume. We focused on the blood-flow distribution in the skin. The penetration depth of light is dependent on its wavelength and infrared light reaches deeper tissues than green light ones. To reduce motion artifacts, we applied green LED to wearable PPG device.
Read More
The increase in the elderly population and the prevention of lifestyle diseases such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes highlight the importance of personal health care.
The photoplethysmograph (PPG) is popular for physiological monitoring, because it is simple, inexpensive, and easy to use. In addition, no special techniques are necessary to attach the sensors, but monitoring pulse rates in daily life is difficult because the PPG is sensitive to body movement. The artifacts from body movement are caused by changes in the blood volume at the measurement site.
Here, we consider the motion artifacts related to measurement volume. We focused on the blood-flow distribution in the skin. The penetration depth of light is dependent on its wavelength and infrared light reaches deeper tissues than green light ones. To reduce motion artifacts, we applied green LED to wearable PPG device.
Read More
-
機械知能研究室 人工知能、機械学習、エージェントシステム
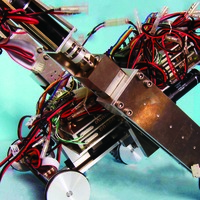 自ら学習し、賢くなっていくシステムを実現するための技術について研究を行っています。 この技術の確立により、ひとつひとつの手順を人が機械に教え込まなくてもよくなり、 設計者の負担軽減はもちろん、周囲にだんだんと適応させていくことが可能になります。 本研究室の基盤技術は、人工知能分野の情報技術です。特に、ニューラルネットワーク・ベイズ推定・強化学習などの機械学習や、 遺伝的アルゴリズム・粒子群最適化などの確率的最適化などの手法を用います。 数理的解析などの基礎研究から、実用を意識したシミュレーション・実機実証などの応用研究まで、 いくつかの段階的な視点にたって研究を進めています。 たとえば、基礎研究では、変化を繰り込んで学習するためのシステムについて検討を行っています。 これは、時々刻々と変化する学習対象をどのように学習するかという課題です。 応用研究では、脚車輪ロボットの動作制御問題や電子回路の自動設計問題などを扱っています。 基盤技術を軸足としながら、さまざまなアプリケーションに適用して、方法論の検証を行っています。
Read More
Machine Intelligence Laboratory Artificial Intelligence, Machine Intelligence, Agent System
自ら学習し、賢くなっていくシステムを実現するための技術について研究を行っています。 この技術の確立により、ひとつひとつの手順を人が機械に教え込まなくてもよくなり、 設計者の負担軽減はもちろん、周囲にだんだんと適応させていくことが可能になります。 本研究室の基盤技術は、人工知能分野の情報技術です。特に、ニューラルネットワーク・ベイズ推定・強化学習などの機械学習や、 遺伝的アルゴリズム・粒子群最適化などの確率的最適化などの手法を用います。 数理的解析などの基礎研究から、実用を意識したシミュレーション・実機実証などの応用研究まで、 いくつかの段階的な視点にたって研究を進めています。 たとえば、基礎研究では、変化を繰り込んで学習するためのシステムについて検討を行っています。 これは、時々刻々と変化する学習対象をどのように学習するかという課題です。 応用研究では、脚車輪ロボットの動作制御問題や電子回路の自動設計問題などを扱っています。 基盤技術を軸足としながら、さまざまなアプリケーションに適用して、方法論の検証を行っています。
Read More
Machine Intelligence Laboratory Artificial Intelligence, Machine Intelligence, Agent System The aim of our laboratory is to develop methods to make systems which learn autonomously. Our research field are machine learning(neural network, Bayesian estimation, reinforcement learning etc.), meta-heuristic optimization and related theories. We currently approach from fundamental side and practical side. From fundamental side, we develop learning algorithm inspired by other theoretical research, such as computational topology, circuit theory. From practical side, we apply machine learning technique to prediction of blasting effects, walking supporting machine and reducing energy cost.
Read More
The aim of our laboratory is to develop methods to make systems which learn autonomously. Our research field are machine learning(neural network, Bayesian estimation, reinforcement learning etc.), meta-heuristic optimization and related theories. We currently approach from fundamental side and practical side. From fundamental side, we develop learning algorithm inspired by other theoretical research, such as computational topology, circuit theory. From practical side, we apply machine learning technique to prediction of blasting effects, walking supporting machine and reducing energy cost.
Read More
-
脳コミュニケーション研究室 認知脳科学、認知心理学、臨床心理学、ニューロエンハンスメント、食と健康
 我々の研究室では、脳科学・認知科学・心理学といった複数の関連分野にまたがる学際的な評価・介入アプローチを用いて、食体験に重要な認知機能・心理特性・脳メカニズムの解明、認知機能や食体験を増強するニューロエンハンスメントの開発と社会実装を目指した研究を行っています。我々は特に、脳波に含まれるリズム(脳リズム)を評価することで特定の認知活動や心理特性に関連するメカニズムを理解しようとする評価手法、そして、磁気や電気による非侵襲的脳刺激(NIBS)や心理的な介入手法を活用することで、人の認知・心理・行動の変容を促す複合的なニューロエンハンスメントの実現を目指しています。
Read More
Brain Communication Laboratory Cognitive Neuroscience, Cognitive Psychology, Clinical Psychology, Neuroenhancement, Food Satisfaction, Well-being
我々の研究室では、脳科学・認知科学・心理学といった複数の関連分野にまたがる学際的な評価・介入アプローチを用いて、食体験に重要な認知機能・心理特性・脳メカニズムの解明、認知機能や食体験を増強するニューロエンハンスメントの開発と社会実装を目指した研究を行っています。我々は特に、脳波に含まれるリズム(脳リズム)を評価することで特定の認知活動や心理特性に関連するメカニズムを理解しようとする評価手法、そして、磁気や電気による非侵襲的脳刺激(NIBS)や心理的な介入手法を活用することで、人の認知・心理・行動の変容を促す複合的なニューロエンハンスメントの実現を目指しています。
Read More
Brain Communication Laboratory Cognitive Neuroscience, Cognitive Psychology, Clinical Psychology, Neuroenhancement, Food Satisfaction, Well-being Our research aims to understand how cognitive functions affect our relationship with food, and ultimately to develop neuroenhancement methods which promote positive food experiences and well-being by improving cognitive functions. To this end, we implement neuroimaging techniques such as electroencephalography and noninvasive brain stimulation techniques such as transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation.
Read More
Our research aims to understand how cognitive functions affect our relationship with food, and ultimately to develop neuroenhancement methods which promote positive food experiences and well-being by improving cognitive functions. To this end, we implement neuroimaging techniques such as electroencephalography and noninvasive brain stimulation techniques such as transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation.
Read More
-
バイオメカニクス研究室 脳卒中、運動機能障害、サイバニクス、バイオエンジニアリング
 人間のあらゆる動作は,高度に発達した神経系によってコントロールされています.事故やけがなどで,脳や脊髄に損傷や機能不全が発生してしまうと,日常生活に支障をきたす運動障害が残ってしまうことも多く,本人や家族に対する精神的・経済的な負担は決して小さくありません.
本研究室では,現在,高齢化が進みつつある我が国において,運動障害に苦しむ患者と家族に希望を与えるために,運動障害者の自立を促進する全く新しい手法の確立に挑戦しています.具体的には,運動障害者の自立に最適な支援法を見いだすために,外骨格ロボットを用いた患者に優しい歩行支援・歩行機能回復技術に取り組んでいます.さらに,臨床中の歩行データを簡単に効率的に収集するための計測技術の確立にも取り組んでいます.
また,本研究室では,四肢の痙縮にも着目しています.意思とは関係なく筋肉の緊張が高まり,手や足が勝手につっぱったり曲がってしまったりしてしまう痙縮は,治療やリハビリテーションを阻害する問題となっています.本研究室では,運動障害者の機能回復の促進と,生活の質の改善に貢献するために,振動を用いる新しい痙縮軽減技術の開発にも取り組んでいます.
なお本研究室は,サイバニクス分野の第一人者である山海教授,医工連携の経験が豊富な鈴木教授,及び附属病院と協力しています.
Read More
Laboratory of Biomechanics Stroke, Motor Impairment, Cybernics, Bioengineering
人間のあらゆる動作は,高度に発達した神経系によってコントロールされています.事故やけがなどで,脳や脊髄に損傷や機能不全が発生してしまうと,日常生活に支障をきたす運動障害が残ってしまうことも多く,本人や家族に対する精神的・経済的な負担は決して小さくありません.
本研究室では,現在,高齢化が進みつつある我が国において,運動障害に苦しむ患者と家族に希望を与えるために,運動障害者の自立を促進する全く新しい手法の確立に挑戦しています.具体的には,運動障害者の自立に最適な支援法を見いだすために,外骨格ロボットを用いた患者に優しい歩行支援・歩行機能回復技術に取り組んでいます.さらに,臨床中の歩行データを簡単に効率的に収集するための計測技術の確立にも取り組んでいます.
また,本研究室では,四肢の痙縮にも着目しています.意思とは関係なく筋肉の緊張が高まり,手や足が勝手につっぱったり曲がってしまったりしてしまう痙縮は,治療やリハビリテーションを阻害する問題となっています.本研究室では,運動障害者の機能回復の促進と,生活の質の改善に貢献するために,振動を用いる新しい痙縮軽減技術の開発にも取り組んでいます.
なお本研究室は,サイバニクス分野の第一人者である山海教授,医工連携の経験が豊富な鈴木教授,及び附属病院と協力しています.
Read More
Laboratory of Biomechanics Stroke, Motor Impairment, Cybernics, Bioengineering Human movement is a highly engineered function mediated by our nervous system. After an injury to the brain or spinal cord, movement disturbances in lower and/or upper limbs are common and patients cannot return to their daily life activities after the injury. Furthermore, some patients require constant care increasing the emotional and financial costs of the family involved. In an aging world where classic rehabilitation cannot achieve satisfactory results in some cases and where the elderly population is constantly growing, new approaches are required to improve the quality of life and independence of patients suffering from motor disorders. Our work covers analyzing changes in gait kinematics after exoskeleton interventions in patients with gait disturbances. The goal is to understand the mechanism underlying robotic supported-enhanced gait in order to improve and refine our strategies to offer appropriate care and treatment to patients, giving them the option to produce healthy gait patterns. Additionally, we are looking for portable and easy-to-use ways to measure kinematics in order to collect data easily for patients in locations apart from our kinematics lab.
Our lab is also interested in spasticity; a symptom accompanying a wide range of neurologic patients that leads to abnormal postures of the limbs and pain, interfering importantly with medical care or rehabilitation of the affected extremity. Using vibration technologies, we are developing new methods to reduce spasticity improving limb usage and quality of life of patients.
Our lab has been working with the Cybernics Laboratory (Professor Yoshiyuki Sankai), the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (Professor Kenji Suzuki), and the University of Tsukuba Hospital.
Read More
Human movement is a highly engineered function mediated by our nervous system. After an injury to the brain or spinal cord, movement disturbances in lower and/or upper limbs are common and patients cannot return to their daily life activities after the injury. Furthermore, some patients require constant care increasing the emotional and financial costs of the family involved. In an aging world where classic rehabilitation cannot achieve satisfactory results in some cases and where the elderly population is constantly growing, new approaches are required to improve the quality of life and independence of patients suffering from motor disorders. Our work covers analyzing changes in gait kinematics after exoskeleton interventions in patients with gait disturbances. The goal is to understand the mechanism underlying robotic supported-enhanced gait in order to improve and refine our strategies to offer appropriate care and treatment to patients, giving them the option to produce healthy gait patterns. Additionally, we are looking for portable and easy-to-use ways to measure kinematics in order to collect data easily for patients in locations apart from our kinematics lab.
Our lab is also interested in spasticity; a symptom accompanying a wide range of neurologic patients that leads to abnormal postures of the limbs and pain, interfering importantly with medical care or rehabilitation of the affected extremity. Using vibration technologies, we are developing new methods to reduce spasticity improving limb usage and quality of life of patients.
Our lab has been working with the Cybernics Laboratory (Professor Yoshiyuki Sankai), the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (Professor Kenji Suzuki), and the University of Tsukuba Hospital.
Read More
-
人工知能研究室 情報通信、人工知能、機械学習、ビックデータ、リハビリテーション医学
 医療と工学の融合を追求した研究を行っています。AR(拡張現実:Augmented Reality)技術に着目しており、スポーツ分野において特にパラスポーツ分野での応用を目指しています。スポーツトレーニングやリハビリテーションに派生する新しい可能性を探求しており、安全かつ効果的、効率的なトレーニングの実現可能な環境を提供します。また、遠隔医療を手段とした予防医療の実現を目指しています。特に運動の永続的な継続、転倒予防などに着目しており、運動継続の可否や転倒に関わる予測因子を抽出・解析し、遠隔的に制御できる社会実装が理想です。情報通信技術、機械学習、ビッグデータを活用し、革新的なソリューション・システムの開発を目標としています。
Read More
Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Information and Communication, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Big Data, Rehabilitation Medicine
医療と工学の融合を追求した研究を行っています。AR(拡張現実:Augmented Reality)技術に着目しており、スポーツ分野において特にパラスポーツ分野での応用を目指しています。スポーツトレーニングやリハビリテーションに派生する新しい可能性を探求しており、安全かつ効果的、効率的なトレーニングの実現可能な環境を提供します。また、遠隔医療を手段とした予防医療の実現を目指しています。特に運動の永続的な継続、転倒予防などに着目しており、運動継続の可否や転倒に関わる予測因子を抽出・解析し、遠隔的に制御できる社会実装が理想です。情報通信技術、機械学習、ビッグデータを活用し、革新的なソリューション・システムの開発を目標としています。
Read More
Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Information and Communication, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Big Data, Rehabilitation Medicine We are conducting research that pursues the fusion of medicine and engineering. Our focus is on Augmented Reality (AR) technology, aiming to apply it in the field of sports, particularly in parasports. We are exploring new possibilities that branch out into sports training and rehabilitation, providing a safe, effective, and efficient training environment. Additionally, we aim to achieve preventive healthcare through telemedicine. Our focus includes the continuous exercise and fall prevention, extracting and analyzing predictive factors related to the continuation of exercise and fall prevention, with the ideal being a socially implemented system that can be remotely controlled. Utilizing information and communication technology, machine learning, and big data, our goal is to develop innovative solutions and systems.
Read More
We are conducting research that pursues the fusion of medicine and engineering. Our focus is on Augmented Reality (AR) technology, aiming to apply it in the field of sports, particularly in parasports. We are exploring new possibilities that branch out into sports training and rehabilitation, providing a safe, effective, and efficient training environment. Additionally, we aim to achieve preventive healthcare through telemedicine. Our focus includes the continuous exercise and fall prevention, extracting and analyzing predictive factors related to the continuation of exercise and fall prevention, with the ideal being a socially implemented system that can be remotely controlled. Utilizing information and communication technology, machine learning, and big data, our goal is to develop innovative solutions and systems.
Read More
-
HEBBS Lab 計算論的神経科学、運動制御と学習、ニューロリハビリテーション、筋シナジー
 運動技能を身につけることは、多くの場合、長期間の練習を必要とする難しい課題であり、その成果は人によって大きく異なります。なぜ人によって学習の成果に差が生じるのでしょうか。より効果的に学習できるような練習方法を体系的に設計することは可能でしょうか。これらの問いは、リハビリテーションにも当てはまります。回復には、運動機能の再学習が不可欠ですが、その成果もまた大きく異なります。我々はこのような問いに答えるために、学習理論、計算モデル、ロボティクス、バイオメカニクスに基づく理論的・実験的なアプローチを組み合わせています。この研究を通じて、健康な人における運動技能の学習を促進するだけでなく、運動障害を持つ人のリハビリテーション戦略の改善にも貢献することを目指しています。
Read More
HEBBS Lab computational neuroscience, motor control and learning, neurorehabilitation, muscle synergies
運動技能を身につけることは、多くの場合、長期間の練習を必要とする難しい課題であり、その成果は人によって大きく異なります。なぜ人によって学習の成果に差が生じるのでしょうか。より効果的に学習できるような練習方法を体系的に設計することは可能でしょうか。これらの問いは、リハビリテーションにも当てはまります。回復には、運動機能の再学習が不可欠ですが、その成果もまた大きく異なります。我々はこのような問いに答えるために、学習理論、計算モデル、ロボティクス、バイオメカニクスに基づく理論的・実験的なアプローチを組み合わせています。この研究を通じて、健康な人における運動技能の学習を促進するだけでなく、運動障害を持つ人のリハビリテーション戦略の改善にも貢献することを目指しています。
Read More
HEBBS Lab computational neuroscience, motor control and learning, neurorehabilitation, muscle synergies Acquiring motor skills is a challenging process that often requires extensive training, with highly variable outcomes across individuals. What factors drive these differences in training success? Can we systematically design training protocols that facilitate motor skill acquisition? These same questions also apply to the rehabilitation of motor impairments, which involves the re-learning of motor function, and for which recovery outcomes are also highly variable. Our approach to answering these questions involves theoretical and empirical methods revolving around machine learning, computational modeling, robotics, and biomechanics. Through this research, we aim not only to enhance skill learning in healthy individuals, but also to improve rehabilitation strategies for people with motor disorders.
Read More
Acquiring motor skills is a challenging process that often requires extensive training, with highly variable outcomes across individuals. What factors drive these differences in training success? Can we systematically design training protocols that facilitate motor skill acquisition? These same questions also apply to the rehabilitation of motor impairments, which involves the re-learning of motor function, and for which recovery outcomes are also highly variable. Our approach to answering these questions involves theoretical and empirical methods revolving around machine learning, computational modeling, robotics, and biomechanics. Through this research, we aim not only to enhance skill learning in healthy individuals, but also to improve rehabilitation strategies for people with motor disorders.
Read More
XR / MediaXR・メディア
VR/MR、ハプティクスおよびメディアに関する学際的システム分野An interdisciplinary systems field, focused on VR/MR, haptics, and media technologies.
-
後藤真孝研究室 音楽情報処理、歌声情報処理、メディアインタラクション
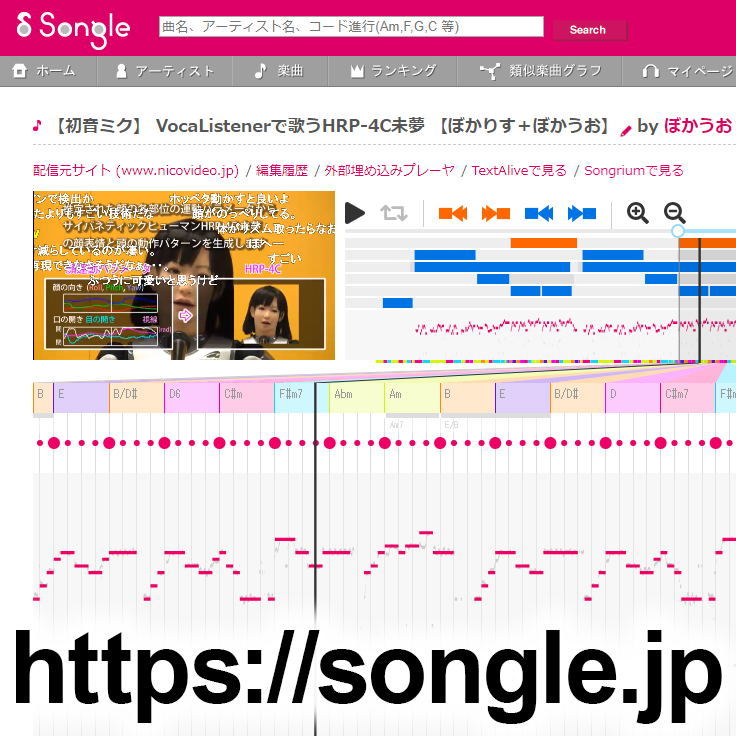 音楽情報処理や歌声情報処理を中心に、人々の生活の豊かさの向上に資するメディアインタラクション技術を研究開発しています。音楽情報処理、特に音楽理解技術やそれに基づく音楽インタフェースに関する29年以上の世界最先端の研究実績から、国内外で広く認知された研究拠点となっています。具体的には、音楽理解技術に基づいて音楽を自動解析する能動的音楽鑑賞サービス「Songle」(https://songle.jp)、Web技術と音楽技術に基づいて大規模コンテンツを俯瞰可能にする音楽視聴支援サービス「Songrium」(https://songrium.jp)、音楽理解技術、HCI、プログラミング言語技術に基づく歌詞アニメーション制作支援サービス「TextAlive」(https://textalive.jp)、音楽に合わせて多様なデバイスを制御できる大規模音楽連動制御プラットフォーム「Songle Sync」(https://api.songle.jp/sync)等のように幅広い研究開発に取り組み、社会実装を進めています。
Read More
Masataka Goto's Laboratory Music Information Processing, Singing Information Processing, Media Interaction
音楽情報処理や歌声情報処理を中心に、人々の生活の豊かさの向上に資するメディアインタラクション技術を研究開発しています。音楽情報処理、特に音楽理解技術やそれに基づく音楽インタフェースに関する29年以上の世界最先端の研究実績から、国内外で広く認知された研究拠点となっています。具体的には、音楽理解技術に基づいて音楽を自動解析する能動的音楽鑑賞サービス「Songle」(https://songle.jp)、Web技術と音楽技術に基づいて大規模コンテンツを俯瞰可能にする音楽視聴支援サービス「Songrium」(https://songrium.jp)、音楽理解技術、HCI、プログラミング言語技術に基づく歌詞アニメーション制作支援サービス「TextAlive」(https://textalive.jp)、音楽に合わせて多様なデバイスを制御できる大規模音楽連動制御プラットフォーム「Songle Sync」(https://api.songle.jp/sync)等のように幅広い研究開発に取り組み、社会実装を進めています。
Read More
Masataka Goto's Laboratory Music Information Processing, Singing Information Processing, Media Interaction With a focus on Music Information Processing and Singing Information Processing, Masataka Goto’s Laboratory conducts research on media interaction technologies that can enrich people’s life. In 1992 Masataka Goto was one of the first to start work on automatic music understanding, and has since been at the forefront of research in music technologies and music interfaces based on those technologies. For example, we have developed “Songle” (https://songle.jp) that is a web service for active music listening based on music-understanding technologies, “Songrium” (https://songrium.jp) that is a web service for music browsing assistance based on web and music technologies, “TextAlive” (https://textalive.jp) that is a web service for creating lyrics animations based on music-understanding, human-computer interaction, and programming language technologies, and “Songle Sync” (https://api.songle.jp/sync) that is a large-scale web-based platform for controlling various devices in synchronization with music.
Read More
With a focus on Music Information Processing and Singing Information Processing, Masataka Goto’s Laboratory conducts research on media interaction technologies that can enrich people’s life. In 1992 Masataka Goto was one of the first to start work on automatic music understanding, and has since been at the forefront of research in music technologies and music interfaces based on those technologies. For example, we have developed “Songle” (https://songle.jp) that is a web service for active music listening based on music-understanding technologies, “Songrium” (https://songrium.jp) that is a web service for music browsing assistance based on web and music technologies, “TextAlive” (https://textalive.jp) that is a web service for creating lyrics animations based on music-understanding, human-computer interaction, and programming language technologies, and “Songle Sync” (https://api.songle.jp/sync) that is a large-scale web-based platform for controlling various devices in synchronization with music.
Read More
-
画像情報研究室、計算科学研究センター 複合現実感、マッシブセンシング、知的画像認識・処理、VR体験の高度計測、 交通移動の知的支援、 eラーニング
 ディアの知能化からスタートして、人の機能を拡張する計算メディアの研究とそれを通じた人類の幸福への貢献に取り組んでいます。
・屋外における複合現実感技術(MR,AR,VR)
・マッシブセンシング[多種多種類のセンサによる日常生活の継続的観測)とそのデータ解析・可視化]
・エモーションセンシング[人間を対象とした精神生理学的観測のための高精度マルチモーダルセンシング]
・VRを通してのスポーツスキル計測および獲得
・生理学的計測を伴うVR体験の客観指標化
・ITSにおける複合現実感技術を用いた交通移動支援
・視覚障がい者に対するナビゲーション知的支援
・映像加工やVRを用いたeラーニング
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Laboratory Mixed Reality, Massive Sensing, Intelligent Computer Vision and Recognition, Advanced Multimodal Measurement of Virtual Reality Experience, Intelligent Support for Traffic Transportation, e-learning
ディアの知能化からスタートして、人の機能を拡張する計算メディアの研究とそれを通じた人類の幸福への貢献に取り組んでいます。
・屋外における複合現実感技術(MR,AR,VR)
・マッシブセンシング[多種多種類のセンサによる日常生活の継続的観測)とそのデータ解析・可視化]
・エモーションセンシング[人間を対象とした精神生理学的観測のための高精度マルチモーダルセンシング]
・VRを通してのスポーツスキル計測および獲得
・生理学的計測を伴うVR体験の客観指標化
・ITSにおける複合現実感技術を用いた交通移動支援
・視覚障がい者に対するナビゲーション知的支援
・映像加工やVRを用いたeラーニング
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Laboratory Mixed Reality, Massive Sensing, Intelligent Computer Vision and Recognition, Advanced Multimodal Measurement of Virtual Reality Experience, Intelligent Support for Traffic Transportation, e-learning We are pursuing the new methodology of computational media on vision in order to realize a better society by the advanced information technology and smart computation.
- Mixed reality technology (MR, AR, VR) for outdoor use
- Massive sensing
- Emotion sensing
- Sports skill measurement and acquisition through VR
- Objective indexing of VR experiences with physiological measurements
- Traffic movement support using mixed reality technology in ITS
- Intelligent navigation support for the visually impaired
- E-learning using video processing and VR
Read More
We are pursuing the new methodology of computational media on vision in order to realize a better society by the advanced information technology and smart computation.
- Mixed reality technology (MR, AR, VR) for outdoor use
- Massive sensing
- Emotion sensing
- Sports skill measurement and acquisition through VR
- Objective indexing of VR experiences with physiological measurements
- Traffic movement support using mixed reality technology in ITS
- Intelligent navigation support for the visually impaired
- E-learning using video processing and VR
Read More
-
画像情報研究室、計算科学研究センター 自由視点映像、実世界イメージング、コンピュータビジョン、映像メディア
 我々は、目に入射した光線情報から、目の前の物体の形状、色合い、素材に始まり、その物体が何であるか、どのような機能を有しているかといった様々な情報を獲得しています。この優れた機能の仕組みを明らかにすることを目的として、コンピュータビジョンや実世界イメージングの研究に取り組んでいます。また、我々は、絵や記号を描くことで、言語ではうまく言い表せない情報を表現しようとします。情報をどのような形態で視覚的に表現すれば、効率的な理解が実現できるのかを明らかにすることを目的として、コンピュータグラフィックスを駆使した映像メディアに関する研究にも取り組んでいます。さらに、両研究分野を融合し、画像情報から獲得したシーン情報を活用して、画像情報をより視聴しやすい形に加工・提示する、先進的映像メディアの研究にも取り組んでいます。例えば、多視点で撮影した画像を計算機内部で統合し、そのデータに基づき任意の視点からの見え方を再現する自由視点映像の研究や、現実世界の見え方に仮想世界の見え方をシームレスに重畳提示することにより、視覚機能の増強を実現する複合現実感/拡張現実の研究に取り組んでいます。
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Laboratory Computer Vision, Computational Media, Free Viewpoint Video, Augmented/Mixed Reality, Real World Oriented Imaging
我々は、目に入射した光線情報から、目の前の物体の形状、色合い、素材に始まり、その物体が何であるか、どのような機能を有しているかといった様々な情報を獲得しています。この優れた機能の仕組みを明らかにすることを目的として、コンピュータビジョンや実世界イメージングの研究に取り組んでいます。また、我々は、絵や記号を描くことで、言語ではうまく言い表せない情報を表現しようとします。情報をどのような形態で視覚的に表現すれば、効率的な理解が実現できるのかを明らかにすることを目的として、コンピュータグラフィックスを駆使した映像メディアに関する研究にも取り組んでいます。さらに、両研究分野を融合し、画像情報から獲得したシーン情報を活用して、画像情報をより視聴しやすい形に加工・提示する、先進的映像メディアの研究にも取り組んでいます。例えば、多視点で撮影した画像を計算機内部で統合し、そのデータに基づき任意の視点からの見え方を再現する自由視点映像の研究や、現実世界の見え方に仮想世界の見え方をシームレスに重畳提示することにより、視覚機能の増強を実現する複合現実感/拡張現実の研究に取り組んでいます。
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Laboratory Computer Vision, Computational Media, Free Viewpoint Video, Augmented/Mixed Reality, Real World Oriented Imaging Vision is one of the most important functions to understand the real world around us. We are acquiring various information such as shape, color, material and so on. My researching interest is based on to unravel this prominent mechanism by researching Computer Vision. We also try to explain information which is difficult to express in words by drawing pictures or symbols. My another interest is understanding suitable methods to express various information using Computer Graphics technology. By merging the results of the two research activities, we are opening up a new field in Image Media research, “Real-World Imaging,” which aims to display captured image data with making them into more understandable or attractive. For example, Free-Viewpoint Video and Augmented Reality are the researching topics.
Read More
Vision is one of the most important functions to understand the real world around us. We are acquiring various information such as shape, color, material and so on. My researching interest is based on to unravel this prominent mechanism by researching Computer Vision. We also try to explain information which is difficult to express in words by drawing pictures or symbols. My another interest is understanding suitable methods to express various information using Computer Graphics technology. By merging the results of the two research activities, we are opening up a new field in Image Media research, “Real-World Imaging,” which aims to display captured image data with making them into more understandable or attractive. For example, Free-Viewpoint Video and Augmented Reality are the researching topics.
Read More
-
応用サービス工学研究室 XR、屋内測位、サービス工学、視覚障害者支援
 サービス、製造、生活の各場面で、ヒト、モノ、コトを計測し、得られたデータを現状把握や改善支援、新しいアイデアの事前評価等に活用するといった「測って図る」という考え方は、サービス工学の根幹です。その実現のために、「現場のラボ化」と「ラボの現場化」という2通りの方法論があると考え、実践しています。「現場のラボ化」とは、仮説・検証を繰り返し行うといった従来はラボでしかできなかった方法論を、実際の現場に持ち込もうとするもので、「ラボの現場化」とは、再現性の高いバーチャル環境を構築し、ラボ実験(仮説・検証)で得られる知見と、現場で実際に得られるはずの知見とを近づけるための方法論のことです。本ラボでは、IoH、AI、XR等の技術をサービス工学的観点で活用し、「測って図る」研究を推進しています。視覚障害者社会進出支援や健康経営なども重点研究テーマとしています。
Read More
Applied Service Engineering Laboratory XR, Indoor Positioning, Service Engineering, Support for the Visually Impaired
サービス、製造、生活の各場面で、ヒト、モノ、コトを計測し、得られたデータを現状把握や改善支援、新しいアイデアの事前評価等に活用するといった「測って図る」という考え方は、サービス工学の根幹です。その実現のために、「現場のラボ化」と「ラボの現場化」という2通りの方法論があると考え、実践しています。「現場のラボ化」とは、仮説・検証を繰り返し行うといった従来はラボでしかできなかった方法論を、実際の現場に持ち込もうとするもので、「ラボの現場化」とは、再現性の高いバーチャル環境を構築し、ラボ実験(仮説・検証)で得られる知見と、現場で実際に得られるはずの知見とを近づけるための方法論のことです。本ラボでは、IoH、AI、XR等の技術をサービス工学的観点で活用し、「測って図る」研究を推進しています。視覚障害者社会進出支援や健康経営なども重点研究テーマとしています。
Read More
Applied Service Engineering Laboratory XR, Indoor Positioning, Service Engineering, Support for the Visually Impaired The concept of measuring people, objects, and things in service, manufacturing, and daily life situations, and using the data obtained to understand the current situation, support improvements, and pre-evaluate new ideas, is the foundation of service engineering. We believe that there are two methodologies to achieve this: "Lab-forming Field (LFF)" and "Field-forming Lab (FFL)". LFF is a methodology that brings into the actual field a methodology that was previously only possible in the lab, such as repeated hypothesis vefirication. On the other hand, FFL is a methodology that builds a highly reproducible virtual environment to bring the findings from lab experiments closer to the actual findings in the field. In this laboratory, we are promoting service engineering research by utilizing technologies such as IoH, AI, and XR. Our priority research themes include support for the visually impaired to participate in society and health and productivity management (HPM).
Read More
The concept of measuring people, objects, and things in service, manufacturing, and daily life situations, and using the data obtained to understand the current situation, support improvements, and pre-evaluate new ideas, is the foundation of service engineering. We believe that there are two methodologies to achieve this: "Lab-forming Field (LFF)" and "Field-forming Lab (FFL)". LFF is a methodology that brings into the actual field a methodology that was previously only possible in the lab, such as repeated hypothesis vefirication. On the other hand, FFL is a methodology that builds a highly reproducible virtual environment to bring the findings from lab experiments closer to the actual findings in the field. In this laboratory, we are promoting service engineering research by utilizing technologies such as IoH, AI, and XR. Our priority research themes include support for the visually impaired to participate in society and health and productivity management (HPM).
Read More
-
ライフエンジニアリング研究室 生体システム工学, 医用人工知能, ハプティクス(力触覚)
 内視鏡・手術ロボット・歩行支援ロボットに代表されるように、医療・介護・福祉分野において工学技術は欠かせないものとなっています。一方で、工学を応用することで安全・快適な環境を提供できるにも関わらず、利便性や費用対効果の観点からまだ工学が適用されていないケースも多々あります。本研究室では、情報・電気・機械的な観点に基づく生体のシステム的理解を深め、医療・介護・日常の現場でユーザに使いやすく快適な情報支援を可能とする、生活支援技術基盤の確立を目指します。具体的には、身体の物理的・生理的・認知的特性を考慮した先進的ソフトウェア・ハードウェア・システムの設計と開発を行うほか、医療・介護分野の専門家と連携して真に有効な工学技術の開発を目指します。
Read More
Life Engineering Laboratory Biology Systems Engineering, Medical Artificial Intelligence, Haptics
内視鏡・手術ロボット・歩行支援ロボットに代表されるように、医療・介護・福祉分野において工学技術は欠かせないものとなっています。一方で、工学を応用することで安全・快適な環境を提供できるにも関わらず、利便性や費用対効果の観点からまだ工学が適用されていないケースも多々あります。本研究室では、情報・電気・機械的な観点に基づく生体のシステム的理解を深め、医療・介護・日常の現場でユーザに使いやすく快適な情報支援を可能とする、生活支援技術基盤の確立を目指します。具体的には、身体の物理的・生理的・認知的特性を考慮した先進的ソフトウェア・ハードウェア・システムの設計と開発を行うほか、医療・介護分野の専門家と連携して真に有効な工学技術の開発を目指します。
Read More
Life Engineering Laboratory Biology Systems Engineering, Medical Artificial Intelligence, Haptics Engineering technologies is inevitable in medicine, nursing, and welfare, as represented by endoscopy, surgical robot, and walking support robot. On the other hand, there are so many cases that engineering technologies have never been applied even though the environment would become safer and more comfort if technologies be applied. Life engineering laboratory aims at establishing the base of life engineering technologies that enables to support a user in medical, welfare, and daily situations by understanding human’s systematic characteristics in terms of informatics, electronics, and mechanics. In concrete, we design and develop the advanced software, hardware, and system considering human body’s physical, biological, and cognitive characteristics, and we also collaborate with the specialists in medicine and welfare to realize real effective technologies.
Read More
Engineering technologies is inevitable in medicine, nursing, and welfare, as represented by endoscopy, surgical robot, and walking support robot. On the other hand, there are so many cases that engineering technologies have never been applied even though the environment would become safer and more comfort if technologies be applied. Life engineering laboratory aims at establishing the base of life engineering technologies that enables to support a user in medical, welfare, and daily situations by understanding human’s systematic characteristics in terms of informatics, electronics, and mechanics. In concrete, we design and develop the advanced software, hardware, and system considering human body’s physical, biological, and cognitive characteristics, and we also collaborate with the specialists in medicine and welfare to realize real effective technologies.
Read More
-
計算知能・マルチメディア研究室 計算知能、マルチメディア情報処理
 計算知能・マルチメディア研究室では、「世の中を快適にするためのマルチメディアのスーパーインフラをつくりあげる」という大局的な目標の下、日夜研究に取り組んでおります。より具体的には、インターネット上を流れる膨大で様々なメディア(テキスト、画像、音など)や、それを生み出すデバイス、消費するデバイスを利用して、いかに人々の生活を「本質的」によりよいものにしてゆくのかを、産業としての視点、また実用から基礎理論の視点で、幅広く研究しています。よって、産業の視点では、農業・災害用の無人航空機の機体設計・開発および画像センシング、次世代学習支援、P2Pインフラを利用した新たな産業創出など、実用の視点では、スマート端末を対象としたレコメンデーションのアプリケーション開発、マルチエージェントシミュレーション技術、超解像技術など、を取り扱っています。もちろん、コンピュータサイエンスの基礎となる離散数理に関する研究も大切にしています。 我々の研究室では、このような数理論理的な思考を大切にしつつ、それらを武器に様々な分野に切り込んでゆける人材を輩出することも目標にしています。
Read More
Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Laboratory Computational / Artificial Intelligence, Drone, Multimedia Information Processing
計算知能・マルチメディア研究室では、「世の中を快適にするためのマルチメディアのスーパーインフラをつくりあげる」という大局的な目標の下、日夜研究に取り組んでおります。より具体的には、インターネット上を流れる膨大で様々なメディア(テキスト、画像、音など)や、それを生み出すデバイス、消費するデバイスを利用して、いかに人々の生活を「本質的」によりよいものにしてゆくのかを、産業としての視点、また実用から基礎理論の視点で、幅広く研究しています。よって、産業の視点では、農業・災害用の無人航空機の機体設計・開発および画像センシング、次世代学習支援、P2Pインフラを利用した新たな産業創出など、実用の視点では、スマート端末を対象としたレコメンデーションのアプリケーション開発、マルチエージェントシミュレーション技術、超解像技術など、を取り扱っています。もちろん、コンピュータサイエンスの基礎となる離散数理に関する研究も大切にしています。 我々の研究室では、このような数理論理的な思考を大切にしつつ、それらを武器に様々な分野に切り込んでゆける人材を輩出することも目標にしています。
Read More
Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Laboratory Computational / Artificial Intelligence, Drone, Multimedia Information Processing The Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Laboratory conducts research day and night with the overall goal of "create a multimedia superinfrastructure to make the world more comfortable". More specifically, we are conducting wide-ranging research on how to make people's lives better "essential" from an industrial point of view and from a practical point of view to a basic theory point of view, using the vast and diverse media (Text, pictures, sounds, and so on) that flow on the Internet, devices that create them, and devices that consume them. Therefore, from the industrial perspective, we handle the design and development of unmanned aircraft systems for agriculture and disasters, image sensing, support for next-generation learning, and the creation of new industries using P2P infrastructure. From the practical perspective, we handle the development of applications for recommendations for smart terminals, multi-agent simulation technology, and super-resolution technology. Of course, we also value research on discrete mathematics, which is the foundation of computer science. In our laboratory, we value this kind of mathematical and logical thinking, and our goal is to produce human resources who can break into various fields using this as a weapon.
Read More
The Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Laboratory conducts research day and night with the overall goal of "create a multimedia superinfrastructure to make the world more comfortable". More specifically, we are conducting wide-ranging research on how to make people's lives better "essential" from an industrial point of view and from a practical point of view to a basic theory point of view, using the vast and diverse media (Text, pictures, sounds, and so on) that flow on the Internet, devices that create them, and devices that consume them. Therefore, from the industrial perspective, we handle the design and development of unmanned aircraft systems for agriculture and disasters, image sensing, support for next-generation learning, and the creation of new industries using P2P infrastructure. From the practical perspective, we handle the development of applications for recommendations for smart terminals, multi-agent simulation technology, and super-resolution technology. Of course, we also value research on discrete mathematics, which is the foundation of computer science. In our laboratory, we value this kind of mathematical and logical thinking, and our goal is to produce human resources who can break into various fields using this as a weapon.
Read More
-
画像情報研究室 画像工学、コンピュータビジョン、AIセンシング
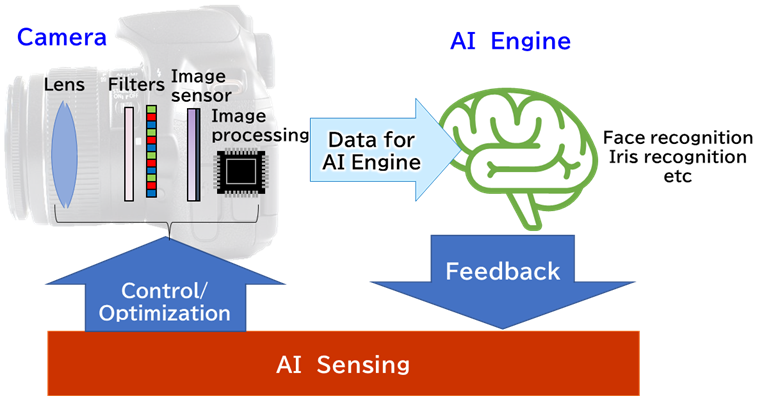 人やモノを認識・理解する画像認識システムは,スマートフォンのログイン時の顔認証など我々の日常生活において利用されるようになってきました.認識対象や応用の拡大,認識性能の向上に向け,認識AIエンジンの研究が盛んに行われており,画像認識システムのさらなる発展が期待できます.一方で,多くの画像認識システムでは,人間の視覚特性に最適化されたカメラ(レンズ,フィルタ,イメージセンサ,画像処理を含む),つまり,人が見るための市販カメラが一般に用いられています.認識AIエンジンが人やモノを認識・理解する上で,人が見るための市販カメラが最適なのでしょうか?本研究では,日々進化する認識AIエンジンの特性を考慮し,その認識AIエンジンが認識対象を理解しやすいように実世界の情報を撮像することで画像認識システムの性能向上を実現する新しいイメージセンシング(AIセンシング)の研究に取り組んでいます.認識エンジンが人やモノを認識する上で必要とする視覚情報は何かを明らかにし,認識AI向けのイメージセンシングの実現にて画像認識システムのさらなる発展に貢献したいと考えています.
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Laboratory Image engineering, Computer vision, AI sensing
人やモノを認識・理解する画像認識システムは,スマートフォンのログイン時の顔認証など我々の日常生活において利用されるようになってきました.認識対象や応用の拡大,認識性能の向上に向け,認識AIエンジンの研究が盛んに行われており,画像認識システムのさらなる発展が期待できます.一方で,多くの画像認識システムでは,人間の視覚特性に最適化されたカメラ(レンズ,フィルタ,イメージセンサ,画像処理を含む),つまり,人が見るための市販カメラが一般に用いられています.認識AIエンジンが人やモノを認識・理解する上で,人が見るための市販カメラが最適なのでしょうか?本研究では,日々進化する認識AIエンジンの特性を考慮し,その認識AIエンジンが認識対象を理解しやすいように実世界の情報を撮像することで画像認識システムの性能向上を実現する新しいイメージセンシング(AIセンシング)の研究に取り組んでいます.認識エンジンが人やモノを認識する上で必要とする視覚情報は何かを明らかにし,認識AI向けのイメージセンシングの実現にて画像認識システムのさらなる発展に貢献したいと考えています.
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Laboratory Image engineering, Computer vision, AI sensing Image recognition systems that recognize and understand people and things have come to be used in our daily lives, such as face recognition when logging in to smartphones. Research on AI engines is being actively conducted to expand recognition targets and applications, and to improve recognition performance, and further development of image recognition systems can be expected. On the other hand, many image recognition systems commonly use cameras optimized for human visual characteristics (including lenses, filters, image sensors, and image processing), i.e., commercial cameras. Are commercial cameras for human vision the best choice for AI engines to recognize and understand people and objects? In this research, we are working on a new image sensing (AI sensing) that improves the performance of image recognition systems by considering the characteristics of AI engines, which are constantly evolving, and by capturing real-world information in such a way that the AI engine can easily understand the recognition target. We would like to contribute to the further development of image recognition systems by clarifying what visual information AI engines need to recognize people and objects, and by realizing image sensing for AI engines.
Read More
Image recognition systems that recognize and understand people and things have come to be used in our daily lives, such as face recognition when logging in to smartphones. Research on AI engines is being actively conducted to expand recognition targets and applications, and to improve recognition performance, and further development of image recognition systems can be expected. On the other hand, many image recognition systems commonly use cameras optimized for human visual characteristics (including lenses, filters, image sensors, and image processing), i.e., commercial cameras. Are commercial cameras for human vision the best choice for AI engines to recognize and understand people and objects? In this research, we are working on a new image sensing (AI sensing) that improves the performance of image recognition systems by considering the characteristics of AI engines, which are constantly evolving, and by capturing real-world information in such a way that the AI engine can easily understand the recognition target. We would like to contribute to the further development of image recognition systems by clarifying what visual information AI engines need to recognize people and objects, and by realizing image sensing for AI engines.
Read More
-
バーチャルリアリティー研究室 バーチャルリアリティ,触力覚提示、移動感覚提示
 計算機内に構築したバーチャルな世界の映像や音声に、メカトロニクス技術を用いた、バーチャルな物体に触った感覚(力覚)を提示する力覚提示装置を組み合わせることで、バーチャルな世界を見るだけでなく触ることが出来るようになります。当研究室では、新たな力覚提示装置を開発し、その評価やそのアプリケーションの開発を通して、より直感的にコンピュータと対話する手法や人間の持っている可能性を引き出すシステムを模索しています。これまで手に対して力覚を提示する6自由度のデスクトップ力覚提示装置や手で持ち運びながら用いる非接地型力覚提示装置、逆に1自由度の機構だけでどこまで力覚を提示できるのかなどの研究を行ってきました。また、手に力覚を提示するだけでなく足に対しての提示として、その場にいながら無限に広がるバーチャル空間を自由に歩き回る装置(歩行感覚提示装置)の開発を行っています。これらの応用として、手術シミュレータの開発や麻痺患者のための歩行リハビリテーションシステムの開発を病院や企業と共同で進め、社会に役立つ技術の提案を行っています。
Read More
Virtual Reality Laboratory Virtual Reality, Haptic Interface, Locomotion Interface
計算機内に構築したバーチャルな世界の映像や音声に、メカトロニクス技術を用いた、バーチャルな物体に触った感覚(力覚)を提示する力覚提示装置を組み合わせることで、バーチャルな世界を見るだけでなく触ることが出来るようになります。当研究室では、新たな力覚提示装置を開発し、その評価やそのアプリケーションの開発を通して、より直感的にコンピュータと対話する手法や人間の持っている可能性を引き出すシステムを模索しています。これまで手に対して力覚を提示する6自由度のデスクトップ力覚提示装置や手で持ち運びながら用いる非接地型力覚提示装置、逆に1自由度の機構だけでどこまで力覚を提示できるのかなどの研究を行ってきました。また、手に力覚を提示するだけでなく足に対しての提示として、その場にいながら無限に広がるバーチャル空間を自由に歩き回る装置(歩行感覚提示装置)の開発を行っています。これらの応用として、手術シミュレータの開発や麻痺患者のための歩行リハビリテーションシステムの開発を病院や企業と共同で進め、社会に役立つ技術の提案を行っています。
Read More
Virtual Reality Laboratory Virtual Reality, Haptic Interface, Locomotion Interface By combining a video and audio of the virtual world built in the computer with a force sense presentation device that uses a mechatronics technology to present a sensation (force sense) of touching a virtual object, just looking at the virtual world You will be able to touch without touching. In our laboratory, we are developing a new haptic device, and through its evaluation and development of its application, we are exploring ways to interact more intuitively with computers and systems that can bring out the potential of human beings. Until now, a 6-DOF desktop haptic device that presents haptics to the hand, an ungrounded haptic device that is used while being carried by hand, and how far can a haptic device be presented with only one degree of freedom? And so on. In addition, we are developing a device (walking sensation presentation device) that can freely walk around an infinitely expanding virtual space while being on the spot, as well as presenting force sensation to the hand as well as presentation to the foot. As applications of these, we are working with hospitals and companies to develop surgery simulators and walking rehabilitation systems for paralyzed patients, and propose technologies that will be useful to society.
Read More
By combining a video and audio of the virtual world built in the computer with a force sense presentation device that uses a mechatronics technology to present a sensation (force sense) of touching a virtual object, just looking at the virtual world You will be able to touch without touching. In our laboratory, we are developing a new haptic device, and through its evaluation and development of its application, we are exploring ways to interact more intuitively with computers and systems that can bring out the potential of human beings. Until now, a 6-DOF desktop haptic device that presents haptics to the hand, an ungrounded haptic device that is used while being carried by hand, and how far can a haptic device be presented with only one degree of freedom? And so on. In addition, we are developing a device (walking sensation presentation device) that can freely walk around an infinitely expanding virtual space while being on the spot, as well as presenting force sensation to the hand as well as presentation to the foot. As applications of these, we are working with hospitals and companies to develop surgery simulators and walking rehabilitation systems for paralyzed patients, and propose technologies that will be useful to society.
Read More
-
感触工学研究室 触覚インタフェース、インタラクティブ技術、バーチャルリアリティ、テレイグジスタンス
 我々は何かを感じる際,単一の感覚器官からの刺激だけでなく,複数の感覚器官,言語,記憶などからの情報を統合したものを主観的な感触として捉えています.本研究室では,五感の特性や物事の認識プロセスを理解し,諸感覚や人間の生理学,心理学に基づいた適切な情報提示を行うことにより,ユーザが真に得たい感覚・手ごたえ・体験を提供する新たな人間中心インタフェースの設計を目指します.具体的には,以下に記述した3つのアプローチを柱として研究活動を行い,その成果をスキルトレーニング,福祉,ウェアラブルコンピューティング,エンタテインメントなど様々な分野に応用しフィードバックを得ていくことで,“感じる”ことの本質を探っていきます.1.諸感覚の知覚特性やクロスモーダル,マルチモーダルの諸現象を利用した独創的な感覚提示(【飲み心地】を【口唇】への【圧力差】で感じる研究など).2.「手応え」などの人間の印象を生理指標や身体応答と関連付け,逆に意図した生理指標や身体応答が生じるように誘導するインタフェースの開発(【歩き方】を【足】への【触覚提示】で変容させる研究など).3.芸術性の高い伝統工芸と先端技術を組み合わせた「琴線に触れる」プロダクトの創出(【漆】をベースとした【電子回路】を構築する研究など)
Read More
Feel Engineering Laboratory Haptic Interface, Human Computer Interaction, Virtual Reality, Telexistence
我々は何かを感じる際,単一の感覚器官からの刺激だけでなく,複数の感覚器官,言語,記憶などからの情報を統合したものを主観的な感触として捉えています.本研究室では,五感の特性や物事の認識プロセスを理解し,諸感覚や人間の生理学,心理学に基づいた適切な情報提示を行うことにより,ユーザが真に得たい感覚・手ごたえ・体験を提供する新たな人間中心インタフェースの設計を目指します.具体的には,以下に記述した3つのアプローチを柱として研究活動を行い,その成果をスキルトレーニング,福祉,ウェアラブルコンピューティング,エンタテインメントなど様々な分野に応用しフィードバックを得ていくことで,“感じる”ことの本質を探っていきます.1.諸感覚の知覚特性やクロスモーダル,マルチモーダルの諸現象を利用した独創的な感覚提示(【飲み心地】を【口唇】への【圧力差】で感じる研究など).2.「手応え」などの人間の印象を生理指標や身体応答と関連付け,逆に意図した生理指標や身体応答が生じるように誘導するインタフェースの開発(【歩き方】を【足】への【触覚提示】で変容させる研究など).3.芸術性の高い伝統工芸と先端技術を組み合わせた「琴線に触れる」プロダクトの創出(【漆】をベースとした【電子回路】を構築する研究など)
Read More
Feel Engineering Laboratory Haptic Interface, Human Computer Interaction, Virtual Reality, Telexistence When a person feels something, it is greatly affected not only by stimulation from a single sensory organ, but also by information that integrates multiple sensory organs, experiences, and memories. This lab provides a new human-centric interface that provides the sensations, responsiveness, and experiences that users really want by presenting the right sensations and information based on five sensory characteristics and various impressions mechanisms Design aim. Currently, we are conducting research based on the following three approaches and applying the results to various fields such as skill training, welfare, wearable computing, and entertainment. 1. Unique sensory presentation using perceptual characteristics of each sensory, cross-modal and multi-modal phenomena. 2. Development of an interface that correlates responses to physiological indicators and physical responses, and conversely guides the intended physiological indicators and physical responses to occur. 3. Creating new products that combine traditional art with high artistic quality and advanced technology.
Read More
When a person feels something, it is greatly affected not only by stimulation from a single sensory organ, but also by information that integrates multiple sensory organs, experiences, and memories. This lab provides a new human-centric interface that provides the sensations, responsiveness, and experiences that users really want by presenting the right sensations and information based on five sensory characteristics and various impressions mechanisms Design aim. Currently, we are conducting research based on the following three approaches and applying the results to various fields such as skill training, welfare, wearable computing, and entertainment. 1. Unique sensory presentation using perceptual characteristics of each sensory, cross-modal and multi-modal phenomena. 2. Development of an interface that correlates responses to physiological indicators and physical responses, and conversely guides the intended physiological indicators and physical responses to occur. 3. Creating new products that combine traditional art with high artistic quality and advanced technology.
Read More
-
エンタテインメントコンピューティング研究室 ゲームテクノロジー、デジタルストーリーテリング、エデュテインメントの研究
 エンタテインメントは私たちの生活を豊かにするとともに経済的にも大きな影響力を持っています.エンタテインメントの原型となるゲーム,音楽,ストーリーテリングなどは古くからありますが,近年のIoT,ビッグデータAI,移動通信システム(5G)などの浸透によりエンタテインメントのあり方も変わってきています.エンタテインメントコンピューティング研究室では,人間と生命の表現技術や,没入感と楽しさを創るインタラクションデザインにより,人の交流,健康,学習などの生活の質を高めるエンタテインメントを実現して社会的インパクトの評価を行います.具体的なテーマとしては,高齢者の健康維持のためのゲームシステム,子供の学習を支援するエンタテインメントロボット,接客訓練のためのシナリオベースVRシステム,購買体験のエンタテインメント性の向上などの研究やこれらの社会実装を行っています.
Read More
Entertainment Computing Laboratory Game Technology, Digital Storytelling, Edutainment
エンタテインメントは私たちの生活を豊かにするとともに経済的にも大きな影響力を持っています.エンタテインメントの原型となるゲーム,音楽,ストーリーテリングなどは古くからありますが,近年のIoT,ビッグデータAI,移動通信システム(5G)などの浸透によりエンタテインメントのあり方も変わってきています.エンタテインメントコンピューティング研究室では,人間と生命の表現技術や,没入感と楽しさを創るインタラクションデザインにより,人の交流,健康,学習などの生活の質を高めるエンタテインメントを実現して社会的インパクトの評価を行います.具体的なテーマとしては,高齢者の健康維持のためのゲームシステム,子供の学習を支援するエンタテインメントロボット,接客訓練のためのシナリオベースVRシステム,購買体験のエンタテインメント性の向上などの研究やこれらの社会実装を行っています.
Read More
Entertainment Computing Laboratory Game Technology, Digital Storytelling, Edutainment Entertainment plays important role to enrich our daily life, and have big social impacts. Prototypes of entertainments such as game, music, storytelling have long history. However, recent development of technologies such as IoT, Big Data and AI, 5G mobile communication change the form of entertainment. In Entertainment Computing Lab, we we develop new entertainment for increasing quality of life based on the representation technologies of human and life, and interaction design to create fun and immersion. Research topics include health exercise game system for elderly, entertainment robot for learning children, scenario-based VR system for customer service training, and entertainment for e-commerce.
Read More
Entertainment plays important role to enrich our daily life, and have big social impacts. Prototypes of entertainments such as game, music, storytelling have long history. However, recent development of technologies such as IoT, Big Data and AI, 5G mobile communication change the form of entertainment. In Entertainment Computing Lab, we we develop new entertainment for increasing quality of life based on the representation technologies of human and life, and interaction design to create fun and immersion. Research topics include health exercise game system for elderly, entertainment robot for learning children, scenario-based VR system for customer service training, and entertainment for e-commerce.
Read More
-
視覚メディア研究室 3次元画像工学、立体ディスプレイ、メディア工学、医用画像工学、自然言語処理
 当研究室では、メディア工学をテーマに研究を行っています。 具体的には、3次元ディスプレイと人工知能の研究に取り組んでいます。
3次元ディスプレイグループは、 医療手術シミュレーションや自動車運転支援など、 3次元位置の正確な把握がなければ実現できない用途への応用を目指し、 フルハイビジョン裸眼立体表示や自然な目の焦点調節を再現する裸眼立体ディスプレイの研究開発を行っています。
人工知能グループは、CT画像からの臓器や腫瘍の自動検出と、政治経済に関する文書(国会議事録、新聞の社説、本の書評、会社の広報資料など)の分類・整理・可視化の研究に取り組んでいます。
Read More
Visual Media Laboratory 3D Displays, Media Technology, Medical Imaging, Natural Language Processing
当研究室では、メディア工学をテーマに研究を行っています。 具体的には、3次元ディスプレイと人工知能の研究に取り組んでいます。
3次元ディスプレイグループは、 医療手術シミュレーションや自動車運転支援など、 3次元位置の正確な把握がなければ実現できない用途への応用を目指し、 フルハイビジョン裸眼立体表示や自然な目の焦点調節を再現する裸眼立体ディスプレイの研究開発を行っています。
人工知能グループは、CT画像からの臓器や腫瘍の自動検出と、政治経済に関する文書(国会議事録、新聞の社説、本の書評、会社の広報資料など)の分類・整理・可視化の研究に取り組んでいます。
Read More
Visual Media Laboratory 3D Displays, Media Technology, Medical Imaging, Natural Language Processing We are engaged in media technologies, including 3D imaging and artificial intelligence. As for 3D imaging, we are developing new autostereoscopic (glassless) 3D displays with higher resolutions and less eyestrains. We are also applying our original 3D displays to surgery simulations and HUD for assistance of vehicle drivers. As for artificial intelligence, we are focusing on detection and segmentation of human abdominal organs and tumors from CT data, and analysis of social documents such as minutes of Japanese Diet, editorials in the newspapers, book reviews on the net, and the interviews of CEOs.
Read More
We are engaged in media technologies, including 3D imaging and artificial intelligence. As for 3D imaging, we are developing new autostereoscopic (glassless) 3D displays with higher resolutions and less eyestrains. We are also applying our original 3D displays to surgery simulations and HUD for assistance of vehicle drivers. As for artificial intelligence, we are focusing on detection and segmentation of human abdominal organs and tumors from CT data, and analysis of social documents such as minutes of Japanese Diet, editorials in the newspapers, book reviews on the net, and the interviews of CEOs.
Read More
-
バーチャルリアリティ研究室 バーチャルリアリティ、多感覚伝送・遠隔体験、ロボティクス
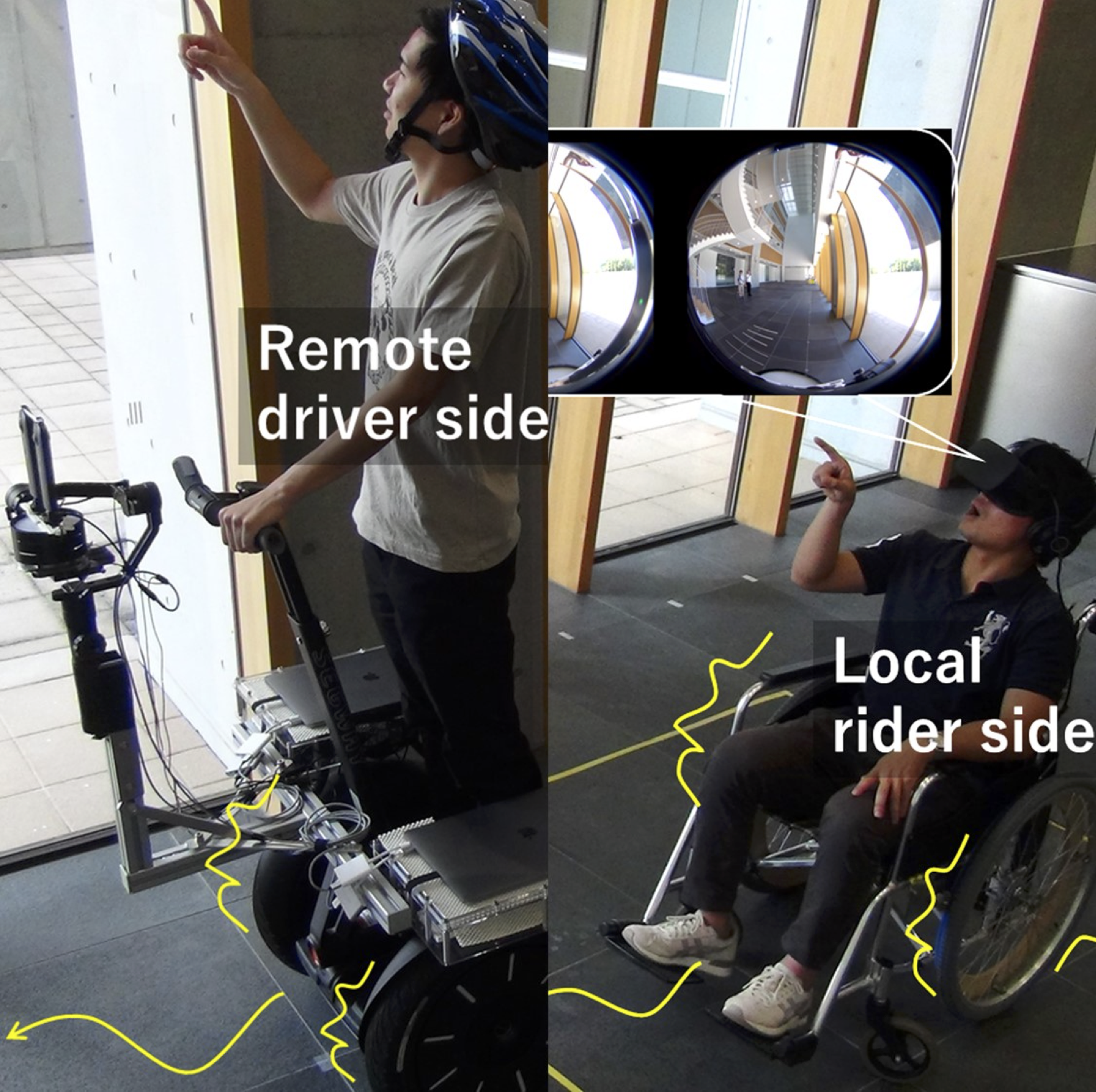 メタバース、デジタルツイン、テレイグジスタンス(またはテレプレゼンス)の人気が高まり、広く受け入れられています。本研究の関心は、これらのデジタル環境でのより高品位なバーチャル体験、および多感覚伝送によるより良いテレコミュニケーションのための新しい技術の開発です。本研究のミッションは、触覚や物体把持の感覚、歩行や運転などの様々な身体感覚を再現するための人間の感覚特性を解明することです。また、感覚受容器を直接活動させる電気刺激および機械刺激を組み合わせた力触覚フィードバックデバイス、歩行感覚または車両乗車感覚フィードバックシミュレータ、および様々アバターロボットシステムの開発も行っています。本技術の応用例としては、エンターテインメント(VRゲームやバーチャルツーリズム)、スキルトレーニング、リハビリテーション、テレオペレーションなどです。
Read More
Virtual Reality Laboratory Virtual reality, multisensory transmission/tele-experience, robotics
メタバース、デジタルツイン、テレイグジスタンス(またはテレプレゼンス)の人気が高まり、広く受け入れられています。本研究の関心は、これらのデジタル環境でのより高品位なバーチャル体験、および多感覚伝送によるより良いテレコミュニケーションのための新しい技術の開発です。本研究のミッションは、触覚や物体把持の感覚、歩行や運転などの様々な身体感覚を再現するための人間の感覚特性を解明することです。また、感覚受容器を直接活動させる電気刺激および機械刺激を組み合わせた力触覚フィードバックデバイス、歩行感覚または車両乗車感覚フィードバックシミュレータ、および様々アバターロボットシステムの開発も行っています。本技術の応用例としては、エンターテインメント(VRゲームやバーチャルツーリズム)、スキルトレーニング、リハビリテーション、テレオペレーションなどです。
Read More
Virtual Reality Laboratory Virtual reality, multisensory transmission/tele-experience, robotics Metaverse, digital twins and telexistence (or telepresence) are growing in popularity and gaining wider acceptance. Our research interests are the development of new technologies for higher fidelity virtual experience in such the digital environments as well as for better tele-communications by multisensory transmitting. Our mission is to elucidate human sensory characteristics to reproduce various kinds of body sensation such as sense of touch or grasping an object, walking, or driving activities. We are also developing some haptic feedback devices by combining electrical stimulation that activates sensory nerves directly with mechanical stimulation, gait motion or vehicle riding sensation feedback simulators, and some robotic avatar systems. The applications of our technologies are for entertainment (VR gaming or virtual tourism), skill training, rehabilitation, tele-operations, etc.
Read More
Metaverse, digital twins and telexistence (or telepresence) are growing in popularity and gaining wider acceptance. Our research interests are the development of new technologies for higher fidelity virtual experience in such the digital environments as well as for better tele-communications by multisensory transmitting. Our mission is to elucidate human sensory characteristics to reproduce various kinds of body sensation such as sense of touch or grasping an object, walking, or driving activities. We are also developing some haptic feedback devices by combining electrical stimulation that activates sensory nerves directly with mechanical stimulation, gait motion or vehicle riding sensation feedback simulators, and some robotic avatar systems. The applications of our technologies are for entertainment (VR gaming or virtual tourism), skill training, rehabilitation, tele-operations, etc.
Read More
-
知覚拡張システム研究室 人間行動計測,大規模データ活用・統合,アレー信号処理,感覚代行,サービス工学
 我々は,物理的制約に捕らえられて日々の生活をしている。知覚拡張システム研究室(XperLab; eXtended Perception Lab.)では,人の機能を拡張するコンピューター技術・インタラクション技術の研究を行っている。計算機がどこにでも存在する現在,物理的制約から開放され,物理的空間だけではなく異なる社会や情報空間とシームレスに繋がることで,情報平等な人間のあり方を探索しています。
例えば,
・視覚障害支援のための立体音響提示される地図・ナビゲーション,可聴化ゲーム
・聴覚障害支援のための吹き出しAR技術,後方知覚のためのハプティクデバイス
・遠隔医療・診療のための憑依型テレイグジスタンスシステム
・ユーザーの状態に応じた情報提示システム
・物理情報と干渉することで復号されるサイバー情報
・画像の可聴化システム
・屋内測位センサーネットワーク
・価値共創を生み出す間合いの良い接客
などが研究対象である。
これらの実現のために本研究室ではハード・ソフトウェアの両面に加えサービス応用を見越した一連の流れを通じて,人の知覚の拡張を図っている。
Read More
eXtended Perception Laboratory Augmentation of Human Perception, Sensory Substitution, Disability Support, Human Augmentation Engineering, HCI/Value Co-creation on Sound Information
我々は,物理的制約に捕らえられて日々の生活をしている。知覚拡張システム研究室(XperLab; eXtended Perception Lab.)では,人の機能を拡張するコンピューター技術・インタラクション技術の研究を行っている。計算機がどこにでも存在する現在,物理的制約から開放され,物理的空間だけではなく異なる社会や情報空間とシームレスに繋がることで,情報平等な人間のあり方を探索しています。
例えば,
・視覚障害支援のための立体音響提示される地図・ナビゲーション,可聴化ゲーム
・聴覚障害支援のための吹き出しAR技術,後方知覚のためのハプティクデバイス
・遠隔医療・診療のための憑依型テレイグジスタンスシステム
・ユーザーの状態に応じた情報提示システム
・物理情報と干渉することで復号されるサイバー情報
・画像の可聴化システム
・屋内測位センサーネットワーク
・価値共創を生み出す間合いの良い接客
などが研究対象である。
これらの実現のために本研究室ではハード・ソフトウェアの両面に加えサービス応用を見越した一連の流れを通じて,人の知覚の拡張を図っている。
Read More
eXtended Perception Laboratory Augmentation of Human Perception, Sensory Substitution, Disability Support, Human Augmentation Engineering, HCI/Value Co-creation on Sound Information We live in our daily lives, being caught by physical constraints. XperLab (eXtended Perception Lab.) is studying computer and interaction technologies that extend human functions. Now that computers are everywhere, we are exploring the ideal way of humans who are equal in information by being released from physical constraints and seamlessly connecting not only to the physical space but also to different societies and information spaces.
For example, Maps and Navigation with stereophonic sound for visual impairment support, audible games / Speech balloon AR technology for hearing impairment support, haptic device for backward perception / Possessed telexistence system for telemedicine and medical care / Information presentation system according to user status / Cyber information decrypted by interfering with physical information / Image sonification system / Indoor positioning sensor network / customer service with good MAAI that creates value co-creation, are the subjects of research.
To achieve these goals, our laboratory aims to expand human perception through a series of flows that allow for service applications in addition to hardware and software.
Read More
We live in our daily lives, being caught by physical constraints. XperLab (eXtended Perception Lab.) is studying computer and interaction technologies that extend human functions. Now that computers are everywhere, we are exploring the ideal way of humans who are equal in information by being released from physical constraints and seamlessly connecting not only to the physical space but also to different societies and information spaces.
For example, Maps and Navigation with stereophonic sound for visual impairment support, audible games / Speech balloon AR technology for hearing impairment support, haptic device for backward perception / Possessed telexistence system for telemedicine and medical care / Information presentation system according to user status / Cyber information decrypted by interfering with physical information / Image sonification system / Indoor positioning sensor network / customer service with good MAAI that creates value co-creation, are the subjects of research.
To achieve these goals, our laboratory aims to expand human perception through a series of flows that allow for service applications in addition to hardware and software.
Read More
-
応用触覚研究室 触覚,身体接触,ウェアラブルデバイス
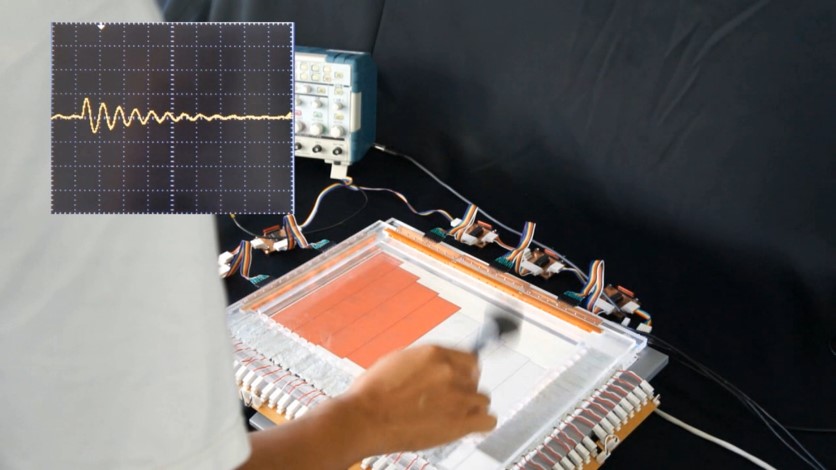 本研究室では,メカトロニクスを基に,ときに社会科学の知見を借り:1) 触覚を通じた知覚・体験の多角的な観察,計量;2) 得られた知見を活用した人々の行動を変容させるヒューマンインタフェースの設計開発,に取り組んでいます.視聴覚に続くデジタルメディアのチャネルとして触覚が注目を浴びています.一方で,触覚研究の歴史は比較的浅く,未知なことや特異なことがたくさんあります.例えば,同様な物理刺激であっても,好きな相手からの接触は快く,嫌いな相手からの接触は不快に感じるといった文脈依存性が挙げられます(全てが文脈で説明できるわけではありません).また,カメラやモニタ(視覚),マイクとスピーカ(聴覚)のようなユニバーサルなセンサやディスプレイが触覚においては未だないことから,目的に応じて自分たちで設計開発する必要があります.こうした挑戦的な分野において,当研究室では世界で役立つもの・知見を目標に応用的研究を行っています.具体的にはバーチャルリアリティ等の人とコンピュータ,あるいは身体接触等の人と人のインタラクションを触覚的に拡張することに取り組んでいます.
Read More
Applied Haptics Laboratory Haptics, Touch, Wearable Device
本研究室では,メカトロニクスを基に,ときに社会科学の知見を借り:1) 触覚を通じた知覚・体験の多角的な観察,計量;2) 得られた知見を活用した人々の行動を変容させるヒューマンインタフェースの設計開発,に取り組んでいます.視聴覚に続くデジタルメディアのチャネルとして触覚が注目を浴びています.一方で,触覚研究の歴史は比較的浅く,未知なことや特異なことがたくさんあります.例えば,同様な物理刺激であっても,好きな相手からの接触は快く,嫌いな相手からの接触は不快に感じるといった文脈依存性が挙げられます(全てが文脈で説明できるわけではありません).また,カメラやモニタ(視覚),マイクとスピーカ(聴覚)のようなユニバーサルなセンサやディスプレイが触覚においては未だないことから,目的に応じて自分たちで設計開発する必要があります.こうした挑戦的な分野において,当研究室では世界で役立つもの・知見を目標に応用的研究を行っています.具体的にはバーチャルリアリティ等の人とコンピュータ,あるいは身体接触等の人と人のインタラクションを触覚的に拡張することに取り組んでいます.
Read More
Applied Haptics Laboratory Haptics, Touch, Wearable Device Based on mechatronics and social science, this laboratory aims: 1) to observe and quantify haptic perception and experience; 2) to design and develop human interfaces that modify human behavior. Haptics is a trending field in the area of emerging digital media. However, because of the relatively short research history, there are a number of questions to be explored in haptics. For example, you may feel good when you are touched by a person you like although you may not feel good when touched by a person you do not like even though the stimuli are physically identical (the context may partially affect the experience). In addition, because there are no universal haptic sensors / displays / monitor and microphone / speaker, we need to design and develop them based on purposes. In such a challenging field, the laboratory performs applied research to offer explore and answer the key questions in haptics. Our interests include, are but not limited to, human-computer interactions such as VR/AR and human-human interactions such as interpersonal touch.
Read More
Based on mechatronics and social science, this laboratory aims: 1) to observe and quantify haptic perception and experience; 2) to design and develop human interfaces that modify human behavior. Haptics is a trending field in the area of emerging digital media. However, because of the relatively short research history, there are a number of questions to be explored in haptics. For example, you may feel good when you are touched by a person you like although you may not feel good when touched by a person you do not like even though the stimuli are physically identical (the context may partially affect the experience). In addition, because there are no universal haptic sensors / displays / monitor and microphone / speaker, we need to design and develop them based on purposes. In such a challenging field, the laboratory performs applied research to offer explore and answer the key questions in haptics. Our interests include, are but not limited to, human-computer interactions such as VR/AR and human-human interactions such as interpersonal touch.
Read More
-
松本研究室 バーチャルリアリティ,空間知覚,時間知覚,個人最適化,知覚運動連関
 バーチャルリアリティ(VR)を用いた空間知覚、時間知覚、個人最適化の研究を行っています。空間知覚に関する研究では、リダイレクションと呼ばれる視覚と体性感覚などの相互作用を利用して物理的な制約を超えたインタラクションを実現する技術について研究をおこなっています。時間知覚に関する研究では、複数のユーザ間における因果関係やタイミングの整合性を保持しながら、心理的時間を調整できる時間変調手法の設計および評価を行っています。個人最適化に関する研究では、ユーザの感覚特性を推定し最適な感覚情報提示を行うことで、より自然で没入感のあるVR体験を提供する手法について研究しています。こうした研究を通して、VRにおける新たなインタラクション体験の提供や、個々のユーザに最適化されたVRシステムの構築を目指しています。
Read More
Matsumoto Lab. Virtual reality, spatial perception, time perception, individual optimization, sensory-motor coupling
バーチャルリアリティ(VR)を用いた空間知覚、時間知覚、個人最適化の研究を行っています。空間知覚に関する研究では、リダイレクションと呼ばれる視覚と体性感覚などの相互作用を利用して物理的な制約を超えたインタラクションを実現する技術について研究をおこなっています。時間知覚に関する研究では、複数のユーザ間における因果関係やタイミングの整合性を保持しながら、心理的時間を調整できる時間変調手法の設計および評価を行っています。個人最適化に関する研究では、ユーザの感覚特性を推定し最適な感覚情報提示を行うことで、より自然で没入感のあるVR体験を提供する手法について研究しています。こうした研究を通して、VRにおける新たなインタラクション体験の提供や、個々のユーザに最適化されたVRシステムの構築を目指しています。
Read More
Matsumoto Lab. Virtual reality, spatial perception, time perception, individual optimization, sensory-motor coupling We are conducting research on spatial perception, time perception, and personal optimization using virtual reality (VR). In our research on spatial perception, we are studying technology that uses interactions between vision and somatosensation, etc., called “redirection,” to achieve interaction that transcends physical constraints. In our research on temporal perception, we are designing and evaluating time modulation methods that can adjust psychological time while maintaining consistency of causality and timing between multiple users. In our research on personal optimization, we are studying methods for providing more natural and immersive VR experiences by estimating users' sensory characteristics and presenting sensory information in an optimal way. Through this research, we aim to provide new interaction experiences in VR and to build VR systems that are optimized for each user.
Read More
We are conducting research on spatial perception, time perception, and personal optimization using virtual reality (VR). In our research on spatial perception, we are studying technology that uses interactions between vision and somatosensation, etc., called “redirection,” to achieve interaction that transcends physical constraints. In our research on temporal perception, we are designing and evaluating time modulation methods that can adjust psychological time while maintaining consistency of causality and timing between multiple users. In our research on personal optimization, we are studying methods for providing more natural and immersive VR experiences by estimating users' sensory characteristics and presenting sensory information in an optimal way. Through this research, we aim to provide new interaction experiences in VR and to build VR systems that are optimized for each user.
Read More
-
計算撮像研究室 コンピュテーショナルイメージング,コンピュータグラフィクス,視覚質感ファブリケーション
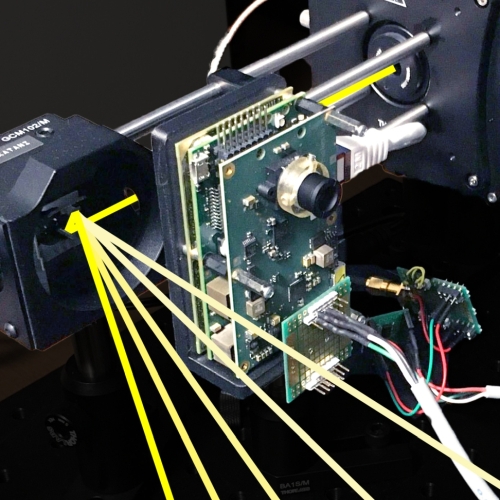 本研究室では,従来観測することができなかったものを観測可能にする新しいイメージング技術の研究に取り組んでいます.我々の視覚系は物質と光との複雑な相互作用を観察することで,例えば,本物のリンゴか,プラスティックのリンゴかを識別します.しかし,従来のカメラは光情報を二次元画像に圧縮するため,物質に関する情報を取りこぼしていました.一方で,情報科学に加え,最新の応用光学と電子工学とを融合した「計算撮像技術」では,光が物質表面でどのように反射し,物質内をどのように伝播するのかを明らかにすることができ,機械知能を大幅に向上する可能性を秘めています.また,本研究室では,観測した光学現象をコンピュータ上で再現する従来のコンピュータグラフィクスに加えて,3Dプリンティングなどのデジタルファブリケーションによって物理的に視覚質感を再現する技術についても研究しています.将来的には,例えば,計測に基づいて本人の肌質感を正確に再現した人工皮膚への貢献が考えられます.
Read More
Computational Imaging & Graphics Laboratory Computational Imaging, Computer Graphics, Appearance Fabrication
本研究室では,従来観測することができなかったものを観測可能にする新しいイメージング技術の研究に取り組んでいます.我々の視覚系は物質と光との複雑な相互作用を観察することで,例えば,本物のリンゴか,プラスティックのリンゴかを識別します.しかし,従来のカメラは光情報を二次元画像に圧縮するため,物質に関する情報を取りこぼしていました.一方で,情報科学に加え,最新の応用光学と電子工学とを融合した「計算撮像技術」では,光が物質表面でどのように反射し,物質内をどのように伝播するのかを明らかにすることができ,機械知能を大幅に向上する可能性を秘めています.また,本研究室では,観測した光学現象をコンピュータ上で再現する従来のコンピュータグラフィクスに加えて,3Dプリンティングなどのデジタルファブリケーションによって物理的に視覚質感を再現する技術についても研究しています.将来的には,例えば,計測に基づいて本人の肌質感を正確に再現した人工皮膚への貢献が考えられます.
Read More
Computational Imaging & Graphics Laboratory Computational Imaging, Computer Graphics, Appearance Fabrication We are working on next-gen imaging technologies for making the unobservable observable. Our vision system observes complicated interactions between light and matters, and then recognizes if it is an actual apple or a plastic one. However, conventional cameras shrink such optical information into a 2-D image, resulting in loss of the information. On the other hand, “computational imaging” where state-of-the-art applied optics and electronics are fused with information science may drastically improve the machine intelligence, because it observes how light reflects off and propagates in matters. Additionally, we study not only traditional computer graphics but also appearance fabrication techniques using digital fabrication, such as 3-D printing, to virtually and physically reproduce the observed optical phenomena. In the future, for example, our work will contribute artificial skins to reproduce the appearance of patient’s skins based on measurements.
Read More
We are working on next-gen imaging technologies for making the unobservable observable. Our vision system observes complicated interactions between light and matters, and then recognizes if it is an actual apple or a plastic one. However, conventional cameras shrink such optical information into a 2-D image, resulting in loss of the information. On the other hand, “computational imaging” where state-of-the-art applied optics and electronics are fused with information science may drastically improve the machine intelligence, because it observes how light reflects off and propagates in matters. Additionally, we study not only traditional computer graphics but also appearance fabrication techniques using digital fabrication, such as 3-D printing, to virtually and physically reproduce the observed optical phenomena. In the future, for example, our work will contribute artificial skins to reproduce the appearance of patient’s skins based on measurements.
Read More
-
画像情報研究室 コンピュータービジョン、拡張現実、AI生成コンテンツ
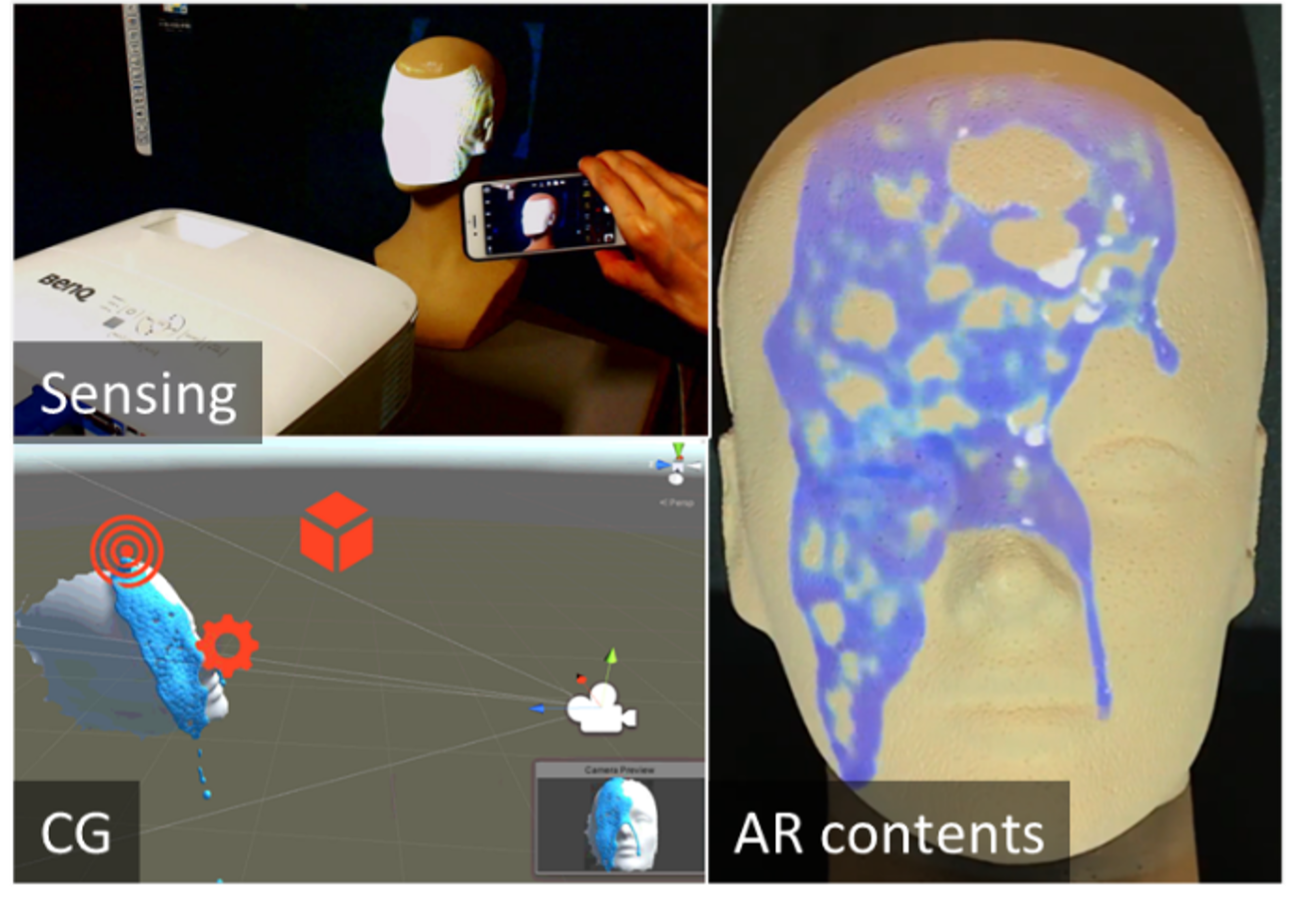 コンピュータビジョンの技術は、日々進化し続けるAIの世界において重要な役割を果たしています。拡張現実(AR)やAI生成コンテンツ(AIGC)の分野では、この技術が核となり、多様な応用が可能になっています。本研究グループでは、コンピュータビジョンを活用した革新的な研究開発に取り組んでおり、医療、教育、デザイン、エンターテイメントなど、幅広い分野における発展に貢献しています。
医療分野では、ARとAIGC技術を用いて、外科手術の精度を向上させるシステムを開発しています。リアルタイムでの画像認識により、医師がより正確な手術を行えるようになります。また、教育分野では、インタラクティブな学習コンテンツを作成。学習者がより深く、実践的に学べる環境を提供しています。
デザイン分野では、新たなビジュアル表現の手法を開発し、デザイナーが現実とデジタルの境界を越えた創造を実現できるよう支援しています。また、エンターテイメント分野では、AIGCによるリアルタイムのコンテンツ生成を行い、映画やゲーム産業に新たな可能性をもたらしています。
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Lab Computer Vision, Augmented Reality, AIGC
コンピュータビジョンの技術は、日々進化し続けるAIの世界において重要な役割を果たしています。拡張現実(AR)やAI生成コンテンツ(AIGC)の分野では、この技術が核となり、多様な応用が可能になっています。本研究グループでは、コンピュータビジョンを活用した革新的な研究開発に取り組んでおり、医療、教育、デザイン、エンターテイメントなど、幅広い分野における発展に貢献しています。
医療分野では、ARとAIGC技術を用いて、外科手術の精度を向上させるシステムを開発しています。リアルタイムでの画像認識により、医師がより正確な手術を行えるようになります。また、教育分野では、インタラクティブな学習コンテンツを作成。学習者がより深く、実践的に学べる環境を提供しています。
デザイン分野では、新たなビジュアル表現の手法を開発し、デザイナーが現実とデジタルの境界を越えた創造を実現できるよう支援しています。また、エンターテイメント分野では、AIGCによるリアルタイムのコンテンツ生成を行い、映画やゲーム産業に新たな可能性をもたらしています。
Read More
Computer Vision and Image Media Lab Computer Vision, Augmented Reality, AIGC The technology of computer vision plays a vital role in the ever-evolving world of AI. In the fields of augmented reality (AR) and AI-generated content (AIGC), this technology is central and enables a variety of applications. Our research group is engaged in innovative research and development utilizing computer vision, contributing to the advancement across a broad spectrum of fields including medicine, education, design, and entertainment.
In the medical field, we are developing systems to improve the precision of surgical operations using AR and AIGC technologies. Real-time image recognition allows doctors to perform more accurate surgeries. In the field of education, we create interactive learning content, providing an environment where learners can study more deeply and practically.
In the design field, we are developing new methods of visual expression, supporting designers to realize creations that transcend the boundaries between reality and digital. Furthermore, in the entertainment field, we produce real-time content using AIGC, bringing new possibilities to the movie and gaming industries.
Read More
The technology of computer vision plays a vital role in the ever-evolving world of AI. In the fields of augmented reality (AR) and AI-generated content (AIGC), this technology is central and enables a variety of applications. Our research group is engaged in innovative research and development utilizing computer vision, contributing to the advancement across a broad spectrum of fields including medicine, education, design, and entertainment.
In the medical field, we are developing systems to improve the precision of surgical operations using AR and AIGC technologies. Real-time image recognition allows doctors to perform more accurate surgeries. In the field of education, we create interactive learning content, providing an environment where learners can study more deeply and practically.
In the design field, we are developing new methods of visual expression, supporting designers to realize creations that transcend the boundaries between reality and digital. Furthermore, in the entertainment field, we produce real-time content using AIGC, bringing new possibilities to the movie and gaming industries.
Read More





























































